Nanoscopy with focused light
... Throughout the 20th century it was widely accepted that a light microscope relying on conventional optical lenses cannot discern details that are much finer than about half the wavelength of light (200-400 nm), due to diffraction. However, in the 1990s, the viability to overcome the diffraction barr ...
... Throughout the 20th century it was widely accepted that a light microscope relying on conventional optical lenses cannot discern details that are much finer than about half the wavelength of light (200-400 nm), due to diffraction. However, in the 1990s, the viability to overcome the diffraction barr ...
Ch14 Review
... Recognize how additive colors affect the color of light. Recognize how pigments affect the color of reflected light. Explain how linearly polarized light is formed and detected. Chapter 14 Key Ideas Light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
... Recognize how additive colors affect the color of light. Recognize how pigments affect the color of reflected light. Explain how linearly polarized light is formed and detected. Chapter 14 Key Ideas Light is electromagnetic radiation that consists of oscillating electric and magnetic fields ...
Properties of Multilayer Optics
... Upon strong reflection off a layer a standing wave is formed which effectively changes the refractive index felt by the total field. If the Bragg peak is placed near Brewster’s angle, only the s-component feels this electric field modulation and change in refractive index which causes a phase shift ...
... Upon strong reflection off a layer a standing wave is formed which effectively changes the refractive index felt by the total field. If the Bragg peak is placed near Brewster’s angle, only the s-component feels this electric field modulation and change in refractive index which causes a phase shift ...
Abstract : Fiber interfaces between single atoms and single photons Sébastien Garcia,
... requires development of compact, robust and versatile systems. Motivated by miniaturization, stability et flexibility provided by optical fibers as light wave-guides, we present two experiments where optical fibers are used as interfaces for single atoms trapping and single photons collection into t ...
... requires development of compact, robust and versatile systems. Motivated by miniaturization, stability et flexibility provided by optical fibers as light wave-guides, we present two experiments where optical fibers are used as interfaces for single atoms trapping and single photons collection into t ...
Link to PowerPoint Presentation
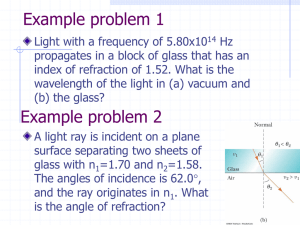
... of incidence and refraction between two different media ٭Media possess a Refractive Index (n) ٭Measures how much speed of light is slowed down by the medium ٭The more light is slowed, the higher its Refractive Index ...
... of incidence and refraction between two different media ٭Media possess a Refractive Index (n) ٭Measures how much speed of light is slowed down by the medium ٭The more light is slowed, the higher its Refractive Index ...
Polarized light and polarizers
... Land in 1929 to construct the first type of Polaroid sheet polarizer. He did this by embedding herapathite crystals in a polymer instead of growing a single large crystal. Land established Polaroid Corporation in 1937 in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The company initially produced Polaroid Day Glasses, ...
... Land in 1929 to construct the first type of Polaroid sheet polarizer. He did this by embedding herapathite crystals in a polymer instead of growing a single large crystal. Land established Polaroid Corporation in 1937 in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The company initially produced Polaroid Day Glasses, ...
Polarization
... • The first polarizer reduces the intensity by half. • The second polarizer reduces the intensity by another factor of cos2q. • The second polarizer projects the electric field onto a new axis, rotated by q from the axis of the first polarizer ...
... • The first polarizer reduces the intensity by half. • The second polarizer reduces the intensity by another factor of cos2q. • The second polarizer projects the electric field onto a new axis, rotated by q from the axis of the first polarizer ...
James Powenski - Optical Computing
... Matrix calculations Convolution as a from a arithmetic for pure optical computers ...
... Matrix calculations Convolution as a from a arithmetic for pure optical computers ...
Mark scheme for Topic 11 - Cambridge Resources for the IB Diploma
... rotation is measured. The concentration of the optically active solution is changed and the process is repeated to see the variation with concentration of the rotation angle. ...
... rotation is measured. The concentration of the optically active solution is changed and the process is repeated to see the variation with concentration of the rotation angle. ...
Geometric optics
... respect to the normal to the surface. If the refractive index is lower on the other side of the boundary and the incident angle is greater than the critical angle, the wave cannot pass through and is entirely reflected. The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which the total internal refl ...
... respect to the normal to the surface. If the refractive index is lower on the other side of the boundary and the incident angle is greater than the critical angle, the wave cannot pass through and is entirely reflected. The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which the total internal refl ...
Study the Effect of the Sugar Solutions on the Rotation of the
... It is the rotation of linearly polarized light as it travels through materials. It appears in solutions of chiral molecules such as sucrose (sugar), solid with rotated crystal planes such as quartz, and spin-polarized gases of atoms or molecules. Chirality is the property of an object of being non-s ...
... It is the rotation of linearly polarized light as it travels through materials. It appears in solutions of chiral molecules such as sucrose (sugar), solid with rotated crystal planes such as quartz, and spin-polarized gases of atoms or molecules. Chirality is the property of an object of being non-s ...
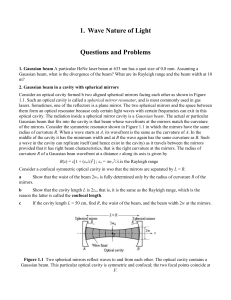
1. Wave Nature of Light
... 2. Gaussian beam in a cavity with spherical mirrors Consider an optical cavity formed b two aligned spherical mirrors facing each other as shown in Figure 1.1. Such an optical cavity is called a spherical mirror resonator, and is most commonly used in gas lasers. Sometimes, one of the reflectors is ...
... 2. Gaussian beam in a cavity with spherical mirrors Consider an optical cavity formed b two aligned spherical mirrors facing each other as shown in Figure 1.1. Such an optical cavity is called a spherical mirror resonator, and is most commonly used in gas lasers. Sometimes, one of the reflectors is ...
Lab
... goes to zero at some angle between 0° and 90°, the reflected light at that angle is linearly polarized with its electric field vectors perpendicular to the plane of incidence. The angle at which this occurs is called the polarizing angle or the Brewster angle. At other angles the reflected light is ...
... goes to zero at some angle between 0° and 90°, the reflected light at that angle is linearly polarized with its electric field vectors perpendicular to the plane of incidence. The angle at which this occurs is called the polarizing angle or the Brewster angle. At other angles the reflected light is ...
Two Quick Light Experiments
... We will send laser light through a pattern of slits. According to Huygens' Principle, the light that passes through these slits can be thought of as a new source. (We use laser light for this part because we are looking at interference which involves phases and wavelengths; lasers are monochromatic ...
... We will send laser light through a pattern of slits. According to Huygens' Principle, the light that passes through these slits can be thought of as a new source. (We use laser light for this part because we are looking at interference which involves phases and wavelengths; lasers are monochromatic ...
Unit 7 Lab Review - Harrison High School
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
... speed of sound? 2. In this lab what factor did we have to use to find the theoretical value for the speed of sound? ...
Lab 5: Polarization of Light 1 Introduction 2 Linear Polarization 3
... structure, with the following interesting property: light polarized parallel to the optic axis experiences a different index of refraction (and therefore has a different velocity) than light polarized perpendicular to the optic axis. Such crystals are called birefringent, and can be used to make a r ...
... structure, with the following interesting property: light polarized parallel to the optic axis experiences a different index of refraction (and therefore has a different velocity) than light polarized perpendicular to the optic axis. Such crystals are called birefringent, and can be used to make a r ...
Light Tree.pdf - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... The concept of light tree is introduced in a wavelength routed optical network, which employs wavelength -division multiplexing (WDM). Light Tree was designed by Omar Ivan Huerta Cardoso. Cardoso designed a plastic tree with some water in it which is used to conduce the light from Light Emitting Dio ...
... The concept of light tree is introduced in a wavelength routed optical network, which employs wavelength -division multiplexing (WDM). Light Tree was designed by Omar Ivan Huerta Cardoso. Cardoso designed a plastic tree with some water in it which is used to conduce the light from Light Emitting Dio ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... a function of the wavelength of the incident light, n=n() This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), Snell’s law of refraction implies that different wavelength light is bent at different refractio ...
... a function of the wavelength of the incident light, n=n() This implies that the speed of light inside the medium depends on The dependence of wave speed v and n on is called dispersion Since n=n(), Snell’s law of refraction implies that different wavelength light is bent at different refractio ...
Equipment list: Description Supplier Model Optical test bench
... Index accuracy: ±.0005 (accuracy of up to ±.0001 available for many applications) Index resolution: ±.0003 (resolution of up to ±.00005 available for many applications) Thickness accuracy: ±(0.5% + 5 nm) Thickness resolution: ±0.3% high accuracy index measurement of bulk, substrate, or liquid materi ...
... Index accuracy: ±.0005 (accuracy of up to ±.0001 available for many applications) Index resolution: ±.0003 (resolution of up to ±.00005 available for many applications) Thickness accuracy: ±(0.5% + 5 nm) Thickness resolution: ±0.3% high accuracy index measurement of bulk, substrate, or liquid materi ...