Supplementary Information (doc 4223K)
... want to achieve giant slow light effect. Gold rectangles have been investigated in many papers, and the group index for gold rectangles is not large. While, few works of slow light effect on triangle are found, and the curiosity on triangles encouraged us to investigate. Secondly, we want to achieve ...
... want to achieve giant slow light effect. Gold rectangles have been investigated in many papers, and the group index for gold rectangles is not large. While, few works of slow light effect on triangle are found, and the curiosity on triangles encouraged us to investigate. Secondly, we want to achieve ...
ECE 463/626: Optoelectronics Instructor: Prof. H. Grebel, Rm 302
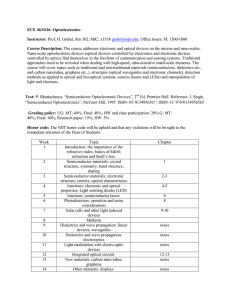
... Honor code: The NJIT honor code will be upheld and that any violations will be brought to the immediate attention of the Dean of Students. Week ...
... Honor code: The NJIT honor code will be upheld and that any violations will be brought to the immediate attention of the Dean of Students. Week ...
Polarization of Light Mica Sheet
... rotated by different amounts as the polarized light passes through the plastic, so you see rainbow colors. They actually use polarizers in manufacturing to test products and make sure that there isn’t too much stress on any part of a product that may cause it to break when it’s not supposed to. ...
... rotated by different amounts as the polarized light passes through the plastic, so you see rainbow colors. They actually use polarizers in manufacturing to test products and make sure that there isn’t too much stress on any part of a product that may cause it to break when it’s not supposed to. ...
Document
... • We have assumed that the paraxial approximation applies in that all rays make small angles with respect to the optical axis. We also assume that the rays strike close to th e centre of the mirror. • In real systems the rays hit the whole mirror. We find that rays that hit near the outside of mirro ...
... • We have assumed that the paraxial approximation applies in that all rays make small angles with respect to the optical axis. We also assume that the rays strike close to th e centre of the mirror. • In real systems the rays hit the whole mirror. We find that rays that hit near the outside of mirro ...
Advantages of FTIR spectroscopy
... 400 and about 5 cm-1 wavenumbers. This range covers the vibrational frequencies of both backbone vibrations of large molecules, as well as fundamental vibrations of molecules that include heavy atoms (e.g. inorganic or organometallic compounds). ...
... 400 and about 5 cm-1 wavenumbers. This range covers the vibrational frequencies of both backbone vibrations of large molecules, as well as fundamental vibrations of molecules that include heavy atoms (e.g. inorganic or organometallic compounds). ...
Experimental proposal for electromagnetically
... The leftmost one is what we call a single crystal, that is, it is highly perfect which gives rise to its transparency. The center one is composed of numerous and very small interconnected single crystals that the boundaries between these small crystals scatter a portion of the light reflected from t ...
... The leftmost one is what we call a single crystal, that is, it is highly perfect which gives rise to its transparency. The center one is composed of numerous and very small interconnected single crystals that the boundaries between these small crystals scatter a portion of the light reflected from t ...
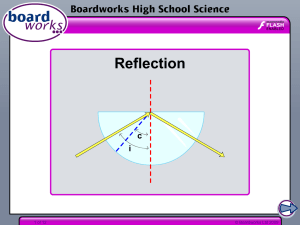
law of reflection
... between two materials of different densities, and is reflected rather than refracted. There are two conditions for total internal reflection: 1. The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle. 2. The light must be passing from a high refractive index to a low one. Sometimes only part ...
... between two materials of different densities, and is reflected rather than refracted. There are two conditions for total internal reflection: 1. The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle. 2. The light must be passing from a high refractive index to a low one. Sometimes only part ...
JAP04 - Anglictina pro fyziky 4 Refractive index
... Let summarize it all. The refractive index of a medium is a measure for how much the speed of light (or other waves such as sound waves) is reduced inside the medium. For example, typical glass has a refractive index of 1.5, which means that light travels at 0.67 times the speed in air or vacuum. Tw ...
... Let summarize it all. The refractive index of a medium is a measure for how much the speed of light (or other waves such as sound waves) is reduced inside the medium. For example, typical glass has a refractive index of 1.5, which means that light travels at 0.67 times the speed in air or vacuum. Tw ...
Homework Set #6 Due: 3-28-14
... Another difficulty is that the index of refraction seen by the light will vary if the light is not normally incident upon the waveplate. The ordinary and extradinary polarization directions and the extraordinary wave index of refraction depend on input angle. If normal incidence is not used, a half- ...
... Another difficulty is that the index of refraction seen by the light will vary if the light is not normally incident upon the waveplate. The ordinary and extradinary polarization directions and the extraordinary wave index of refraction depend on input angle. If normal incidence is not used, a half- ...
L16
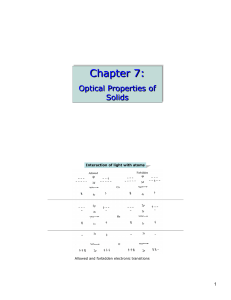
... not molecules) are placed in a strong magnetic field (~ 1 tesla), splitting of electronic energy levels takes place. The simplest splitting of one energy level results in three energy levels, one at a higher energy, another at a lower energy (two s satellite lines) and the third remains at the same ...
... not molecules) are placed in a strong magnetic field (~ 1 tesla), splitting of electronic energy levels takes place. The simplest splitting of one energy level results in three energy levels, one at a higher energy, another at a lower energy (two s satellite lines) and the third remains at the same ...
Chapter1 Fundamental law of geometrical optics 第一章 几何光学的
... Wavelength λ: dividing the velocity by the frequency. λ=v/ν λ: 0.4μm~0.75μm(micrometer) Velocity v=3*10 10 cm/sec in empty space ...
... Wavelength λ: dividing the velocity by the frequency. λ=v/ν λ: 0.4μm~0.75μm(micrometer) Velocity v=3*10 10 cm/sec in empty space ...
Document
... Maxwell's Equations and the Constitutive Equations Light beams are represented by electromagnetic waves propagating in space. An electromagnetic wave is described by two vector fields: the electric field E(r, t) and the magnetic field H(r, t). In free space (i.e. in vacuum or air) they satisfy a se ...
... Maxwell's Equations and the Constitutive Equations Light beams are represented by electromagnetic waves propagating in space. An electromagnetic wave is described by two vector fields: the electric field E(r, t) and the magnetic field H(r, t). In free space (i.e. in vacuum or air) they satisfy a se ...
The Polarization of Light
... elliptically polarized. There is a class of materials, crystals, that are birefringent; as the name implies there two indices of refraction, depending on direction of propagation and the direction the electric field points. The two indices are call the ordinary index (no ) and the extraordinary inde ...
... elliptically polarized. There is a class of materials, crystals, that are birefringent; as the name implies there two indices of refraction, depending on direction of propagation and the direction the electric field points. The two indices are call the ordinary index (no ) and the extraordinary inde ...
All Optical Networks
... Current fiber networks use electronic switching and are therefore limited to electronic speeds of a few gigabits per second. For higher speeds, it is important that the signal remain photonic throughout its path. Such networks, which use optical switching and routing, are called all-optical. ...
... Current fiber networks use electronic switching and are therefore limited to electronic speeds of a few gigabits per second. For higher speeds, it is important that the signal remain photonic throughout its path. Such networks, which use optical switching and routing, are called all-optical. ...
Refractive index
... called optically sparser while the medium with higher refractive index is called optically denser. When light is refracted into the optically sparser medium, the refractive angle can be 90 degrees for certain incident angle. This incident angle is called critical and for angles of incidence above th ...
... called optically sparser while the medium with higher refractive index is called optically denser. When light is refracted into the optically sparser medium, the refractive angle can be 90 degrees for certain incident angle. This incident angle is called critical and for angles of incidence above th ...
PHE-09 (2007
... vi) In the context of interference of light, differentiate between division of amplitude and division of wavefront. Give one example each. ...
... vi) In the context of interference of light, differentiate between division of amplitude and division of wavefront. Give one example each. ...
Titel
... Isolator: used in systems at the output of amplifiers and lasers to prevent reflections Filter: to multiplex and demultiplex wavelengths in a WDM system, and to provide equalization of the gain and filtering of noise in optical amplifier MUX & DEMUX: MUX combines signals at different wavelengths on ...
... Isolator: used in systems at the output of amplifiers and lasers to prevent reflections Filter: to multiplex and demultiplex wavelengths in a WDM system, and to provide equalization of the gain and filtering of noise in optical amplifier MUX & DEMUX: MUX combines signals at different wavelengths on ...
Chapter 24
... Change of phase due to reflection When light reflects off of a medium that has a higher index of refraction than the initial medium, the electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 1800. See fig. 24.6 and 24.7 In figure 24.7 the two reflected beam interfere with each other. ...
... Change of phase due to reflection When light reflects off of a medium that has a higher index of refraction than the initial medium, the electromagnetic wave undergoes a phase change of 1800. See fig. 24.6 and 24.7 In figure 24.7 the two reflected beam interfere with each other. ...
Interference
... The Physics of Structural Colour • Light reflects from slightly different places along the surface. An optical path difference is introduced ...
... The Physics of Structural Colour • Light reflects from slightly different places along the surface. An optical path difference is introduced ...
Optical Activity - Chemistry With BT
... Physical Properties of Stereoisomers • Since enantiomers have identical physical properties, they cannot be separated by common physical techniques like distillation. • Diastereomers and constitutional isomers have different physical properties, and therefore can be separated by common physical ...
... Physical Properties of Stereoisomers • Since enantiomers have identical physical properties, they cannot be separated by common physical techniques like distillation. • Diastereomers and constitutional isomers have different physical properties, and therefore can be separated by common physical ...
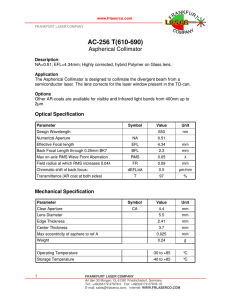
AC-256 T(610-690) - Frankfurt Laser Company
... The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrared light bands from 400nm up to 2µm ...
... The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrared light bands from 400nm up to 2µm ...