Fiber Optic Light Sources - Electrical and Computer
... LEDs produce nonlinear incoherent light whereas a Laser Diode produces linear coherent light. Incoherent light sources used in multimode systems as where Laser Diodes/Tunable Lasers in single mode systems Laser diodes must operate above their threshold region to produce coherent light, otherwise ope ...
... LEDs produce nonlinear incoherent light whereas a Laser Diode produces linear coherent light. Incoherent light sources used in multimode systems as where Laser Diodes/Tunable Lasers in single mode systems Laser diodes must operate above their threshold region to produce coherent light, otherwise ope ...
3.7.4 Summary to: Dielectrics and Optics
... (with the imaginary part expressed as conductivity σDK), we have (simple) optics completely covered! ...
... (with the imaginary part expressed as conductivity σDK), we have (simple) optics completely covered! ...
IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light - FSU
... or π/2, the emergent light is plane-polarized, while if φ = π/4, then a = b, and the emergent light is circularly polarized. Let light from the collimator of a spectrometer be polarized in a known direction, and a Nicol crossed with this to extinguish the light. Introduce a quarter-wave plate with i ...
... or π/2, the emergent light is plane-polarized, while if φ = π/4, then a = b, and the emergent light is circularly polarized. Let light from the collimator of a spectrometer be polarized in a known direction, and a Nicol crossed with this to extinguish the light. Introduce a quarter-wave plate with i ...
Ray Box Lab - Iona Physics
... 1. Place the ray box near the edge of a piece of paper in such a way that the rays cross most of the width of the page. Note the rays are diverging. 2. Place the plano-convex lens in front of the ray box with the flat side facing the ray box. 3. Adjust the position of the lens so that the rays are p ...
... 1. Place the ray box near the edge of a piece of paper in such a way that the rays cross most of the width of the page. Note the rays are diverging. 2. Place the plano-convex lens in front of the ray box with the flat side facing the ray box. 3. Adjust the position of the lens so that the rays are p ...
View PDF - OMICS Group
... superposed, during constructive interference they become stronger and the color is striking. The amplitude of the resulting wave is greater than the amplitude of the reflected rays. When the resulting amplitude is smaller, destructive interference is said to occur. Destructive interference can lead ...
... superposed, during constructive interference they become stronger and the color is striking. The amplitude of the resulting wave is greater than the amplitude of the reflected rays. When the resulting amplitude is smaller, destructive interference is said to occur. Destructive interference can lead ...
Light II - Galileo and Einstein
... A. No, it would always get out. B. Yes, but the distance between reflections would have to be greater. C. Same but smaller. ...
... A. No, it would always get out. B. Yes, but the distance between reflections would have to be greater. C. Same but smaller. ...
Growth, Optical Properties, and Optimization of Infrared
... High-performance III-V semiconductors based on ternary alloys and superlattice systems are fabricated, studied, and compared for infrared optoelectronic applications. InAsBi is a ternary alloy near the GaSb lattice constant that is not as thoroughly investigated as other III-V alloys and that is cha ...
... High-performance III-V semiconductors based on ternary alloys and superlattice systems are fabricated, studied, and compared for infrared optoelectronic applications. InAsBi is a ternary alloy near the GaSb lattice constant that is not as thoroughly investigated as other III-V alloys and that is cha ...
Nano-optical Imaging using Scattering Scanning Near-Field Optical Microscopy
... We investigate a nano-imaging technique, known as scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due t ...
... We investigate a nano-imaging technique, known as scattering scanning near-field optical microscopy (s-SNOM) and image several different materials using said technique. We report our data provide potential paths for future work. I. INTRODUCTION Scientists have long studied optical spectroscopy due t ...
No Slide Title
... How they interfere will depend on the relative indices of refraction. In the example above the first ray suffers a 180 degree phase change (1/2 a wavelength) upon reflection. The second ray does not change phase in reflection, but has to travel a longer distance to come back up. The distance is twic ...
... How they interfere will depend on the relative indices of refraction. In the example above the first ray suffers a 180 degree phase change (1/2 a wavelength) upon reflection. The second ray does not change phase in reflection, but has to travel a longer distance to come back up. The distance is twic ...
Lecture 28 - LSU Physics
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). •How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? ...
... A red light beam with wavelength λ=0.625µm travels through glass (n=1.46) a distance of 1mm. A second beam, parallel to the first one and originally in phase with it, travels the same distance through sapphire (n=1.77). •How many wavelengths are there of each beam inside the material? ...
DG Papazoglou et al.
... Optical aberrations can be envisioned as a way to impose polynomial phase distributions on plane wave! Coma aberration Cubic phase ! ...
... Optical aberrations can be envisioned as a way to impose polynomial phase distributions on plane wave! Coma aberration Cubic phase ! ...
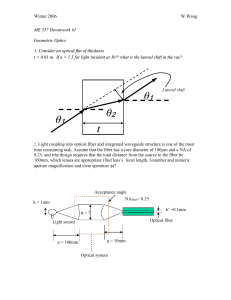
ME 557 Howmwork #1
... 3. Fiber coupling spheres. Tiny glass balls are often used as lenses to couple light into and out of optical fibers. The fiber end is located at a distance f from the sphere. For a sphere of radius a=1 mm and refractive index n =1.8, determine f such that a ray parallel to the optical axis at a dist ...
... 3. Fiber coupling spheres. Tiny glass balls are often used as lenses to couple light into and out of optical fibers. The fiber end is located at a distance f from the sphere. For a sphere of radius a=1 mm and refractive index n =1.8, determine f such that a ray parallel to the optical axis at a dist ...
Chapter 1 - Liceo Crespi
... oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation. Unlike a wave on a string or a sound wave, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium in which to propagate. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or through substances (depending on the absorptio ...
... oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation. Unlike a wave on a string or a sound wave, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium in which to propagate. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or through substances (depending on the absorptio ...
Research Directions
... application of resonant nonlinear magneto-optical effects. We have discussed the connections and parallels between this and other subfields of modern spectroscopy, and pointed out open questions and directions for future work. Numerous and diverse applications of NMOE include precision magnetometr ...
... application of resonant nonlinear magneto-optical effects. We have discussed the connections and parallels between this and other subfields of modern spectroscopy, and pointed out open questions and directions for future work. Numerous and diverse applications of NMOE include precision magnetometr ...
HALL EFFECT IN THIN FILMS When a current
... Place the sample in the centre of the magnet gap with its broad side perpendicular to the field. Determine RH and its sign by using Eq. (1) and making the appropriate plots. The thickness of the Hall samples can be determined from the interferometric photographs provided by the manufacturers. In our ...
... Place the sample in the centre of the magnet gap with its broad side perpendicular to the field. Determine RH and its sign by using Eq. (1) and making the appropriate plots. The thickness of the Hall samples can be determined from the interferometric photographs provided by the manufacturers. In our ...
Document
... that will allow multiple users to work and interact. Perceptive Pixel’s technology is currently being utilized, in the form of the Multi-Touch Collaboration Wall. ...
... that will allow multiple users to work and interact. Perceptive Pixel’s technology is currently being utilized, in the form of the Multi-Touch Collaboration Wall. ...
Critical angle - Kelso High School
... showing this. 9. What is the critical angle? 10. What is diffraction? Why do radio waves diffract around hills that block TV waves? 11. Waves have the following properties – reflection, diffraction, refraction and interference. Can particles be reflected, diffracted and refracted? We will find out a ...
... showing this. 9. What is the critical angle? 10. What is diffraction? Why do radio waves diffract around hills that block TV waves? 11. Waves have the following properties – reflection, diffraction, refraction and interference. Can particles be reflected, diffracted and refracted? We will find out a ...
Demonstration: quarter-wave plate and half-wave plate
... shape of a plate with properly chosen optical axis orientation and thickness. The optical axis of the crystal should be parallel to the plate surface, as in Fig. 1 we set the x-axis parallel to the optical axis. In such a way, two polarization directions can be defined for a normal incident plane wa ...
... shape of a plate with properly chosen optical axis orientation and thickness. The optical axis of the crystal should be parallel to the plate surface, as in Fig. 1 we set the x-axis parallel to the optical axis. In such a way, two polarization directions can be defined for a normal incident plane wa ...
WINDOWS During the Apollo (manned lunar exploration) space
... probably will be air (n1 = 1.0). The other probably will be some other glass (n2 ~ 1.5). Using Equation 3, you can calculate a reflection of ~ 4%. This calculation is for one side of the window. When the rays emerge from the other side, another 4% reflection loss is encountered. In summary, we reali ...
... probably will be air (n1 = 1.0). The other probably will be some other glass (n2 ~ 1.5). Using Equation 3, you can calculate a reflection of ~ 4%. This calculation is for one side of the window. When the rays emerge from the other side, another 4% reflection loss is encountered. In summary, we reali ...
Internship
... Inorganic ions can be identified using absorbance based measurements with UV light. A relative new way is to identify them using NIR light. This light can probe the overtones of OH bonds. These bonds are influence by ions and thus ions can indirectly be probed by NIR light (see Figure 1). ...
... Inorganic ions can be identified using absorbance based measurements with UV light. A relative new way is to identify them using NIR light. This light can probe the overtones of OH bonds. These bonds are influence by ions and thus ions can indirectly be probed by NIR light (see Figure 1). ...
Optical Properties of Condensed Matters
... may consider only the real parts of n and ; In the absorption region, one need to know both the real and imaginary parts of n and . ...
... may consider only the real parts of n and ; In the absorption region, one need to know both the real and imaginary parts of n and . ...
Singularities of interference of three waves with different polarization
... interferometer is linearly or circularly polarized with linearly changed phase difference along the y-axis. The interference of three plane waves with different polarization states (LLL – linear-linear-linear or LLC – linear-linear-circular) and variable change difference produce twodimensional ligh ...
... interferometer is linearly or circularly polarized with linearly changed phase difference along the y-axis. The interference of three plane waves with different polarization states (LLL – linear-linear-linear or LLC – linear-linear-circular) and variable change difference produce twodimensional ligh ...