Physics 234 Exam # 2 Review
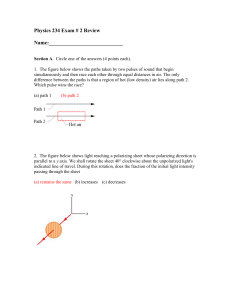
... Section A. Circle one of the answers (4 points each). 1. The figure below shows the paths taken by two pulses of sound that begin simultaneously and then race each other through equal distances in air. The only difference between the paths is that a region of hot (low density) air lies along path 2. ...
... Section A. Circle one of the answers (4 points each). 1. The figure below shows the paths taken by two pulses of sound that begin simultaneously and then race each other through equal distances in air. The only difference between the paths is that a region of hot (low density) air lies along path 2. ...
Background: Polarimetry is the measurement and interpretation of
... Racemic mixture: is a mixture which contains equal amounts of each enantiomer. (50% D and 50% L) and is optically inactive because the rotation cancel each other. ...
... Racemic mixture: is a mixture which contains equal amounts of each enantiomer. (50% D and 50% L) and is optically inactive because the rotation cancel each other. ...
Prof. Lan Yang - Microlasers for Nanoscale
... due to their superior capability to significantly enhance the interactions of light with the sensing targets. A WGM resonator traps light in circular orbits in a way similar to a whisper, i.e., a sound wave, traveling along a circular wall, an effect found in the whispering gallery of St. Paul’s Cat ...
... due to their superior capability to significantly enhance the interactions of light with the sensing targets. A WGM resonator traps light in circular orbits in a way similar to a whisper, i.e., a sound wave, traveling along a circular wall, an effect found in the whispering gallery of St. Paul’s Cat ...
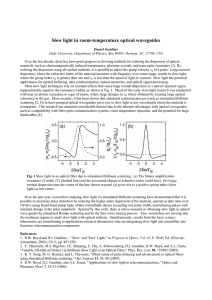
Refractive Index and Thickness Analysis of Natural Silicon Dioxide
... Rutherford backscattering, and electrical methods of capacitance-voltage (C-V). The electronic structure, properties of ultrathin gate oxides, and imaging of individual dopant atoms and clusters in bulk Si at the atomic scale have been investigated with TEM (2–4). Ellipsometry also has been used to ...
... Rutherford backscattering, and electrical methods of capacitance-voltage (C-V). The electronic structure, properties of ultrathin gate oxides, and imaging of individual dopant atoms and clusters in bulk Si at the atomic scale have been investigated with TEM (2–4). Ellipsometry also has been used to ...
Optical Coherence Tomography
... these two amplitudes. Note only the phase difference between the two interface signals are used for the calculation. These three spectral attributes are dependent on the complex refractive index and the film thickness. Equations (4)–(6) must be inverted to obtain these optical parameters of the film ...
... these two amplitudes. Note only the phase difference between the two interface signals are used for the calculation. These three spectral attributes are dependent on the complex refractive index and the film thickness. Equations (4)–(6) must be inverted to obtain these optical parameters of the film ...
Abstract
... manipulate a nucleus by (VUV) laser light for the first time. Apart from exciting fundamental research questions (including the search for temporal variations of fundamental constants), this well-shielded narrow-linewidth transition opens up the possibility to realize a compact solid-state optical t ...
... manipulate a nucleus by (VUV) laser light for the first time. Apart from exciting fundamental research questions (including the search for temporal variations of fundamental constants), this well-shielded narrow-linewidth transition opens up the possibility to realize a compact solid-state optical t ...
Slow light in room-temperature optical waveguides
... Over the last decade, there has been great progress in devising methods for tailoring the dispersion of optical materials, such as electromagnetically induced transparency, photonic crystals, and nano-optic resonators [1]. By tailoring the dispersion using all-optical methods, it is possible to adju ...
... Over the last decade, there has been great progress in devising methods for tailoring the dispersion of optical materials, such as electromagnetically induced transparency, photonic crystals, and nano-optic resonators [1]. By tailoring the dispersion using all-optical methods, it is possible to adju ...
PH4035 - Principles of Optics
... interfaces; reflection and transmission of multi-layer thin films plus their use in interference filters; interpretation of diffraction patterns in terms of Fourier theory; spatial filters; the theory and use of Fabry-Perot etalons; laser cavities and Gaussian beams. Aims & Objectives The course wil ...
... interfaces; reflection and transmission of multi-layer thin films plus their use in interference filters; interpretation of diffraction patterns in terms of Fourier theory; spatial filters; the theory and use of Fabry-Perot etalons; laser cavities and Gaussian beams. Aims & Objectives The course wil ...
2-Day Intensive Training
... • Waveguide layers are grown at high temperatures The materials have different thermal expansion coefficients, i ...
... • Waveguide layers are grown at high temperatures The materials have different thermal expansion coefficients, i ...
Optical Activity
... pure material. Specific rotations are published for many optically active substances at various temperatures and wavelengths of light. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of organic substances by measurements of specific rotations of the plane of polarization, are very important tools in biochemic ...
... pure material. Specific rotations are published for many optically active substances at various temperatures and wavelengths of light. Quantitative and qualitative analyses of organic substances by measurements of specific rotations of the plane of polarization, are very important tools in biochemic ...
Design technique for all-dielectric non
... mum even for n = n0 = 1.52, if the light is incident from air, the variation of np does not show a minimum. The first case when the light is incident from glass was very ingeniously solved by Gilo in order to design a non− −polarizing beam splitter inside a glass cube [5]. He noted that if two diffe ...
... mum even for n = n0 = 1.52, if the light is incident from air, the variation of np does not show a minimum. The first case when the light is incident from glass was very ingeniously solved by Gilo in order to design a non− −polarizing beam splitter inside a glass cube [5]. He noted that if two diffe ...
MOCT(Magneto Optic Current Transformer)
... is 45 0 oriented with the polarizer, to convert the orientation variation of the polarized light into intensity variation of the light with two outputs, and then these two outputs are send to photo detectors. The purpose of using the analyzer is that photo detectors can only detect the intensity of ...
... is 45 0 oriented with the polarizer, to convert the orientation variation of the polarized light into intensity variation of the light with two outputs, and then these two outputs are send to photo detectors. The purpose of using the analyzer is that photo detectors can only detect the intensity of ...
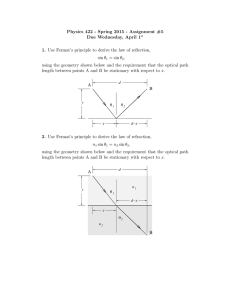
Physics 422 - Spring 2015 - Assignment #5
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
... 3. (a) Calculate the distance to the object focal point, fo , and the image focal point fi for a single spherical concave refracting surface with radius of curvature R = −10 cm, made of a material with index of refraction n2 = 1.5, and with air (n1 = 1) on the object side. (b) Calculate fo and fi f ...
4.6 Optical Fibres
... Light has to be launched into a fibre. Communication fibre uses lasers but for local networks light-emitting diodes may be used. Light travels through the fibre by total internal reflection bouncing off the interface between the core and cladding. The cladding must have a lower refractive index comp ...
... Light has to be launched into a fibre. Communication fibre uses lasers but for local networks light-emitting diodes may be used. Light travels through the fibre by total internal reflection bouncing off the interface between the core and cladding. The cladding must have a lower refractive index comp ...
Berry`s Phase
... and even classical mechanics. • It occurs when more than one physical parameter of the particle’s path are changed adiabatically. • Although the parameters are returned to their original values the measured quantity (spin or polarization) does not. • EXAMPLE: Two parameters characterizing an EM wave ...
... and even classical mechanics. • It occurs when more than one physical parameter of the particle’s path are changed adiabatically. • Although the parameters are returned to their original values the measured quantity (spin or polarization) does not. • EXAMPLE: Two parameters characterizing an EM wave ...
Lect 4 - Components - Sonoma State University
... Thus, each filer must have a flat passband (accommodating for small changes in WL) The flatness of the filer is measure by 1-dB bandwidth ...
... Thus, each filer must have a flat passband (accommodating for small changes in WL) The flatness of the filer is measure by 1-dB bandwidth ...
File
... Total internal reflection occurs when light is coming out of something dense, such as glass, water or perspex ...
... Total internal reflection occurs when light is coming out of something dense, such as glass, water or perspex ...
Practice Problems_sources
... 3. A double heterojunction InGaAsP LED emitting at a peak wavelength of 1310 nm has radiative and non-radiative recombination times of 25 and 90 ns, respectively. The drive current is 35 mA. (a) Find the internal quantum efficiency and the internal power level. (b) If the refractive index of the med ...
... 3. A double heterojunction InGaAsP LED emitting at a peak wavelength of 1310 nm has radiative and non-radiative recombination times of 25 and 90 ns, respectively. The drive current is 35 mA. (a) Find the internal quantum efficiency and the internal power level. (b) If the refractive index of the med ...
Electro-Optic Ceramics
... refractive index as a function of an externally applied electric field. In unisotropic materials the index of refraction depends on the direction of propagation and the direction of polarization of the light. This means that the two components of light polarization can propagate at a different speed ...
... refractive index as a function of an externally applied electric field. In unisotropic materials the index of refraction depends on the direction of propagation and the direction of polarization of the light. This means that the two components of light polarization can propagate at a different speed ...
Wollaston and Nomarski Prisms
... axis oriented at a 45-degree angle (northwest to southeast) to the polarizer and analyzer. The prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of ...
... axis oriented at a 45-degree angle (northwest to southeast) to the polarizer and analyzer. The prisms are composed of two precisely ground and polished wedge-shaped slabs produced from high-grade optical quartz, a uniaxial birefringent crystal. Two quartz wedges having perpendicular orientations of ...