Chapter 33. Electromagnetic Waves
... The Speed of Light • All electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum at the same speed, which is known as the speed of light c=3.00×108 m/s. • All electromagnetic waves travel through a material substance with the speeds less than the speed of light in vacuum c=3.00×108 m/s. The waves with differ ...
... The Speed of Light • All electromagnetic waves travel through a vacuum at the same speed, which is known as the speed of light c=3.00×108 m/s. • All electromagnetic waves travel through a material substance with the speeds less than the speed of light in vacuum c=3.00×108 m/s. The waves with differ ...
OPTICAL MINERALOGY
... Light- a form of energy, detectable with the eye, which can be transmitted from one place to another at finite velocity. Visible light is a small portion of a continuous spectrum of radiation ranging from cosmic rays to radio waves. White or visible light, that which the eye detects, is only a fract ...
... Light- a form of energy, detectable with the eye, which can be transmitted from one place to another at finite velocity. Visible light is a small portion of a continuous spectrum of radiation ranging from cosmic rays to radio waves. White or visible light, that which the eye detects, is only a fract ...
ETM4106Tutorial3
... which give an attenuation of 0.8 dB each. Determine the minimum mean optical power, which must be launched into the fiber in order to maintain a mean optical power level of 0.30 W at the detector. Ans. 703 W. Q.4 Determine the theoretical attenuation in decibels per km due to the Rayleight scatt ...
... which give an attenuation of 0.8 dB each. Determine the minimum mean optical power, which must be launched into the fiber in order to maintain a mean optical power level of 0.30 W at the detector. Ans. 703 W. Q.4 Determine the theoretical attenuation in decibels per km due to the Rayleight scatt ...
Lab 1
... your data. Print out the graph and fit, along with your initial values of A, B, and C. The fit may not be very good on this first try; that's OK. Now, go back and change the values of A, B, and C until you have a good fit. Print this graph out including raw data, the fit, and the values of A, B, and ...
... your data. Print out the graph and fit, along with your initial values of A, B, and C. The fit may not be very good on this first try; that's OK. Now, go back and change the values of A, B, and C until you have a good fit. Print this graph out including raw data, the fit, and the values of A, B, and ...
Resonators and Mode Matching
... Determine the ABCD matrix for one round trip in the resonator matrix depends on starting point Solve equation ...
... Determine the ABCD matrix for one round trip in the resonator matrix depends on starting point Solve equation ...
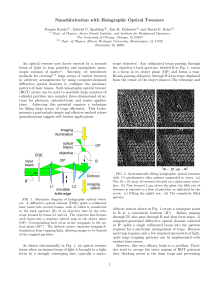
Nanofabrication with Holographic Optical Tweezers
... particles past the exposed traps with a pressure differential, through electrophoresis or electro-osmosis, using a temperature gradient, or by translating the entire pattern through the suspension like a fishing net. Starting from a particle concentration on the order of 10−4 µm−3 , a reasonable flo ...
... particles past the exposed traps with a pressure differential, through electrophoresis or electro-osmosis, using a temperature gradient, or by translating the entire pattern through the suspension like a fishing net. Starting from a particle concentration on the order of 10−4 µm−3 , a reasonable flo ...
Talk, ppt
... Polarimetry refers to the art or process of measuring the polarization of the light. A more scientific definition: the science of measuring the polarization state of a light beam and the diattenuating, retarding and depolarizing properties of materials. Considering a plane wave, the Electric field v ...
... Polarimetry refers to the art or process of measuring the polarization of the light. A more scientific definition: the science of measuring the polarization state of a light beam and the diattenuating, retarding and depolarizing properties of materials. Considering a plane wave, the Electric field v ...
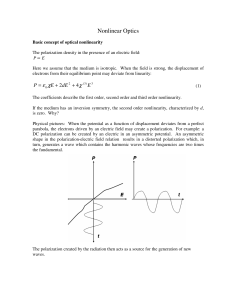
10NonlinearOptics.pdf
... The coefficients describe the first order, second order and third order nonlinearity. If the medium has an inversion symmetry, the second order nonlinearity, characterized by d, is zero. Why? Physical pictures: When the potential as a function of displacement deviates from a perfect parabola, the el ...
... The coefficients describe the first order, second order and third order nonlinearity. If the medium has an inversion symmetry, the second order nonlinearity, characterized by d, is zero. Why? Physical pictures: When the potential as a function of displacement deviates from a perfect parabola, the el ...
Wave Optics
... Light with a wavelength of 650nm strikes two slits that are 7.65x10-5m apart and produce an interference pattern on a screen 4.00m away. How wide will the central fringe be that appears on the screen? ...
... Light with a wavelength of 650nm strikes two slits that are 7.65x10-5m apart and produce an interference pattern on a screen 4.00m away. How wide will the central fringe be that appears on the screen? ...
Extinction Coefficient Measurements of Turbid Media
... A 1 mW He–Ne laser source emitting at 632.8 nm operating in continuous wave (cw) [which has proved suitable for low-power laser interaction with matter], was directed horizontally to a cell (glass box) of thickness 25 mm containing the sample . The collimated transmitted (unscattered ) light was det ...
... A 1 mW He–Ne laser source emitting at 632.8 nm operating in continuous wave (cw) [which has proved suitable for low-power laser interaction with matter], was directed horizontally to a cell (glass box) of thickness 25 mm containing the sample . The collimated transmitted (unscattered ) light was det ...
Theory - BrainMass
... Ni is the refractive index of the medium the light is leaving, Ai is the incident angle between the light ray and the normal to the meduim to medium interface, Nr is the refractive index of the medium the light is entering, Ar is the refractive angle between the light ray and the normal to the medui ...
... Ni is the refractive index of the medium the light is leaving, Ai is the incident angle between the light ray and the normal to the meduim to medium interface, Nr is the refractive index of the medium the light is entering, Ar is the refractive angle between the light ray and the normal to the medui ...
A. Menegolli
... useful as it provides an absolute time measurement and a trigger for ionizing events occurring in Liquid Noble Gases ...
... useful as it provides an absolute time measurement and a trigger for ionizing events occurring in Liquid Noble Gases ...
Chapter 24 Wave Optics Diffraction Grating Interference by Thin
... In terms of the wavelength, what is the thickness of the thinnest film for which the reflected light will be a maximum? ...
... In terms of the wavelength, what is the thickness of the thinnest film for which the reflected light will be a maximum? ...
Introduction to light 2
... Dispersion and Refractive Index For the normal dispersion of the refractive indices, the index of refraction decreases with increasing wavelength. To describe the dispersion of a particular material it is necessary to report the index of refraction at several wavelengths. By convention indices of r ...
... Dispersion and Refractive Index For the normal dispersion of the refractive indices, the index of refraction decreases with increasing wavelength. To describe the dispersion of a particular material it is necessary to report the index of refraction at several wavelengths. By convention indices of r ...
Optics - Mr. Gallagher's Physics
... • The incident ray is the light ray that strikes the mirror. • The reflected ray is the light ray that bounces off the mirror • Between the incident and reflected rays, there is an imaginary line called the normal line which is perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. • The angle between the inci ...
... • The incident ray is the light ray that strikes the mirror. • The reflected ray is the light ray that bounces off the mirror • Between the incident and reflected rays, there is an imaginary line called the normal line which is perpendicular to the surface of the mirror. • The angle between the inci ...
Advantages of Infinity-Corrected Optics in FT
... polarizing optics are available and useful with microscopes that are not infinity-corrected. However, these are placed in focused beams (though not necessarily at field stop positions), reducing the efficiency of the polarization and introducing extra light loss. In addition to the ability to add po ...
... polarizing optics are available and useful with microscopes that are not infinity-corrected. However, these are placed in focused beams (though not necessarily at field stop positions), reducing the efficiency of the polarization and introducing extra light loss. In addition to the ability to add po ...
Measurement of Surface Quality 1. Lyot Test 2. FECO 3. Nomarski
... range can be determined. Two disadvantages are 1) we are getting data only along a line and 2) the sample being measured must have a high reflectivity. ...
... range can be determined. Two disadvantages are 1) we are getting data only along a line and 2) the sample being measured must have a high reflectivity. ...
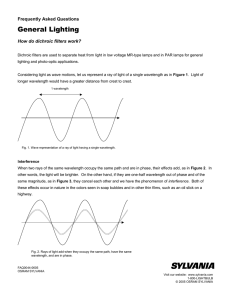
How do Dichroic Filters work?
... When the film has a thickness equal to ¼ wavelength, the ray c will be reflected with change of phase, and will therefore add to ray a, increasing the brightness of the reflection. These results also occur when the thickness is multiple of ¼ wavelength. As a general rule, therefore, for a particular ...
... When the film has a thickness equal to ¼ wavelength, the ray c will be reflected with change of phase, and will therefore add to ray a, increasing the brightness of the reflection. These results also occur when the thickness is multiple of ¼ wavelength. As a general rule, therefore, for a particular ...