spectroscopic ellipsometry as a versatile tool to study thin films
... Thus, ellipsometry is mainly used to determine film thickness and optical constants (refractive index, n and extinction coefficient, k) not only for single-layers but also for multi-layer thin films. However, it is also applied to characterize composition, crystallinity, roughness, doping concentrat ...
... Thus, ellipsometry is mainly used to determine film thickness and optical constants (refractive index, n and extinction coefficient, k) not only for single-layers but also for multi-layer thin films. However, it is also applied to characterize composition, crystallinity, roughness, doping concentrat ...
Unit-3
... exact information signal back. High impedance amplifier and Trans impedance amplifier are the two popular configurations of front end amplifier, the design of which is very critical for sensible performance of the receiver. The two most common photodetectors are p-i-n diodes and avalanche photodiode ...
... exact information signal back. High impedance amplifier and Trans impedance amplifier are the two popular configurations of front end amplifier, the design of which is very critical for sensible performance of the receiver. The two most common photodetectors are p-i-n diodes and avalanche photodiode ...
ABOUT THE EXTRAORDINARY REFRACTIVE INDEX
... The ammonium dihydrogen phosphates are single-crystals with electrooptical properties, shortly known as ADP crystals, used for frequency conversion in high power nonlinear optical devices . The single - crystals of ADP are uniaxial, so they having different properties when a beam of light passes thr ...
... The ammonium dihydrogen phosphates are single-crystals with electrooptical properties, shortly known as ADP crystals, used for frequency conversion in high power nonlinear optical devices . The single - crystals of ADP are uniaxial, so they having different properties when a beam of light passes thr ...
A list of some commonly used formulas in optics
... constant over a fairly wide range of angles around normal incidence. For such wedges the deviation is: δ ≈ (n - 1)α ...
... constant over a fairly wide range of angles around normal incidence. For such wedges the deviation is: δ ≈ (n - 1)α ...
Ay 105 Lab Experiment #P: Polarization!!!!
... Set up a rail with a laser at one end. Make sure you are able to rotate the laser on its mount. Add the cheap polarizer on a square mount in front of the laser. On the other end1 mount the lens and photodiode and focus the laser onto the photodiode. Rotate the laser so that it’s in line with the pol ...
... Set up a rail with a laser at one end. Make sure you are able to rotate the laser on its mount. Add the cheap polarizer on a square mount in front of the laser. On the other end1 mount the lens and photodiode and focus the laser onto the photodiode. Rotate the laser so that it’s in line with the pol ...
Chapter 3 - People @ EECS at UC Berkeley
... (a) What is the normal incidence reflectivity for 13.4 nm radiation at a single vacuummolybdenum (Z = 42) surface? (b) What is it for a single silicon surface at normal incidence and this wavelength? (c) Make an educated guess as to how many Mo/Si interfaces would be required in a multilayer mirror ...
... (a) What is the normal incidence reflectivity for 13.4 nm radiation at a single vacuummolybdenum (Z = 42) surface? (b) What is it for a single silicon surface at normal incidence and this wavelength? (c) Make an educated guess as to how many Mo/Si interfaces would be required in a multilayer mirror ...
P5G
... P5G Refraction Light waves change speed when they pass across the boundary between two substances with different densities, such as air and glass. This causes them to change direction and this effect is called refraction. ...
... P5G Refraction Light waves change speed when they pass across the boundary between two substances with different densities, such as air and glass. This causes them to change direction and this effect is called refraction. ...
Instrumental Analysis as Applied to Architectural Materials
... assist in identification of specific minerals. Light entering into a mineral specimen is refracted at different angles that are related to the crystal structure. This condition results in a phenomenon called birefringence, or double refraction. The amount of birefringence can be measured for a miner ...
... assist in identification of specific minerals. Light entering into a mineral specimen is refracted at different angles that are related to the crystal structure. This condition results in a phenomenon called birefringence, or double refraction. The amount of birefringence can be measured for a miner ...
Ellipsometry of light scattering from multilayer coatings
... angle-resolved ellipsometer. Ten axis are fully computer controlled in this experimental setup. Specular and diffuse measurements can be performed at different incidence and scattering angles. Several sources can be used with wavelengths from the UV ~325 nm! to the mid-IR ~10.6 mm!. ...
... angle-resolved ellipsometer. Ten axis are fully computer controlled in this experimental setup. Specular and diffuse measurements can be performed at different incidence and scattering angles. Several sources can be used with wavelengths from the UV ~325 nm! to the mid-IR ~10.6 mm!. ...
289-1028-1
... In the present work the refractive index spectra of Poly(2,2’-oxybis(methylene)bis(4-(hydroxyl(4hydroxymethyl)naphthalene-1-yl)(phenyl)methyl)naphthalene-l-ol) (PHMNP) thin film have been studied at room temperature. The transmission and reflectance spectra , at normal incidence of PHMNP thin film w ...
... In the present work the refractive index spectra of Poly(2,2’-oxybis(methylene)bis(4-(hydroxyl(4hydroxymethyl)naphthalene-1-yl)(phenyl)methyl)naphthalene-l-ol) (PHMNP) thin film have been studied at room temperature. The transmission and reflectance spectra , at normal incidence of PHMNP thin film w ...
1.3.6 Electromagnetic radiation Name Symbol Definition SI
... power α/γl, or the molar optical rotatory power α/cl, where γ is the mass concentration, c is the amount (of substance) concentration, and l is the path length. Most tabulations give the specific optical rotatory power, denoted [α]. The wavelength of light used λ (frequently the sodium D line) and t ...
... power α/γl, or the molar optical rotatory power α/cl, where γ is the mass concentration, c is the amount (of substance) concentration, and l is the path length. Most tabulations give the specific optical rotatory power, denoted [α]. The wavelength of light used λ (frequently the sodium D line) and t ...
Introduction to Optical Engineering and Design ENSC 376
... Optical Engineering is the study of the how optical elements can be applied to the design and construction of optical instruments, and their application to practical engineering problems. The course concentrates on the practical application of optics, and less on the physics behind the behaviour. It ...
... Optical Engineering is the study of the how optical elements can be applied to the design and construction of optical instruments, and their application to practical engineering problems. The course concentrates on the practical application of optics, and less on the physics behind the behaviour. It ...
Introduction to Fiber Optics
... What if the hallway is very winding with multiple bends? You might line the walls with mirrors and angle the beam so that it bounces from side-to-side all along the hallway. This is exactly what happens in an optical fiber. ...
... What if the hallway is very winding with multiple bends? You might line the walls with mirrors and angle the beam so that it bounces from side-to-side all along the hallway. This is exactly what happens in an optical fiber. ...
Anisotropic Minerals
... cancelling each other out, producing the resultant wave (R), which has no amplitude or wavelength. ...
... cancelling each other out, producing the resultant wave (R), which has no amplitude or wavelength. ...
full Lab Facts summary
... • In a solid prism retroreflector, the beam undergoes total internal reflection at each surface. • A beam entering normal to the base will be incident upon each face at a 55˚ angle (cos-1(1/√3)) [1]. • S- and p-polarization components reflect from each face differently based on the Fresnel reflectio ...
... • In a solid prism retroreflector, the beam undergoes total internal reflection at each surface. • A beam entering normal to the base will be incident upon each face at a 55˚ angle (cos-1(1/√3)) [1]. • S- and p-polarization components reflect from each face differently based on the Fresnel reflectio ...
没有幻灯片标题
... If the intensity of incident polarized light is I0, and the polarizing axis makes an angle with the displacement of the incident light, the intensity of the light transmitted through the polarizer is: I=I0 cos 2 ...
... If the intensity of incident polarized light is I0, and the polarizing axis makes an angle with the displacement of the incident light, the intensity of the light transmitted through the polarizer is: I=I0 cos 2 ...
Communications Employing Binary Polarization Shift Keying (2PolSK)
... 1. No need for synchronization at the receiver since the optical reference signal is transmitted at a different state of polarization; 2. No error floor and no power penalty in the BER performance due to the intermediate angular frequency (IF) and the IF phase noise are eliminated by employing polar ...
... 1. No need for synchronization at the receiver since the optical reference signal is transmitted at a different state of polarization; 2. No error floor and no power penalty in the BER performance due to the intermediate angular frequency (IF) and the IF phase noise are eliminated by employing polar ...
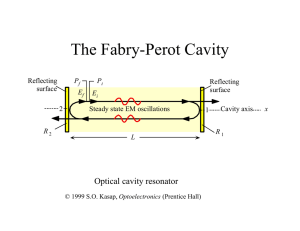
Lecture 22 - LSU Physics
... We can add more layers to keep reflecting the light, until no light is transmitted: all the light is either absorbed or reflected. ...
... We can add more layers to keep reflecting the light, until no light is transmitted: all the light is either absorbed or reflected. ...
Past Questions On Stationary Waves and Refractive Index
... takes certain values. (a) Explain these observations by reference to the physical principles involved. You may be awarded marks for the quality of written communication in your answer. ...
... takes certain values. (a) Explain these observations by reference to the physical principles involved. You may be awarded marks for the quality of written communication in your answer. ...
Intro to light
... Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. ...
... Birefringence is the optical property of a material having a refractive index that depends on the polarization and propagation direction of light. ...
HP unit 12 - wave optics student handout
... This first half of unit deals with the wave aspects of light, where only wave theory can explain the phenomena and particle/quantum theory falls short. The three primary topics of wave optics is interference, diffraction, and polarization. ...
... This first half of unit deals with the wave aspects of light, where only wave theory can explain the phenomena and particle/quantum theory falls short. The three primary topics of wave optics is interference, diffraction, and polarization. ...