Earthquake Locations/Terminology Elastic Rebound Theory Seismic
... Deformation: A change in the shape ...
... Deformation: A change in the shape ...
Earthquake Definitions - Red Hook Central Schools
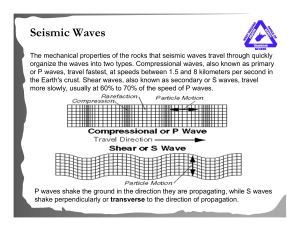
... - P-waves can travel through any material- solid, liquid or gas ...
... - P-waves can travel through any material- solid, liquid or gas ...
Locating Earthquakes
... At every layer interface, some energy is reflected and some is refracted. ...
... At every layer interface, some energy is reflected and some is refracted. ...
Chapter 19
... Happen oEarthquakes occur when rocks under stress suddenly shift along a fault. oVibration of Earth caused by the release of energy by the movement of the fault or plate. oAssociated with movements along faults and plate boundaries ...
... Happen oEarthquakes occur when rocks under stress suddenly shift along a fault. oVibration of Earth caused by the release of energy by the movement of the fault or plate. oAssociated with movements along faults and plate boundaries ...
Blank Jeopardy - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... This wave phenomenon is caused by a shift in frequency due to the motion of the source of a wave relative to the ...
... This wave phenomenon is caused by a shift in frequency due to the motion of the source of a wave relative to the ...
I have, Who has
... Who has the 3 main types of waves? I have Seismograph. Who has cracks in the Earth’s surface where tectonic plates meet and can lead to earthquakes? I have Richter Scale. Who has the force that is carried through waves? ...
... Who has the 3 main types of waves? I have Seismograph. Who has cracks in the Earth’s surface where tectonic plates meet and can lead to earthquakes? I have Richter Scale. Who has the force that is carried through waves? ...
Waves and Tides
... When the trough of a wave gets close to land, it starts to drag while the crest moves on, getting higher and higher until it tumbles over. ...
... When the trough of a wave gets close to land, it starts to drag while the crest moves on, getting higher and higher until it tumbles over. ...
Earthquakes
... If the fault is locked, stress increases. When stress reaches passed a certain point, the rocks fracture, separate at weakest point, and spring back or rebound, to original shape. As they fracture and slip the rocks along the fault release energy in the form of an earthquake. ...
... If the fault is locked, stress increases. When stress reaches passed a certain point, the rocks fracture, separate at weakest point, and spring back or rebound, to original shape. As they fracture and slip the rocks along the fault release energy in the form of an earthquake. ...
Upper mantle anisotropic structure of the Eastern Alps E. Qorbani, G
... Preferred alignment in upper mantle structure develops in response to past/presentday tectonic deformation. Such an alignment causes direction-dependent differences in seismic wave velocities, so called seismic anisotropy. The effect of anisotropy due to upper mantle fabrics can be easily seen in se ...
... Preferred alignment in upper mantle structure develops in response to past/presentday tectonic deformation. Such an alignment causes direction-dependent differences in seismic wave velocities, so called seismic anisotropy. The effect of anisotropy due to upper mantle fabrics can be easily seen in se ...
Earthquake Epicenters Plate Tectonics
... movement. (push-pull like a slinky) • Travel faster than any other wave (6-8 km./s) • Travel through solids, liquids, and gases ...
... movement. (push-pull like a slinky) • Travel faster than any other wave (6-8 km./s) • Travel through solids, liquids, and gases ...
New Title - TeacherWeb
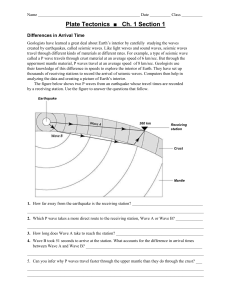
... travel through different kinds of materials at different rates. For example, a type of seismic wave called a P wave travels through crust material at an average speed of 6 km/sec. But through the uppermost mantle material, P waves travel at an average speed of 8 km/sec. Geologists use their knowledg ...
... travel through different kinds of materials at different rates. For example, a type of seismic wave called a P wave travels through crust material at an average speed of 6 km/sec. But through the uppermost mantle material, P waves travel at an average speed of 8 km/sec. Geologists use their knowledg ...
Earthquake Vocabulary - Garnet Valley School District
... when P waves and S waves reach Earth’s surface ...
... when P waves and S waves reach Earth’s surface ...
Shear wave splitting

Shear wave splitting, also called seismic birefringence, is the phenomenon that occurs when a polarized shear wave enters an anisotropic medium (Fig. 1). The incident shear wave splits into two polarized shear waves (Fig. 2). Shear wave splitting is typically used as a tool for testing the anisotropy of an area of interest. These measurements reflect the degree of anisotropy and lead to a better understanding of the area’s crack density and orientation or crystal alignment.We can think of the anisotropy of a particular area as a black box and the shear wave splitting measurements as a way of looking at what is in the box.