Earthquakes
... away from, or past another. • When rocks move in any direction along a fault, an earthquake occurs. ...
... away from, or past another. • When rocks move in any direction along a fault, an earthquake occurs. ...
Earthquakes
... • P-waves have greatest velocity (4-7 km/s in crust and ~8 km/s in mantle). As such, they are the first waves to arrive at a distant point. ...
... • P-waves have greatest velocity (4-7 km/s in crust and ~8 km/s in mantle). As such, they are the first waves to arrive at a distant point. ...
Surface Waves
... • Attentuation is the “amplification” or “de-amplification” of seismic waves from the source to the surface. • Geometrical spreading leads to a reduction in amplitude of body waves proportional to 1/r, where r is the distance form the source • surface wave reduce in amplitude according to r-0.5. • A ...
... • Attentuation is the “amplification” or “de-amplification” of seismic waves from the source to the surface. • Geometrical spreading leads to a reduction in amplitude of body waves proportional to 1/r, where r is the distance form the source • surface wave reduce in amplitude according to r-0.5. • A ...
Vocabulary #3
... a sudden release of energy in the earth's crust or upper mantle, usually caused by movement along a fault plane or by volcanic activity. ...
... a sudden release of energy in the earth's crust or upper mantle, usually caused by movement along a fault plane or by volcanic activity. ...
Study guide - Earthquakes, volcanoes, fault types
... ... difference between hanging wall and foot wall and be able to identify each in a fault diagram ... what an earthquake is (shaking after elastic limit of rock is reached) and where most earthquakes occur ... the 3 main types of seismic waves (P, S, and Surface) and which causes most damage ... the ...
... ... difference between hanging wall and foot wall and be able to identify each in a fault diagram ... what an earthquake is (shaking after elastic limit of rock is reached) and where most earthquakes occur ... the 3 main types of seismic waves (P, S, and Surface) and which causes most damage ... the ...
Tracing meteoric fluids in fault and detachment systems
... collectively document that meteoric fluids can be traced to significant depths during deformation. In particular we highlight how combined geochronological and isotope geochemical data can track changes in fluid composition through time either as a result of changing meteoric water compositions or d ...
... collectively document that meteoric fluids can be traced to significant depths during deformation. In particular we highlight how combined geochronological and isotope geochemical data can track changes in fluid composition through time either as a result of changing meteoric water compositions or d ...
Structure of the Earth`s Deep Interior
... Colors are flow model predictions of upwelling (red)/ downwelling (blue) for two different global shear wave velocity models… White squares indicate where Ps converted waves suggest very low vS just below the transition zone! ...
... Colors are flow model predictions of upwelling (red)/ downwelling (blue) for two different global shear wave velocity models… White squares indicate where Ps converted waves suggest very low vS just below the transition zone! ...
File
... or P-waves, travel the fastest, so they are the first to arrive at some other point on Earth’s crust. Secondary waves, or Swaves, arrive next and these tend to cause more damage than P-waves. Although they do not travel as far as primary waves and move at relatively low speeds, surface waves tend to ...
... or P-waves, travel the fastest, so they are the first to arrive at some other point on Earth’s crust. Secondary waves, or Swaves, arrive next and these tend to cause more damage than P-waves. Although they do not travel as far as primary waves and move at relatively low speeds, surface waves tend to ...
Seismic Waves
... miles/hour). They and are the first to arrive at a given location and can travel through solid and liquid layers of the earth. They alternately compresses and expands material in the same direction it is traveling. They travel similar to the way an earthworm travels in a push-pull linear motion. Bec ...
... miles/hour). They and are the first to arrive at a given location and can travel through solid and liquid layers of the earth. They alternately compresses and expands material in the same direction it is traveling. They travel similar to the way an earthworm travels in a push-pull linear motion. Bec ...
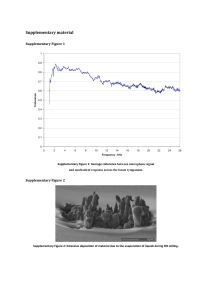
Supplementary Figure 1
... waves are derived by considering a square element Δx Δy of the membrane. When the membrane is displaced, there arises a force in the z direction from each of the two pairs of tensile forces T Δx and T Δy acting on the four edges of the square element. If we consider strips of the membrane of width Δ ...
... waves are derived by considering a square element Δx Δy of the membrane. When the membrane is displaced, there arises a force in the z direction from each of the two pairs of tensile forces T Δx and T Δy acting on the four edges of the square element. If we consider strips of the membrane of width Δ ...
blocks of crust slide past each other with no up or down motion
... blocks of crust slide past each other with no up or down motion ...
... blocks of crust slide past each other with no up or down motion ...
CLASSICAL MECHANICS II - Makerere University Courses
... Makerere University. The course builds on classical mechanics I. It describes the motion of bodies or systems of bodies more explicitly from different considerations of position. The following are the major topics: Waves and Wave Motion Superposition and Interference of Waves Special Relativit ...
... Makerere University. The course builds on classical mechanics I. It describes the motion of bodies or systems of bodies more explicitly from different considerations of position. The following are the major topics: Waves and Wave Motion Superposition and Interference of Waves Special Relativit ...
Earthquakes
... What causes Earthquakes? Movement along faults: occurs when the energy exceeds the friction holding the sides of the fault together and is suddenly released. Movement of magma (volcanic) ...
... What causes Earthquakes? Movement along faults: occurs when the energy exceeds the friction holding the sides of the fault together and is suddenly released. Movement of magma (volcanic) ...
Chapter 10
... P - waves - are Primary waves. They travel with a velocity that depends on the elastic properties of the rock through which they travel. P-waves are the same thing as sound waves. They move through the material by compressing it, but after it has been compressed it expands, so that the wave moves by ...
... P - waves - are Primary waves. They travel with a velocity that depends on the elastic properties of the rock through which they travel. P-waves are the same thing as sound waves. They move through the material by compressing it, but after it has been compressed it expands, so that the wave moves by ...
Shear wave splitting

Shear wave splitting, also called seismic birefringence, is the phenomenon that occurs when a polarized shear wave enters an anisotropic medium (Fig. 1). The incident shear wave splits into two polarized shear waves (Fig. 2). Shear wave splitting is typically used as a tool for testing the anisotropy of an area of interest. These measurements reflect the degree of anisotropy and lead to a better understanding of the area’s crack density and orientation or crystal alignment.We can think of the anisotropy of a particular area as a black box and the shear wave splitting measurements as a way of looking at what is in the box.