Review Exam #1 - Seattle Central College
... Characteristics (Electrons have Mass and Momentum) Electromagnetic Radiation (Light) has Both Wave Characteristics (Waves can be Diffracted by Crystals) and Particle Characteristics (Photons have Momentum, but No Mass) Emission spectra of elements demonstrate that the energy of electrons is quantize ...
... Characteristics (Electrons have Mass and Momentum) Electromagnetic Radiation (Light) has Both Wave Characteristics (Waves can be Diffracted by Crystals) and Particle Characteristics (Photons have Momentum, but No Mass) Emission spectra of elements demonstrate that the energy of electrons is quantize ...
Scale, structure and behaviour
... In 1901, Max Planck published an analysis that succeeded in reproducing the observed spectrum of light emitted by a glowing object. To accomplish this, Planck had to make an ad hoc mathematical assumption of quantized energy of the oscillators (atoms of the blackbody) that emit radiation. It was Ein ...
... In 1901, Max Planck published an analysis that succeeded in reproducing the observed spectrum of light emitted by a glowing object. To accomplish this, Planck had to make an ad hoc mathematical assumption of quantized energy of the oscillators (atoms of the blackbody) that emit radiation. It was Ein ...
CHAPTER 7 READING GUIDE – IONIC COMPOUNDS AND METALS
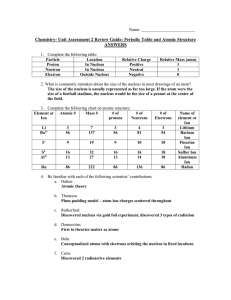
... 11. An ________________ is a negatively charged ion. 12. The ________________ force that holds oppositely charged particles together in an ionic compound is referred to as an ____________________ bond. 13. Many ionic compounds are ________________, which means that they contain only two different el ...
... 11. An ________________ is a negatively charged ion. 12. The ________________ force that holds oppositely charged particles together in an ionic compound is referred to as an ____________________ bond. 13. Many ionic compounds are ________________, which means that they contain only two different el ...
Exam on Matter through Bonding
... atom, the orbitals are regions of the most probable location of (1) protons (3) electrons (2) neutrons (4) positrons 5. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another? (1) covalent (3) hydrogen (2) ionic (4) metallic 6. Which substance can not be decomposed by a ...
... atom, the orbitals are regions of the most probable location of (1) protons (3) electrons (2) neutrons (4) positrons 5. Which type of bond is formed when electrons are transferred from one atom to another? (1) covalent (3) hydrogen (2) ionic (4) metallic 6. Which substance can not be decomposed by a ...
Problem-set-6
... Values of the energies are as often in Spectroscopy given in units of cm-1. The ionisation energy (or the ionisation potentiaal IP) of Na is 41449.65 cm-1. Note that the energy scale is different now: the ground state is at E=0 and the ionization energy has a positive value. Treat Sodium (Natrium) ...
... Values of the energies are as often in Spectroscopy given in units of cm-1. The ionisation energy (or the ionisation potentiaal IP) of Na is 41449.65 cm-1. Note that the energy scale is different now: the ground state is at E=0 and the ionization energy has a positive value. Treat Sodium (Natrium) ...
Section 13.2 - CPO Science
... • Danish physicist Neils Bohr proposed the concept of energy levels to explain the spectrum of hydrogen. • When an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower one, the atom gives up the energy difference between the two levels. • The energy comes out as different colors of light. ...
... • Danish physicist Neils Bohr proposed the concept of energy levels to explain the spectrum of hydrogen. • When an electron moves from a higher energy level to a lower one, the atom gives up the energy difference between the two levels. • The energy comes out as different colors of light. ...
Atomic Structure 1. Historical perspective of the model of the atom a
... which stated that all matter is made of atoms, atoms of the same type of element have the same chemical properties, compounds are formed by two or more different types of atoms, and that a chemical reaction involves either, joining, separating, or rearranging atoms. b.) In 1910, Ernest Rutherford pa ...
... which stated that all matter is made of atoms, atoms of the same type of element have the same chemical properties, compounds are formed by two or more different types of atoms, and that a chemical reaction involves either, joining, separating, or rearranging atoms. b.) In 1910, Ernest Rutherford pa ...
Review Sheet
... Endothermic vs. exothermic Stoichiometry using energy (using enthalpy of reaction and balanced chemical reactions) Calculating H using Hess’s Law, Enthalpy Diagrams, and/or H° of formations Calorimetry calculations to determine H and q Standard States and enthalpy of formation Using Hess’s Law eq ...
... Endothermic vs. exothermic Stoichiometry using energy (using enthalpy of reaction and balanced chemical reactions) Calculating H using Hess’s Law, Enthalpy Diagrams, and/or H° of formations Calorimetry calculations to determine H and q Standard States and enthalpy of formation Using Hess’s Law eq ...
2008 Midterm Multiple Choice
... A) contains a small percentage of the mass of the atom B) contains most of the mass of the atom C) has no charge D) has a negative charge ...
... A) contains a small percentage of the mass of the atom B) contains most of the mass of the atom C) has no charge D) has a negative charge ...
Chem Unit 2 Review Guide ANSWERS
... The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what valence electrons are and how to know how many an element from the representative group has. Valence electrons are an a ...
... The Law of Conservation of Mass holds true during chemical reactions, but is not during a nuclear reaction, as mass is converted directly to energy and vice versa. 18.) Define what valence electrons are and how to know how many an element from the representative group has. Valence electrons are an a ...
Document
... an electric field to accelerate a beam of positively charged ions – electrically charged plates attract the positive ions from the mixture in the ionisation chamber and accelerate them. By arranging the plates and choosing their voltage a fine beam of ions with only a narrow range of kinetic energie ...
... an electric field to accelerate a beam of positively charged ions – electrically charged plates attract the positive ions from the mixture in the ionisation chamber and accelerate them. By arranging the plates and choosing their voltage a fine beam of ions with only a narrow range of kinetic energie ...
Chapter 7, 8, and 9 Exam 2014 Name I. 50% of your grade will come
... 15. In the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) It remains constant. (B) It increases only. (C) It increases, then decreases. (D) It decreases only. (E) It decreases, then increases. 16. In a molecule in which the central atom exhibits ...
... 15. In the periodic table, as the atomic number increases from 11 to 17, what happens to the atomic radius? (A) It remains constant. (B) It increases only. (C) It increases, then decreases. (D) It decreases only. (E) It decreases, then increases. 16. In a molecule in which the central atom exhibits ...
Chemistry Notes
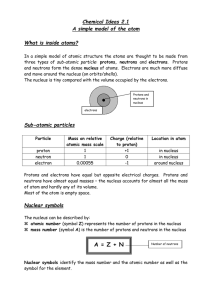
... A. All matter in the universe is composed of atoms. B. Parts of an atom 1. Electron Shell – The outer part of an atom. This is where the electrons are found. a) Electrons – Negatively charged particles found in the electron shell. Electrons orbit the nucleus. 2. Nucleus – The center of the atom. Com ...
... A. All matter in the universe is composed of atoms. B. Parts of an atom 1. Electron Shell – The outer part of an atom. This is where the electrons are found. a) Electrons – Negatively charged particles found in the electron shell. Electrons orbit the nucleus. 2. Nucleus – The center of the atom. Com ...
Physics 535 lectures notes: 1 * Sep 4th 2007
... 5V approach the barrier. What percentage of electrons will tunnel through the barrier? 3) Consider a infinite 3D box potential with L2=2L1 and L3=4L1. What are the quantum numbers of the lowest degenerate energy levels? List, ordered by energy, the quantum numbers and energies of all the levels up t ...
... 5V approach the barrier. What percentage of electrons will tunnel through the barrier? 3) Consider a infinite 3D box potential with L2=2L1 and L3=4L1. What are the quantum numbers of the lowest degenerate energy levels? List, ordered by energy, the quantum numbers and energies of all the levels up t ...
CHEMISTRY
... Smallest unit nucleus: center/core is most of the mass of the atom a. protons: + charge ...
... Smallest unit nucleus: center/core is most of the mass of the atom a. protons: + charge ...
Chemistry Science Notebook
... List the three reasons scientists found Rutherford’s nuclear atomic model to be fundamentally incomplete. ...
... List the three reasons scientists found Rutherford’s nuclear atomic model to be fundamentally incomplete. ...
MIDTERM REVIEW GAME 16-17
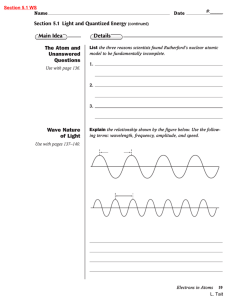
... 5) The product of the frequency and the wavelength is the: 1. Speed of the wave 2. Number of waves passing a point per second 3. Distance between waves 4. Time for a wave to ...
... 5) The product of the frequency and the wavelength is the: 1. Speed of the wave 2. Number of waves passing a point per second 3. Distance between waves 4. Time for a wave to ...
Modern Physics
... from the nucleus for the hydrogen atom is 2 ao. Find the probability of finding the 1-s electron at a distance greater than 2 ao according to quantum mechanics. ...
... from the nucleus for the hydrogen atom is 2 ao. Find the probability of finding the 1-s electron at a distance greater than 2 ao according to quantum mechanics. ...
ap chemistry review – multiple choice
... Questions 15-18 refer to the following (a) Heisenbery uncertainty principle (b) Pauli exclusion principle (c) Hund’s rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (d) Shielding effect (e) Wave nature of matter 15. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in it ground state is paramagnetic 16. E ...
... Questions 15-18 refer to the following (a) Heisenbery uncertainty principle (b) Pauli exclusion principle (c) Hund’s rule (principle of maximum multiplicity) (d) Shielding effect (e) Wave nature of matter 15. Can be used to predict that a gaseous carbon atom in it ground state is paramagnetic 16. E ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.