LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 1. Find the determinant value of the Loerntz transformation matrix. 2. State the relation between relativistic energy and relativistic momentum. 3. Define 4-current and write down the continuity equation in terms of it. 4. State the covariant form of Lorentz force equation. 5. Define differential sc ...
... 1. Find the determinant value of the Loerntz transformation matrix. 2. State the relation between relativistic energy and relativistic momentum. 3. Define 4-current and write down the continuity equation in terms of it. 4. State the covariant form of Lorentz force equation. 5. Define differential sc ...
Unit 3: Electrons
... Light (Einstein) and electrons (de Broglie) have a dual nature: particle and wave. The nature of light/electrons depends on the technique one uses to study them. Complex mathematical models are the basis for the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Schrödinger’s wavefunctions produc atomic orbi ...
... Light (Einstein) and electrons (de Broglie) have a dual nature: particle and wave. The nature of light/electrons depends on the technique one uses to study them. Complex mathematical models are the basis for the quantum mechanical model of the atom. Schrödinger’s wavefunctions produc atomic orbi ...
Sample Exam 1
... c) ºC = ºF – 273 d) ºC = ºF(1.80) + 32 6. How does the amount of energy needed to heat a sample of water from 15 ºC to 45 ºC compare to that needed to heat this sample from 50 ºC to 80 ºC ? a) more energy is needed to go from 15 ºC to 45 ºC. b) it depends on the size of the sample c) the same amount ...
... c) ºC = ºF – 273 d) ºC = ºF(1.80) + 32 6. How does the amount of energy needed to heat a sample of water from 15 ºC to 45 ºC compare to that needed to heat this sample from 50 ºC to 80 ºC ? a) more energy is needed to go from 15 ºC to 45 ºC. b) it depends on the size of the sample c) the same amount ...
CHEMISTRY
... • A compound is a pure substance made up of atoms of two or more elements – The proportion of atoms are always fixed • Chemical formula shows the kind and proportion of atoms of each element that occurs in a particular compound C6H12O6 ...
... • A compound is a pure substance made up of atoms of two or more elements – The proportion of atoms are always fixed • Chemical formula shows the kind and proportion of atoms of each element that occurs in a particular compound C6H12O6 ...
Exam 2 with Solutions - Little Dumb Doctor .Com
... 15. What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the sulfur atom in the compound SF6? e. sp3d2 16. Consider the diatomic molecules of the second period Li2, Be2, and C2. Which is (are) unlikely to exist? c. Be2 17. In order to create a p-type semiconductor, a silicon crystal could be doped with a. Ga ...
... 15. What type of hybrid orbital set is used by the sulfur atom in the compound SF6? e. sp3d2 16. Consider the diatomic molecules of the second period Li2, Be2, and C2. Which is (are) unlikely to exist? c. Be2 17. In order to create a p-type semiconductor, a silicon crystal could be doped with a. Ga ...
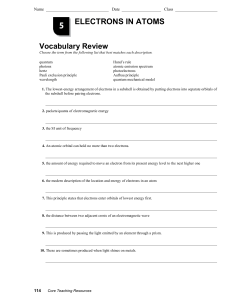
Ch.5 VocabReview
... 1. The lowest-energy arrangement of electrons in a subshell is obtained by putting electrons into separate orbitals of the subshell before pairing electrons. ...
... 1. The lowest-energy arrangement of electrons in a subshell is obtained by putting electrons into separate orbitals of the subshell before pairing electrons. ...
Moderne Methoden der Materialcharakterisierung
... Cathode material determines emission current density ...
... Cathode material determines emission current density ...
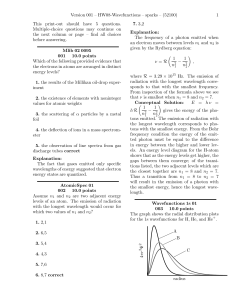
HW 8
... tons emitted. The emission of radiation with the longest wavelength corresponds to photons with the smallest energy. From the Bohr frequency condition the energy of the emitted photon must be equal to the difference in energy between the higher and lower levels. An energy level diagram for the H-ato ...
... tons emitted. The emission of radiation with the longest wavelength corresponds to photons with the smallest energy. From the Bohr frequency condition the energy of the emitted photon must be equal to the difference in energy between the higher and lower levels. An energy level diagram for the H-ato ...
Chap 11 Sect 1 Notes Atomic Theory
... negative charge, like negativelycharged “plums” surrounded by positively-charged “pudding”. ...
... negative charge, like negativelycharged “plums” surrounded by positively-charged “pudding”. ...
Atom (A) or Ion (I)
... 83. What is molarity? 84. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .30 L of solution, what is the molarity? 85. If I have 700.0 mL of a 5.0 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 86. What is meant by chemical equilibrium? 87. What factors affect the rate of a reacti ...
... 83. What is molarity? 84. If I have 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate in .30 L of solution, what is the molarity? 85. If I have 700.0 mL of a 5.0 M NaOH solution, how many grams of NaOH were used to make the solution? 86. What is meant by chemical equilibrium? 87. What factors affect the rate of a reacti ...
Section 1 Atoms, Elements, and Compounds
... Neutrons- neutral charged particle in the nucleus Electrons- negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. Very small. o Energy Levels- 2 electrons in first energy level. 8 in every level after that o Valence- Outermost, used in chemical bonds What makes an atom neutral? Elements What i ...
... Neutrons- neutral charged particle in the nucleus Electrons- negatively charged particles that orbit the nucleus. Very small. o Energy Levels- 2 electrons in first energy level. 8 in every level after that o Valence- Outermost, used in chemical bonds What makes an atom neutral? Elements What i ...
PHYSICS 215 - Thermodynamics and Modern Physics Name:
... Speed of light, c = 3.00E8 m/s Charge of an electron, -e = -1.6E-19 C Mass of the electron, me = 9.1E-31 kg = 511 keV/c2 = 5.49E-4 u Mass of the proton, mp = 1.67E-27 kg = 938 MeV/c2 = 1.00728 u Mass of the α particle, mα = 3727.4 MeV/c2 = 4.00151 u ...
... Speed of light, c = 3.00E8 m/s Charge of an electron, -e = -1.6E-19 C Mass of the electron, me = 9.1E-31 kg = 511 keV/c2 = 5.49E-4 u Mass of the proton, mp = 1.67E-27 kg = 938 MeV/c2 = 1.00728 u Mass of the α particle, mα = 3727.4 MeV/c2 = 4.00151 u ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI
... change in wavelength of X-ray ray in Compton scattering (ii) Establish the work-energy energy theorem of relativity. relativity ...
... change in wavelength of X-ray ray in Compton scattering (ii) Establish the work-energy energy theorem of relativity. relativity ...
Learning Standards vocab chemical basis and molecules of life 09
... Given the number of protons, identify the element using a Periodic Table. Explain the arrangement of the elements on the Periodic Table, including the significant relationships among elements in a given column or row. Explain how ions and ionic bonds are formed (e.g., sodium atoms lose an elec ...
... Given the number of protons, identify the element using a Periodic Table. Explain the arrangement of the elements on the Periodic Table, including the significant relationships among elements in a given column or row. Explain how ions and ionic bonds are formed (e.g., sodium atoms lose an elec ...
Slide 1
... m: mass of the ion z: charge of the ion H: applied magnetic field r: radius of arc of deflection V: applied accelerating voltage ...
... m: mass of the ion z: charge of the ion H: applied magnetic field r: radius of arc of deflection V: applied accelerating voltage ...
Ideas of Modern Physics
... 7. A particular quantum system has quantum states with energies E(n=1)=1 eV, E(n=2)=4 eV, E(n=3)=9, E(n=4)=16 eV, … This is NOT a hydrogen atom. Calculate the wavelength of a photon emitted as a result of the n=3 to n=2 transition. a. 140 nm b. 410 nm c. 250 nm d. 1240 nm e. 620 nm 8. For the wavefu ...
... 7. A particular quantum system has quantum states with energies E(n=1)=1 eV, E(n=2)=4 eV, E(n=3)=9, E(n=4)=16 eV, … This is NOT a hydrogen atom. Calculate the wavelength of a photon emitted as a result of the n=3 to n=2 transition. a. 140 nm b. 410 nm c. 250 nm d. 1240 nm e. 620 nm 8. For the wavefu ...
Physics 107: Ideas of Modern Physics
... 7. A particular quantum system has quantum states with energies E(n=1)=1 eV, E(n=2)=4 eV, E(n=3)=9, E(n=4)=16 eV, … This is NOT a hydrogen atom. Calculate the wavelength of a photon emitted as a result of the n=3 to n=2 transition. a. 140 nm b. 410 nm c. 250 nm d. 1240 nm e. 620 nm 8. For the wavefu ...
... 7. A particular quantum system has quantum states with energies E(n=1)=1 eV, E(n=2)=4 eV, E(n=3)=9, E(n=4)=16 eV, … This is NOT a hydrogen atom. Calculate the wavelength of a photon emitted as a result of the n=3 to n=2 transition. a. 140 nm b. 410 nm c. 250 nm d. 1240 nm e. 620 nm 8. For the wavefu ...
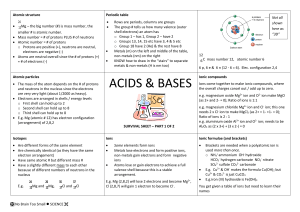
acids and bases - No Brain Too Small
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
... KNOW how to draw in the “stairs” to separate metals & non-metals (H is nm too) ...
Chapter 2
... 9. Given the following sets of quantum numbers, set up the orbital notation (labeled with the sublevel designation) for the indicated sublevel of electrons and circle the indicated orbital. Assume that electrons fill from more negative to more positive ml values. Example: n = 5, l = 1, ml = 0 ...
... 9. Given the following sets of quantum numbers, set up the orbital notation (labeled with the sublevel designation) for the indicated sublevel of electrons and circle the indicated orbital. Assume that electrons fill from more negative to more positive ml values. Example: n = 5, l = 1, ml = 0 ...
1. Millikan did his experiments with the balance of
... Mo3+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. b.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Au+ : [Xe] 6s2, 4f14,5d8 Au+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. c.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Mn2+ : [Ar ...
... Mo3+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. b.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Au+ : [Xe] 6s2, 4f14,5d8 Au+ is paramagnetic because in the d orbital there are unpaired electrons. c.) The condensed ground-state electron configuration of Mn2+ : [Ar ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.