Unit - eBoard
... Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Internal Energy - ∆E = q + w Importance of the sign in a quantity indicating direction of flow Energy Units – calorie, joule, converting between units Specific Heat Capacity Measuring Energy Changes – Q = m x s x ∆T Lab: Identification of Unknown Metals using Spe ...
... Energy Changes in Chemical Reactions Internal Energy - ∆E = q + w Importance of the sign in a quantity indicating direction of flow Energy Units – calorie, joule, converting between units Specific Heat Capacity Measuring Energy Changes – Q = m x s x ∆T Lab: Identification of Unknown Metals using Spe ...
Document
... Use “bath” of Rb to cool a sample of K atoms Goal 1 – Achieve Fermi degeneracy for 40K atoms Goal 2 – (After #1 did not seem to work) Achieve Bose-Einstein condensation for 41K ...
... Use “bath” of Rb to cool a sample of K atoms Goal 1 – Achieve Fermi degeneracy for 40K atoms Goal 2 – (After #1 did not seem to work) Achieve Bose-Einstein condensation for 41K ...
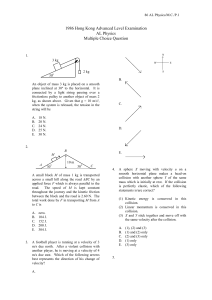
1. An object of mass 3 kg is placed on a smooth plane inclined at 30º
... possible to find an angle of incidence such that A. none of the light is reflected. B. all of the light is reflected. C. the reflected light is completely plane polarised. D. the transmitted light is completely plane polarised. ...
... possible to find an angle of incidence such that A. none of the light is reflected. B. all of the light is reflected. C. the reflected light is completely plane polarised. D. the transmitted light is completely plane polarised. ...
Lectures 7-9 - U of L Class Index
... elements. Atoms can be excited by heating in a hot flame (e.g. Bunsen burner). When they relax back to their ground state, they emit only the wavelengths of light in their line spectra. Thus, each element imparts a characteristic colour to the flame: ...
... elements. Atoms can be excited by heating in a hot flame (e.g. Bunsen burner). When they relax back to their ground state, they emit only the wavelengths of light in their line spectra. Thus, each element imparts a characteristic colour to the flame: ...
Energy level
... get it to give off colors. • Passing this light through a prism does something different. ...
... get it to give off colors. • Passing this light through a prism does something different. ...
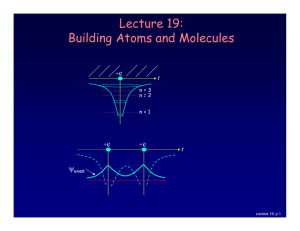
Lecture 19: Building Atoms and Molecules
... Example: Nuclear Spin and MRI Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) depends on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the nuclear spin of the hydrogen atoms in our bodies. The nucleus is a proton with spin ½, so in a magnetic field B there are two energy states. The proton’s magnetic moment is µ ...
... Example: Nuclear Spin and MRI Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) depends on the absorption of electromagnetic radiation by the nuclear spin of the hydrogen atoms in our bodies. The nucleus is a proton with spin ½, so in a magnetic field B there are two energy states. The proton’s magnetic moment is µ ...
Lectures 7-9
... elements. Atoms can be excited by heating in a hot flame (e.g. Bunsen burner). When they relax back to their ground state, they emit only the wavelengths of light in their line spectra. Thus, each element imparts a characteristic colour to the flame: ...
... elements. Atoms can be excited by heating in a hot flame (e.g. Bunsen burner). When they relax back to their ground state, they emit only the wavelengths of light in their line spectra. Thus, each element imparts a characteristic colour to the flame: ...
Name Date Class Period ______
... Matching: Using the word box below, write the letter of the correct vocabulary word for each definition. ...
... Matching: Using the word box below, write the letter of the correct vocabulary word for each definition. ...
Chapter 1
... A. Protons have an elementary positive charge of 1. B. Protons have one Dalton of mass. C. Protons are always found in the nucleus of the atom. D. Any atom found in nature always has the same number of protons as electrons. 2. Which of the following statements about electron orbitals is FALSE? A. Th ...
... A. Protons have an elementary positive charge of 1. B. Protons have one Dalton of mass. C. Protons are always found in the nucleus of the atom. D. Any atom found in nature always has the same number of protons as electrons. 2. Which of the following statements about electron orbitals is FALSE? A. Th ...
Physical Science
... •In a physical change, substances keep the same physical properties, while in a chemical change, new substances are created with new chemical properties. •A physical change is reversible by physical methods, while a chemical change is not reversible by physical methods. •In a physical change, substa ...
... •In a physical change, substances keep the same physical properties, while in a chemical change, new substances are created with new chemical properties. •A physical change is reversible by physical methods, while a chemical change is not reversible by physical methods. •In a physical change, substa ...
Some Success Applications for Local
... bonding electron moves between the two hydrogen nuclei, no superluminal interaction—the extranuclear electron is local. If the bonding electron between the two nuclei is the phase trajectory ring, the relationship between each particle is the exact causation, and this extranuclear electron must be i ...
... bonding electron moves between the two hydrogen nuclei, no superluminal interaction—the extranuclear electron is local. If the bonding electron between the two nuclei is the phase trajectory ring, the relationship between each particle is the exact causation, and this extranuclear electron must be i ...
KINETIC ENERGY DISTRIBUTION OF IONS GENERATED BY
... The measurement control and data processing software was developed in our laboratory based on the integrated scientific environment ASYST [22]. By using this code supplemented with a few machine language subroutines, a complete measurement cycle needed less than 9 s which included 7 s waiting time f ...
... The measurement control and data processing software was developed in our laboratory based on the integrated scientific environment ASYST [22]. By using this code supplemented with a few machine language subroutines, a complete measurement cycle needed less than 9 s which included 7 s waiting time f ...
Few-body insights into the fractional quantum Hall effect
... 3. Since these states are identifiable by a property of noninteracting electrons, it should be possible to probe these exceptional degeneracy states in other ways, e.g. without a magnetic field, or with neutral, ultracold polarized fermionic (or bosonic atoms) 4. One can use the approximate separabi ...
... 3. Since these states are identifiable by a property of noninteracting electrons, it should be possible to probe these exceptional degeneracy states in other ways, e.g. without a magnetic field, or with neutral, ultracold polarized fermionic (or bosonic atoms) 4. One can use the approximate separabi ...
The Mole: A Measurement of Matter
... The Mole and Avogadro’s Number SI unit that measures the amount of substance 1 mole = 6.022 x 1023 representative particles Representative particles are usually atoms, molecules, or formula units (ions) ...
... The Mole and Avogadro’s Number SI unit that measures the amount of substance 1 mole = 6.022 x 1023 representative particles Representative particles are usually atoms, molecules, or formula units (ions) ...
Derivation of Bohr`s Equations for the One
... Since ao is a constant, equation (6) predicts that the radius increases in direct proportion to the square of the quantum number, n2, and decreases in inverse proportion to the atomic number, Z. Thus, the sizes of the orbits in hydrogen are predicted to be ao, 4ao, 9ao, 16ao, 25ao, etc. Furthermore, ...
... Since ao is a constant, equation (6) predicts that the radius increases in direct proportion to the square of the quantum number, n2, and decreases in inverse proportion to the atomic number, Z. Thus, the sizes of the orbits in hydrogen are predicted to be ao, 4ao, 9ao, 16ao, 25ao, etc. Furthermore, ...
Lecture 38
... Binding energy of the nucleus = [mass of constituents - mass of the nucleus]c2 The strong nuclear, weak nuclear, electromagnetic and gravitational forces are the four known forces in nature. Strong nuclear force binds nucleons together. Weak nuclear force is responsible for radioactivity. ...
... Binding energy of the nucleus = [mass of constituents - mass of the nucleus]c2 The strong nuclear, weak nuclear, electromagnetic and gravitational forces are the four known forces in nature. Strong nuclear force binds nucleons together. Weak nuclear force is responsible for radioactivity. ...
Chem 2 AP Ch 7 MC Review Key
... B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent materials emit a broad spectrum of light. D) Yes, after storing enough visible light energy, the fluorescent material can emit ultraviolet light. ...
... B) No, fluorescent materials only emit purple and green visible light. C) Yes, fluorescent materials emit a broad spectrum of light. D) Yes, after storing enough visible light energy, the fluorescent material can emit ultraviolet light. ...
Finite Nuclear Size Effect - Physics
... problems by simplifying their parts is a modus operandi employed by all physicists. When studying the hydrogen atom in an undergraduate quantum mechanics class, many assumptions are made about the system in order to provide a simple, approachable potential that produces an analytic solution. The poi ...
... problems by simplifying their parts is a modus operandi employed by all physicists. When studying the hydrogen atom in an undergraduate quantum mechanics class, many assumptions are made about the system in order to provide a simple, approachable potential that produces an analytic solution. The poi ...
PHYSICAL SETTING CHEMISTRY
... Graphite and diamond are two crystalline arrangements for carbon. The crystal structure of graphite is organized in layers. The bonds between carbon atoms within each layer of graphite are strong. The bonds between carbon atoms that connect different layers of graphite are weak because the shared el ...
... Graphite and diamond are two crystalline arrangements for carbon. The crystal structure of graphite is organized in layers. The bonds between carbon atoms within each layer of graphite are strong. The bonds between carbon atoms that connect different layers of graphite are weak because the shared el ...
Plasmons, polaritons What are plasmons and what are
... Polaritons are bosonic (quasi‐)particles resulting from strong coupling of electromagnetic waves with an electric or magnetic dipole‐carrying excitation (not to be confused with the polaron, which is a fermion). At the point where the two dispersion relationships of light and excitation are cross ...
... Polaritons are bosonic (quasi‐)particles resulting from strong coupling of electromagnetic waves with an electric or magnetic dipole‐carrying excitation (not to be confused with the polaron, which is a fermion). At the point where the two dispersion relationships of light and excitation are cross ...
Chemistry Final Exam Study Guide
... ____ 92. Which region contains elements with two valence electrons? a. A c. C b. B d. D ____ 93. Which is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from an atom of an element in the gaseous state? a. ionization energy c. ionic radius b. electronegativity d. law of octets ____ 94. Which co ...
... ____ 92. Which region contains elements with two valence electrons? a. A c. C b. B d. D ____ 93. Which is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from an atom of an element in the gaseous state? a. ionization energy c. ionic radius b. electronegativity d. law of octets ____ 94. Which co ...
zinc(II): Zn 2 [(n
... In general, coordination of a ligand to a metal ion causes an increase in the electron density on the metal, resulting in a decrease in the metal ion’s electron binding energy [12]. The Zn(2p)3/2 chemical shift, which are the differences between the Zn(2p)3/2 binding energies of the complex and ZnCl ...
... In general, coordination of a ligand to a metal ion causes an increase in the electron density on the metal, resulting in a decrease in the metal ion’s electron binding energy [12]. The Zn(2p)3/2 chemical shift, which are the differences between the Zn(2p)3/2 binding energies of the complex and ZnCl ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.