Weiguang Zhang 1,* Yun Zhong 1, Minyu Tan 2,*, Ning Tang 2 and
... In general, coordination of a ligand to a metal ion causes an increase in the electron density on the metal, resulting in a decrease in the metal ion’s electron binding energy [12]. The Zn(2p)3/2 chemical shift, which are the differences between the Zn(2p)3/2 binding energies of the complex and ZnCl ...
... In general, coordination of a ligand to a metal ion causes an increase in the electron density on the metal, resulting in a decrease in the metal ion’s electron binding energy [12]. The Zn(2p)3/2 chemical shift, which are the differences between the Zn(2p)3/2 binding energies of the complex and ZnCl ...
Study Guide for Exam 2_old
... Study Guide for Exam 2 You should be able to answer the following questions, solve problems involving the following concepts, or understand the following concepts so that you can describe them and answer questions about them. Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence ...
... Study Guide for Exam 2 You should be able to answer the following questions, solve problems involving the following concepts, or understand the following concepts so that you can describe them and answer questions about them. Periodic trends regarding atomic and ionic radii. What is meant by valence ...
Chemistry exam review
... The metallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. The metallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an entire energy level. The nonmetallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. The nonmetallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an ent ...
... The metallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. The metallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an entire energy level. The nonmetallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. The nonmetallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an ent ...
2011 Spring 1 key
... Answer the following by writing the word, words, letter, letters or number in each blank that best completes each sentence. (1 point each blank) 1. Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. ...
... Answer the following by writing the word, words, letter, letters or number in each blank that best completes each sentence. (1 point each blank) 1. Isotopes are atoms that have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. They have the same atomic number but different mass numbers. ...
Chemistry exam review
... The metallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. The metallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an entire energy level. The nonmetallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. The nonmetallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an ent ...
... The metallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. The metallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an entire energy level. The nonmetallic atom gains electrons, causing a larger effective nuclear pull. The nonmetallic atom loses electrons, resulting in loss of an ent ...
Electromagnetic Waves and Photons are describing the same thing
... Discussion: Given what we know about light, what does this imply about electrons in atoms? Implies that electrons only change between very specific energies. Only way for individual atoms to give off energy is as light. Each time a photon is emitted an electron must be changing in energy by that amo ...
... Discussion: Given what we know about light, what does this imply about electrons in atoms? Implies that electrons only change between very specific energies. Only way for individual atoms to give off energy is as light. Each time a photon is emitted an electron must be changing in energy by that amo ...
The Time-Shift Technique for Measurement of Size and Velocity of
... The time-shift technique is used here in a somewhat modified form. This technique was first introduced by Semidetnov (1985) [3] and is further developed in Damaschke et al (2002) and Albrecht et al (2003). It is realized by creating an illuminated volume considerably smaller than the size of the par ...
... The time-shift technique is used here in a somewhat modified form. This technique was first introduced by Semidetnov (1985) [3] and is further developed in Damaschke et al (2002) and Albrecht et al (2003). It is realized by creating an illuminated volume considerably smaller than the size of the par ...
Foundations, 2
... nothing and the other all of the clicks and vice versa. (This is analogous to changing the angle θ in the double slit intensity equation.) Clearly, this behavior indicates that there is interference between the two paths, just as if the photon were a wave spread out over the whole apparatus. In othe ...
... nothing and the other all of the clicks and vice versa. (This is analogous to changing the angle θ in the double slit intensity equation.) Clearly, this behavior indicates that there is interference between the two paths, just as if the photon were a wave spread out over the whole apparatus. In othe ...
Physical and Chemical Properties
... Elements: If there are 110+ elements, how is it possible to have millions of different substances? • Compounds are substances that form when two or more elements combine from a chemical change. ...
... Elements: If there are 110+ elements, how is it possible to have millions of different substances? • Compounds are substances that form when two or more elements combine from a chemical change. ...
teacher version filled in
... Remember, the number of electrons comes from the letter (the orbital’s momentum, m) ...
... Remember, the number of electrons comes from the letter (the orbital’s momentum, m) ...
A. Menegolli
... it is present a strong asymmetry going from -45° to +45°, maybe due to the shadow from the support of the sample; the two contributions could not properly have been disentangled, so that it was possible just to have an estimate of the opening angle of the diffusive reflection (~ 30° - FWHM) IPRD06 - ...
... it is present a strong asymmetry going from -45° to +45°, maybe due to the shadow from the support of the sample; the two contributions could not properly have been disentangled, so that it was possible just to have an estimate of the opening angle of the diffusive reflection (~ 30° - FWHM) IPRD06 - ...
Ch 8 Notes: Chemical Equations and Reactions
... Use the “Solubility Rules” handout (at end of notes) to determine the solubility. If the compound is soluble that means that it will remain as ions in the solution, if it is insoluble then the compound precipitated out of the reaction (it became the precipitate or solid). 2. If at least one INSOLUBL ...
... Use the “Solubility Rules” handout (at end of notes) to determine the solubility. If the compound is soluble that means that it will remain as ions in the solution, if it is insoluble then the compound precipitated out of the reaction (it became the precipitate or solid). 2. If at least one INSOLUBL ...
EOC_chapter28
... consider a solid iron sphere 2.00 cm in radius. Assume that its temperature is always uniform throughout its volume. (a) Find the mass of the sphere. (b) Assume that it is at 20°C and has emissivity 0.860. Find the power with which it is radiating electromagnetic waves. (c) If it were alone in the U ...
... consider a solid iron sphere 2.00 cm in radius. Assume that its temperature is always uniform throughout its volume. (a) Find the mass of the sphere. (b) Assume that it is at 20°C and has emissivity 0.860. Find the power with which it is radiating electromagnetic waves. (c) If it were alone in the U ...
PowerPoint Template
... the total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction - Antoine Lavoisier (1 743-1 794) The number of substances may change, but the total amount of matter remains constant. ...
... the total mass of substances does not change during a chemical reaction - Antoine Lavoisier (1 743-1 794) The number of substances may change, but the total amount of matter remains constant. ...
Chemistry 212 Name:
... oxidation state (+1, 3, 5, & 7). They all exist as colored diatomic molecules. ...
... oxidation state (+1, 3, 5, & 7). They all exist as colored diatomic molecules. ...
Cell Mechanics
... In the ray optics regime, the size of the object is much larger than the wave lenght of the light, and a single beam can be tracked throughout the particle. (This situation is for example when whole cells are trapped using infrared light while suspended in solution. The incident laser beam can be de ...
... In the ray optics regime, the size of the object is much larger than the wave lenght of the light, and a single beam can be tracked throughout the particle. (This situation is for example when whole cells are trapped using infrared light while suspended in solution. The incident laser beam can be de ...
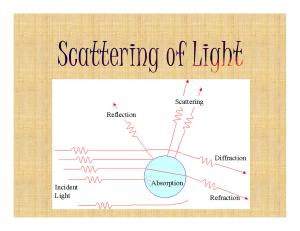
Light scattering described in the mode picture
... a substrate traversed by the beam, or it may be a deviation of a surface from its ideal shape, such as a surface ripple on top of a sphere. Any deviation from wave-front propagation as determined by ideally shaped components may be called scattering. The scattering properties of a component are comm ...
... a substrate traversed by the beam, or it may be a deviation of a surface from its ideal shape, such as a surface ripple on top of a sphere. Any deviation from wave-front propagation as determined by ideally shaped components may be called scattering. The scattering properties of a component are comm ...
Atomic Force Microscopy
... Problems: Can’t use with samples in fluid Used to analyze semiconductors Doesn’t degrade or interfere with samplebetter for soft samples ...
... Problems: Can’t use with samples in fluid Used to analyze semiconductors Doesn’t degrade or interfere with samplebetter for soft samples ...
Untitled
... • Thus, a study of the scattered light intensity as a function of scattering angle gives information about the structure, spatial configuration, or morphology of the scattering medium. With regard to light scattering in liquids and solids, primary material considerations include: 1. Crystalline str ...
... • Thus, a study of the scattered light intensity as a function of scattering angle gives information about the structure, spatial configuration, or morphology of the scattering medium. With regard to light scattering in liquids and solids, primary material considerations include: 1. Crystalline str ...
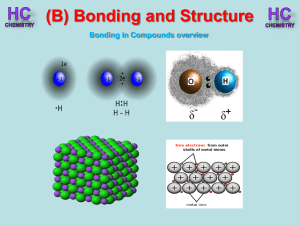
Lesson 1 - Bonding in compounds overview
... chemical formula is SiC. As this compound is linked by strong covalent bonding, it has a high m.p. (2700oC). It is a hard substance as it is very difficult to break the covalent lattice. SiC is used as an abrasive for smoothing very hard materials. Each Si is bonded to 4 C’s and each C is bonded to ...
... chemical formula is SiC. As this compound is linked by strong covalent bonding, it has a high m.p. (2700oC). It is a hard substance as it is very difficult to break the covalent lattice. SiC is used as an abrasive for smoothing very hard materials. Each Si is bonded to 4 C’s and each C is bonded to ...
PRE AP CHEMISTRY REVIEW PROBLEMS NON COLLEGE
... The following are problems that students entering AP Chemistry are expected to solve and answer without difficulty. You may use a scientific calculator. A periodic table and other helpful information are provided on the last page. If you are finding the need to refer to a textbook or other resources ...
... The following are problems that students entering AP Chemistry are expected to solve and answer without difficulty. You may use a scientific calculator. A periodic table and other helpful information are provided on the last page. If you are finding the need to refer to a textbook or other resources ...
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry
Rutherford backscattering spectrometry (RBS) is an analytical technique used in materials science. Sometimes referred to as high-energy ion scattering (HEIS) spectrometry, RBS is used to determine the structure and composition of materials by measuring the backscattering of a beam of high energy ions (typically protons or alpha particles) impinging on a sample.