Slide 1
... The nervous system helps maintain homeostasis by directing the body to respond appropriately to the information it receives. ...
... The nervous system helps maintain homeostasis by directing the body to respond appropriately to the information it receives. ...
Ch 7 The Nervous System Notes
... polygraph- measures stress incurred when tell a lie. You know it is wrong to lie, when you do lie your sympathetic NS kicks in and your adrenal glands cause heart rate to increase. measures changes in heart rate ...
... polygraph- measures stress incurred when tell a lie. You know it is wrong to lie, when you do lie your sympathetic NS kicks in and your adrenal glands cause heart rate to increase. measures changes in heart rate ...
The Nervous System - Cathkin High School
... Divisions of the Nervous System 1. The information from left eye went to the right (cerebral) hemisphere. 2. The right hemisphere controls / moves the left hand (so the patient points to “HE”). 3. The information from right eye went to the left hemisphere. 4. Information cannot be transferred to the ...
... Divisions of the Nervous System 1. The information from left eye went to the right (cerebral) hemisphere. 2. The right hemisphere controls / moves the left hand (so the patient points to “HE”). 3. The information from right eye went to the left hemisphere. 4. Information cannot be transferred to the ...
organ systems - Peoria Public Schools
... from carrying out life processes) or pathogens (break down cells)may disrupt the proper functioning of body systems. • Problems with the structure or function of cells, tissues, or organs can cause problems in the body. • If cells cannot get energy or necessities, they cannot work properly. – disrup ...
... from carrying out life processes) or pathogens (break down cells)may disrupt the proper functioning of body systems. • Problems with the structure or function of cells, tissues, or organs can cause problems in the body. • If cells cannot get energy or necessities, they cannot work properly. – disrup ...
The Nervous System
... • The spinal cord runs along the dorsal side of the body and links the brain to the rest of the body. Vertebrates have their spinal cords encased in a series of (usually) bony vertebrae that comprise the vertebral column. • The gray matter of the spinal cord consists mostly of cell bodies and dendri ...
... • The spinal cord runs along the dorsal side of the body and links the brain to the rest of the body. Vertebrates have their spinal cords encased in a series of (usually) bony vertebrae that comprise the vertebral column. • The gray matter of the spinal cord consists mostly of cell bodies and dendri ...
info EQ - West Ada
... completed in one day and the circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems will be completed in one day as well. This order will make it easier to place the organs in your human body. Make sure that each group member is learning each body system as you proceed through the scavenger hunt. Designing ...
... completed in one day and the circulatory, respiratory, and digestive systems will be completed in one day as well. This order will make it easier to place the organs in your human body. Make sure that each group member is learning each body system as you proceed through the scavenger hunt. Designing ...
PID *****2515 1.Why is it difficult to understand olfactory neural
... multiple steps of olfactory processing. (p45). However, it is hard to classify receptors because it is hard to know their exact function. ...
... multiple steps of olfactory processing. (p45). However, it is hard to classify receptors because it is hard to know their exact function. ...
SYSTEMS OF THE HUMAN BODY
... heart and other nearby organs safe. Bones also store important minerals such as calcium and produce new blood cells. Muscular System: The muscular system, as you might have guessed, includes muscles! It also includes tendons and ligaments. Tendons are tissues that attach bones to muscles. Ligaments ...
... heart and other nearby organs safe. Bones also store important minerals such as calcium and produce new blood cells. Muscular System: The muscular system, as you might have guessed, includes muscles! It also includes tendons and ligaments. Tendons are tissues that attach bones to muscles. Ligaments ...
Reflexes and Homeostasis
... (CNS) structure such as the brain or spinal cord. In short re exes, the interneuron is located in a peripheral ganglion, bypassing the CNS, as shown in Figure 1 (Short and Long Re exes ). Finally, the motor neurons which generates the response can also be classi ed into two general categories. One t ...
... (CNS) structure such as the brain or spinal cord. In short re exes, the interneuron is located in a peripheral ganglion, bypassing the CNS, as shown in Figure 1 (Short and Long Re exes ). Finally, the motor neurons which generates the response can also be classi ed into two general categories. One t ...
Systems of the Human Body
... other nearby organs safe. Bones also store important minerals such as calcium and produce new blood cells. Muscular System: The muscular system, as you might have guessed, includes muscles! It also includes tendons and ligaments. Tendons are tissues that attach bones to muscles. Ligaments are tissue ...
... other nearby organs safe. Bones also store important minerals such as calcium and produce new blood cells. Muscular System: The muscular system, as you might have guessed, includes muscles! It also includes tendons and ligaments. Tendons are tissues that attach bones to muscles. Ligaments are tissue ...
File
... 4) The motor nerve transmits the signal to the muscles and makes it react. This reaction can be voluntary or involuntary ...
... 4) The motor nerve transmits the signal to the muscles and makes it react. This reaction can be voluntary or involuntary ...
Chapter 21 - The Nervous System: Organization
... Reflexes are simple, stereotyped and repeatable motor actions (example: movements) brought about by a specific sensory stimulus. The reflex is involuntary but may involve the use of voluntary (skeletal) muscle and nerves. ...
... Reflexes are simple, stereotyped and repeatable motor actions (example: movements) brought about by a specific sensory stimulus. The reflex is involuntary but may involve the use of voluntary (skeletal) muscle and nerves. ...
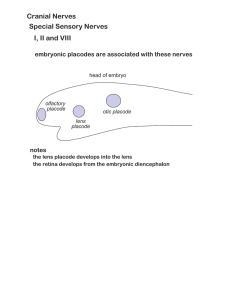
Cranial Nerves Special Sensory Nerves I, II and VIII
... the lens placode develops into the lens the retina develops from the embryonic diencephalon ...
... the lens placode develops into the lens the retina develops from the embryonic diencephalon ...
Document
... To analyze the ‘what’, ‘how’, and ‘when’ of this system, we would have to (i) Model the muscle dynamics, spindle and anterior horn cell synapse (ii) Model the encoding and decoding of spike trains in neurons (iii) Recognize that the effects of other receptors and higher centers are neglected ...
... To analyze the ‘what’, ‘how’, and ‘when’ of this system, we would have to (i) Model the muscle dynamics, spindle and anterior horn cell synapse (ii) Model the encoding and decoding of spike trains in neurons (iii) Recognize that the effects of other receptors and higher centers are neglected ...
presentación - Vicens Vives
... – Recognise in drawings, posters and models the different organs which make up the respiratory, circulatory, excretory and reproductive systems. – Understand the specific functions of the respiratory, circulatory, excretory and reproductive systems. – Differentiate the male and female reproductive s ...
... – Recognise in drawings, posters and models the different organs which make up the respiratory, circulatory, excretory and reproductive systems. – Understand the specific functions of the respiratory, circulatory, excretory and reproductive systems. – Differentiate the male and female reproductive s ...
Education project to be published_Maggy comments
... This activity involves the pupils working in groups of 5 or 6. They are provided with a poster of a blank human body. They are also provided with card cut outs of the main digestive organs including: gall bladder, small intestine, large intestine, stomach, liver and esophagus. The pupils are require ...
... This activity involves the pupils working in groups of 5 or 6. They are provided with a poster of a blank human body. They are also provided with card cut outs of the main digestive organs including: gall bladder, small intestine, large intestine, stomach, liver and esophagus. The pupils are require ...
DO NOW - PBworks
... What are the structures and functions of our body systems? OBJECTIVES: -What are the structures and functions of the reproductive system? ...
... What are the structures and functions of our body systems? OBJECTIVES: -What are the structures and functions of the reproductive system? ...
Dr.Kaan Yücel http://yeditepeanatomy1.org Introduction to
... system supply oxygen and nutrients to and remove waste from these structures; and the sensory organs (especially vision and equilibrium) play important roles in directing their activities in a gravitational environment. 1.1.1. SKELETAL SYSTEM Bones are organs, and along with the cartilages form the ...
... system supply oxygen and nutrients to and remove waste from these structures; and the sensory organs (especially vision and equilibrium) play important roles in directing their activities in a gravitational environment. 1.1.1. SKELETAL SYSTEM Bones are organs, and along with the cartilages form the ...
A103 Anatomy and Physiology
... Understand the different sections of the digestive system and identify the organs found at different sections. Appreciate the general structure of the digestive system and the 4 layers of tissue that makes up the digestive tract. ...
... Understand the different sections of the digestive system and identify the organs found at different sections. Appreciate the general structure of the digestive system and the 4 layers of tissue that makes up the digestive tract. ...
Human Body Systems
... Create a flow chart that shows how the body is organized. • Include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. • Explain / define each component. ...
... Create a flow chart that shows how the body is organized. • Include cells, tissues, organs, and organ systems. • Explain / define each component. ...
The Reflex Arc
... the eye or ear. Receptors are located in each sensory organ (eye, ear, tongue, skin, and nose) ...
... the eye or ear. Receptors are located in each sensory organ (eye, ear, tongue, skin, and nose) ...
Function
... 5) Monitors and makes corrective adjustments in the activities initiated by other parts of the brain 6) Compares the actual motor movements with the intended movements and makes corrective changes. 7) The cerebellum does not initiate movement, but it contributes to coordination, precision, and accur ...
... 5) Monitors and makes corrective adjustments in the activities initiated by other parts of the brain 6) Compares the actual motor movements with the intended movements and makes corrective changes. 7) The cerebellum does not initiate movement, but it contributes to coordination, precision, and accur ...
File
... 3. Responsiveness, or irritability, is the ability to detect changes in the internal or external environment and respond to them. 4. Digestion is the process of breaking down food into molecules that are usable by the body. 5. Metabolism includes all chemical reactions that occur in the body. 6. Exc ...
... 3. Responsiveness, or irritability, is the ability to detect changes in the internal or external environment and respond to them. 4. Digestion is the process of breaking down food into molecules that are usable by the body. 5. Metabolism includes all chemical reactions that occur in the body. 6. Exc ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.