REVIEW OF Nervous system anatomy File
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input – Information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes ...
... Functions of the Nervous System 1. Sensory input – Information gathered by sensory receptors about internal and external changes ...
6.1 The Nervous System - Blyth-Exercise
... Intermediate nerve fibre (adjustor or interneuron) – interprets signal ...
... Intermediate nerve fibre (adjustor or interneuron) – interprets signal ...
Nervous System
... triggered by a stimulus, such as a song or a smell, or they can be deliberately recalled. Recalling memories helps us to refresh them and makes them last a lifetime. • Fainting is often caused by suddenly low blood pressure and insufficient blood flow to the cerebrum. ...
... triggered by a stimulus, such as a song or a smell, or they can be deliberately recalled. Recalling memories helps us to refresh them and makes them last a lifetime. • Fainting is often caused by suddenly low blood pressure and insufficient blood flow to the cerebrum. ...
The Nervous System
... Nervous System: Two Main Parts Part II: Peripheral Nervous System – Consist of all parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord – Function handles the central nervous system’s ...
... Nervous System: Two Main Parts Part II: Peripheral Nervous System – Consist of all parts of the nervous system outside the brain and spinal cord – Function handles the central nervous system’s ...
Chapter 13 - apsubiology.org
... changes in the environment sensory neuron - conducts an impulse from a receptor to its ...
... changes in the environment sensory neuron - conducts an impulse from a receptor to its ...
Pain
... colliculus, geniculate nucleus, primary auditory cortex tonotopic organization Sound localization strategies (superior olive) Organization of primary auditory cortex Vestibular System Otolith organs (utriculus and sacculus) – anatomy and function, sensing gravitational field and linear acceleration ...
... colliculus, geniculate nucleus, primary auditory cortex tonotopic organization Sound localization strategies (superior olive) Organization of primary auditory cortex Vestibular System Otolith organs (utriculus and sacculus) – anatomy and function, sensing gravitational field and linear acceleration ...
Part 1: From Ion Channels to behavior, HT2009 Course
... colliculus, geniculate nucleus, primary auditory cortex tonotopic organization Sound localization strategies (superior olive) Organization of primary auditory cortex Vestibular System Otolith organs (utriculus and sacculus) – anatomy and function, sensing gravitational field and linear acceleration ...
... colliculus, geniculate nucleus, primary auditory cortex tonotopic organization Sound localization strategies (superior olive) Organization of primary auditory cortex Vestibular System Otolith organs (utriculus and sacculus) – anatomy and function, sensing gravitational field and linear acceleration ...
Slide ()
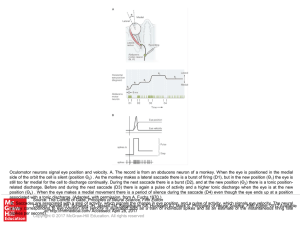
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
... Oculomotor neurons signal eye position and velocity. A. The record is from an abducens neuron of a monkey. When the eye is positioned in the medial side of the orbit the cell is silent (position Θ0) . As the monkey makes a lateral saccade there is a burst of firing (D1), but in the new position (Θ1) ...
Chapter 13 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Phylum Annelida • Triploblastic, coelomate animals • Bilateral symmetry • 1 mm to 3 m in length • Ventral nerve cords • Closed circulatory system ...
... Phylum Annelida • Triploblastic, coelomate animals • Bilateral symmetry • 1 mm to 3 m in length • Ventral nerve cords • Closed circulatory system ...
Natural psychology The EEA and the structure of
... functional model used for all other body tissues and organs. But instead of just adding the simple heuristic that brain mechanisms serve survival or reproduction, EP has brought the full power of evolutionary theory to bear – cognitive mechanisms are adaptations. Research in many domains of psycholo ...
... functional model used for all other body tissues and organs. But instead of just adding the simple heuristic that brain mechanisms serve survival or reproduction, EP has brought the full power of evolutionary theory to bear – cognitive mechanisms are adaptations. Research in many domains of psycholo ...
3.5. Responses to Stimuli – Definitions. Term Definition Tropism
... This joins bone to bone This joins muscle to bone Defence against disease To give the body the ability to fight infections by the production of antibodies by exposure to infection[by vaccines or by illness] “safe dose” of a pathogen/causing antibody production OR causing an immune response This intr ...
... This joins bone to bone This joins muscle to bone Defence against disease To give the body the ability to fight infections by the production of antibodies by exposure to infection[by vaccines or by illness] “safe dose” of a pathogen/causing antibody production OR causing an immune response This intr ...
Chapter 1 PowerPoint
... Gross Anatomy – the study of large body structures visible or observable to the naked eye ...
... Gross Anatomy – the study of large body structures visible or observable to the naked eye ...
introduction-to-anatomy2
... extension, and adduction (or in the opposite order) in such a way that the distal end of the part moves in a circle • Circumduction can occur at any joint at which all the above-mentioned movements are possible (e.g., the shoulder and hip joints). ...
... extension, and adduction (or in the opposite order) in such a way that the distal end of the part moves in a circle • Circumduction can occur at any joint at which all the above-mentioned movements are possible (e.g., the shoulder and hip joints). ...
chapt01_lecture_anim
... Please Note: Once you have used any of the animation functions (such as Play or Pause), you must first click on the slide’s background before you can advance to the next slide. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. ...
... Please Note: Once you have used any of the animation functions (such as Play or Pause), you must first click on the slide’s background before you can advance to the next slide. See separate PowerPoint slides for all figures and tables preinserted into PowerPoint without notes and animations. ...
Human Biology
... List the levels of organization in humans. What are the four basic types of human tissue? List the organ systems of the human body. Using any type of machine as an example, explain how each part of the machine works together with every other part so that the machine can do its job. Compare this with ...
... List the levels of organization in humans. What are the four basic types of human tissue? List the organ systems of the human body. Using any type of machine as an example, explain how each part of the machine works together with every other part so that the machine can do its job. Compare this with ...
Motor control
... • Primary motor cortex (also called the motor strip or M1) - Runs almost the entire length of the central sulcus in the most posterior part of the frontal lobe. Most cortico-spinal fibers start here and project directly into the spinal cord. • Supplementary motor area (SMA) - The medial section imme ...
... • Primary motor cortex (also called the motor strip or M1) - Runs almost the entire length of the central sulcus in the most posterior part of the frontal lobe. Most cortico-spinal fibers start here and project directly into the spinal cord. • Supplementary motor area (SMA) - The medial section imme ...
Comparative study of indriyas in relation to functional
... mahabhuta is more, in srotra indriya aakash mahabhuta is more and in twagendriya vayu mahabhuta is more. Knowledge is obtained with the help of these indrias. In our day to day life we used to come across many eventful features. Some of these features stay in our memory and some are not. Ayurveda sa ...
... mahabhuta is more, in srotra indriya aakash mahabhuta is more and in twagendriya vayu mahabhuta is more. Knowledge is obtained with the help of these indrias. In our day to day life we used to come across many eventful features. Some of these features stay in our memory and some are not. Ayurveda sa ...
sensor
... PSG in History continued • 1957: Eye movements related to dream activity • 1958: International 10-20 (%) system of electrode placement was ...
... PSG in History continued • 1957: Eye movements related to dream activity • 1958: International 10-20 (%) system of electrode placement was ...
How To Process and Confirm Department Space
... Summary of Steps 1. Go to Web Client: Roomscheduling.tufts.edu/emswebclient/ 2. Navigate to: Dashboard>Notification Rules 3. Highlight reservation to review and select “Go To” 4. Highlight reservation or booking to confirm, select Tools>Wizard>Change Booking Status Wizard 5. Select Status to change ...
... Summary of Steps 1. Go to Web Client: Roomscheduling.tufts.edu/emswebclient/ 2. Navigate to: Dashboard>Notification Rules 3. Highlight reservation to review and select “Go To” 4. Highlight reservation or booking to confirm, select Tools>Wizard>Change Booking Status Wizard 5. Select Status to change ...
GAIT AND LOCOMOTION
... visual clues help in alignment, step frequency and even step length. Gives us movement relative to environment. ...
... visual clues help in alignment, step frequency and even step length. Gives us movement relative to environment. ...
Chapters 11: Introduction to the Nervous System and Nervous
... unable to appropriately test beliefs and perceptions against reality); thought to result from excessive release of dopamine; management involves blocking postsynaptic dopamine receptors ____________ disorders – marked by disturbances in mood; decreased levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dop ...
... unable to appropriately test beliefs and perceptions against reality); thought to result from excessive release of dopamine; management involves blocking postsynaptic dopamine receptors ____________ disorders – marked by disturbances in mood; decreased levels of serotonin, norepinephrine, and/or dop ...
Neurologic Assessment
... Biceps reflex Triceps reflex Brachioradialis reflex Quadriceps reflex Achilles reflex (“ankle jerk”) ...
... Biceps reflex Triceps reflex Brachioradialis reflex Quadriceps reflex Achilles reflex (“ankle jerk”) ...
21-1
... • First cell body in DRG with synapses in cord • 2nd cell body in gray matter of cord, sends fibers to other side of cord & up through white matter to synapse in thalamus • 3rd cell body in thalamus projects to cerebral cortex ...
... • First cell body in DRG with synapses in cord • 2nd cell body in gray matter of cord, sends fibers to other side of cord & up through white matter to synapse in thalamus • 3rd cell body in thalamus projects to cerebral cortex ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.