five spaces of cultural criminology - Kent Blogs
... cultural geography. In this body of work, space is understood almost as if it were a living thing, a multi-layered congress of cultural, political and spatial dynamics. I am not naive enough to suggest that cultural geography and attendant concepts such as nonrepresentational theory will subsume exi ...
... cultural geography. In this body of work, space is understood almost as if it were a living thing, a multi-layered congress of cultural, political and spatial dynamics. I am not naive enough to suggest that cultural geography and attendant concepts such as nonrepresentational theory will subsume exi ...
ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGY OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS
... associated receptors by which cells in the body communicate with one another provides many targets for drug action, and has always been a focus of attention for pharmacologists. Chemical transmission in the peripheral nervous system, and the various ways in which the process can be pharmacological ...
... associated receptors by which cells in the body communicate with one another provides many targets for drug action, and has always been a focus of attention for pharmacologists. Chemical transmission in the peripheral nervous system, and the various ways in which the process can be pharmacological ...
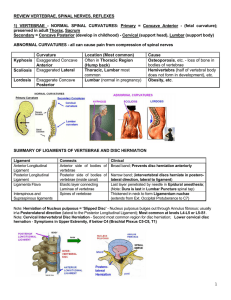
REVIEW VERTEBRAE, SPINAL NERVES, REFLEXES 1
... 5.____A 25-year-old rugby player injured his neck while tackling another player. He felt numbness over the region of the thumb on the palmar surface that persisted for several days.. Physical examination by his physician showed weakness in the biceps muscle. These symptoms could result a sign of he ...
... 5.____A 25-year-old rugby player injured his neck while tackling another player. He felt numbness over the region of the thumb on the palmar surface that persisted for several days.. Physical examination by his physician showed weakness in the biceps muscle. These symptoms could result a sign of he ...
PowerPoint 演示文稿 - Shandong University
... person has several twitch-like contractions of the muscle. ...
... person has several twitch-like contractions of the muscle. ...
nervous system part 6 EEG, walkfulness and sleep
... person has several twitch-like contractions of the muscle. ...
... person has several twitch-like contractions of the muscle. ...
REFLEX ARCS - Anatomy.tv
... A tendon reflex is initiated by a substantial amount of tension in a muscle tendon, and results in the reflex relaxation of the skeletal muscle attached to that tendon. It is less sensitive than the stretch reflex, but produces an opposite effect. 1. Golgi tendon organ The reflex begins when sensory ...
... A tendon reflex is initiated by a substantial amount of tension in a muscle tendon, and results in the reflex relaxation of the skeletal muscle attached to that tendon. It is less sensitive than the stretch reflex, but produces an opposite effect. 1. Golgi tendon organ The reflex begins when sensory ...
Phase IIB / PHGY 825 Organization of the Brain Stem Organization
... Within an intact brain stem, conjugate eye movements are produced in response to vestibular stimulation, i.e., by turning the head or irrigating the ear canal with cool or warm water. Head turn induces eye movements in the opposite direction. Cool water in the ear canal sets up a convection current ...
... Within an intact brain stem, conjugate eye movements are produced in response to vestibular stimulation, i.e., by turning the head or irrigating the ear canal with cool or warm water. Head turn induces eye movements in the opposite direction. Cool water in the ear canal sets up a convection current ...
Modelling Cerebellar Function in Saccadic Adaptation
... • Different regions have different inputs and outputs, (microzones) but same basic organisation • Gives rise to idea of cerebellar chip: ~5000, each with its own particular connections. ...
... • Different regions have different inputs and outputs, (microzones) but same basic organisation • Gives rise to idea of cerebellar chip: ~5000, each with its own particular connections. ...
COURSE TITLE - Metropolitan Community College
... 1. written unit quiz ,assignment Portion of written final exam 2. written unit quiz, assignment Portion of written final exam 3. written unit quiz, assignment Portion of written final exam 4. written unit quiz, assignment Portion of written final exam 5. written unit quiz, assignment Portion of writ ...
... 1. written unit quiz ,assignment Portion of written final exam 2. written unit quiz, assignment Portion of written final exam 3. written unit quiz, assignment Portion of written final exam 4. written unit quiz, assignment Portion of written final exam 5. written unit quiz, assignment Portion of writ ...
Peripheral Nervous System - cK-12
... The motor division of the peripheral system carries messages from the central nervous system to internal organs and muscles. The motor division is also divided into two parts (Figure 1.4), the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system carries messages that c ...
... The motor division of the peripheral system carries messages from the central nervous system to internal organs and muscles. The motor division is also divided into two parts (Figure 1.4), the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. The somatic nervous system carries messages that c ...
The subtle body: an interoceptive map of central nervous system
... models detail three main levels of structure and function: gross (audarika, sthūla), subtle (sūks.ma), and extremely subtle (susūks.ma).23,27 These levels overlap with the five layers or sheaths (kośas) described in the Samkhya-Yoga tradition and the neuropsychology of the Hindu Tantras.11 The c ...
... models detail three main levels of structure and function: gross (audarika, sthūla), subtle (sūks.ma), and extremely subtle (susūks.ma).23,27 These levels overlap with the five layers or sheaths (kośas) described in the Samkhya-Yoga tradition and the neuropsychology of the Hindu Tantras.11 The c ...
The Nervous System
... other neurons. 2. Soma/Cell body = Accepts impulse travelling from the dendrites. 3. Axon = Impulses travel from the soma and are carried along this thin fibre. 4. Axon terminals = Branches at the end of the axon that link with the dendrites of other neurons. ...
... other neurons. 2. Soma/Cell body = Accepts impulse travelling from the dendrites. 3. Axon = Impulses travel from the soma and are carried along this thin fibre. 4. Axon terminals = Branches at the end of the axon that link with the dendrites of other neurons. ...
the organization of the arthropod central nervous system
... particular method has, for technical reasons, only been possible in the crayfish, and it is therefore regrettable that no really good histological study of the crayfish nervous system has been made. Studies of this sort in related forms and in other arthropods have revealed a variety of interneurons ...
... particular method has, for technical reasons, only been possible in the crayfish, and it is therefore regrettable that no really good histological study of the crayfish nervous system has been made. Studies of this sort in related forms and in other arthropods have revealed a variety of interneurons ...
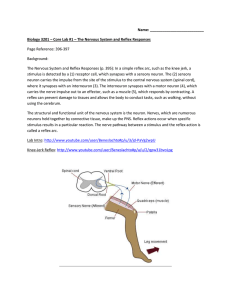
Core Lab #1 - Reflex Responses
... The Nervous System and Reflex Responses (p. 395): In a simple reflex arc, such as the knee jerk, a stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), ...
... The Nervous System and Reflex Responses (p. 395): In a simple reflex arc, such as the knee jerk, a stimulus is detected by a (1) receptor cell, which synapses with a sensory neuron. The (2) sensory neuron carries the impulse from the site of the stimulus to the central nervous system (spinal cord), ...
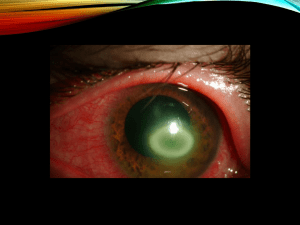
Vision
... • Glaucoma—can cause blindness due to increasing pressure within the eye • Hemianopia—loss of the same side of the visual field of both eyes; results from damage to the visual cortex on one side only ...
... • Glaucoma—can cause blindness due to increasing pressure within the eye • Hemianopia—loss of the same side of the visual field of both eyes; results from damage to the visual cortex on one side only ...
Beyond Control: The Dynamics of Brain-Body
... This integrated perspective on behavior raises both experimental and theoretical challenges. It is difficult enough to study any one component of a brain-body-environment system in isolation, let alone the simultaneous interaction of all three. Not only must one be able to measure and manipulate neu ...
... This integrated perspective on behavior raises both experimental and theoretical challenges. It is difficult enough to study any one component of a brain-body-environment system in isolation, let alone the simultaneous interaction of all three. Not only must one be able to measure and manipulate neu ...
Visual Motion Perception using Critical Branching Neural Computation
... Biological motion perception starts with motion detectors in the retina, where ganglion cells just two or three synapses away from rods and cones detect motion in preferred directions (Vaney et al., 2000). Behaviorally, sensitivity to the direction of motion is demonstrated in motion coherence studi ...
... Biological motion perception starts with motion detectors in the retina, where ganglion cells just two or three synapses away from rods and cones detect motion in preferred directions (Vaney et al., 2000). Behaviorally, sensitivity to the direction of motion is demonstrated in motion coherence studi ...
Motor disorders
... deficits associated with discrete cerebellar lesions caused by gunshot wounds. These descriptions are still considered to be the fundamental basis for our understanding of clinical cerebellar syndromes. Based on Holmes's work, the clinical manifestations of cerebellar disease can be divided into bas ...
... deficits associated with discrete cerebellar lesions caused by gunshot wounds. These descriptions are still considered to be the fundamental basis for our understanding of clinical cerebellar syndromes. Based on Holmes's work, the clinical manifestations of cerebellar disease can be divided into bas ...
Cerebellum
... the parietal cortex). All of these areas are, in various ways, active during or before movements. Presumably, the cerebellum thus receives information about movements that are being planned and about the commands that are sent out from the motor cortex; in response it can modulate the activity of th ...
... the parietal cortex). All of these areas are, in various ways, active during or before movements. Presumably, the cerebellum thus receives information about movements that are being planned and about the commands that are sent out from the motor cortex; in response it can modulate the activity of th ...
Bodily Systems and the Modular Structure of the Human Body
... mathematical tools which leave unanswered precisely those questions pertaining to the nature of bodily systems which we are called upon to answer. We can make some progress, on the other hand, if we examine how the word ‘system’ is most commonly used in both technical and non-technical contexts by s ...
... mathematical tools which leave unanswered precisely those questions pertaining to the nature of bodily systems which we are called upon to answer. We can make some progress, on the other hand, if we examine how the word ‘system’ is most commonly used in both technical and non-technical contexts by s ...
Neural integration
... Primary motor cortex corresponds point by point with specific regions of the body Cortical areas have been mapped out in diagrammatic form Homunculus provides indication of degree of fine motor control available: – hands, face, and tongue, which are capable of varied and complex movements, app ...
... Primary motor cortex corresponds point by point with specific regions of the body Cortical areas have been mapped out in diagrammatic form Homunculus provides indication of degree of fine motor control available: – hands, face, and tongue, which are capable of varied and complex movements, app ...
Lecture 14 (Chapter 13) Last Quiz The Adult Spinal Cord Gross
... Reflex Motor Patterns • Higher centers of brain incorporate lower, reflexive motor patterns • Automatic reflexes: – can be activated by brain as needed – use few nerve impulses to control complex motor functions – e.g. walking, running, jumping ...
... Reflex Motor Patterns • Higher centers of brain incorporate lower, reflexive motor patterns • Automatic reflexes: – can be activated by brain as needed – use few nerve impulses to control complex motor functions – e.g. walking, running, jumping ...
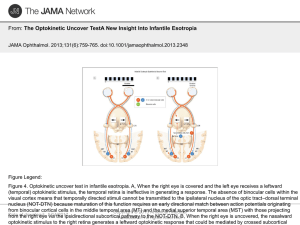
The Optokinetic Uncover TestA New Insight Into Infantile Esotropia
... Figure 3. Normal cortical and subcortical projections during early human development (based on a model proposed by Hoffmann). The brain is viewed from the top of the head, so the left eye is on the left. A, In early infancy, a leftward optokinetic stimulus is transmitted contralaterally via a subcor ...
... Figure 3. Normal cortical and subcortical projections during early human development (based on a model proposed by Hoffmann). The brain is viewed from the top of the head, so the left eye is on the left. A, In early infancy, a leftward optokinetic stimulus is transmitted contralaterally via a subcor ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.