Divisions of the Nervous System
... The Central Nervous System The Spinal Cord Serves as a sort of neural cable, connecting the brain with parts of the peripheral nervous system extending into the trunk and limbs. Does not connect the brain to internal organs. Responsible for simple reflexes. ...
... The Central Nervous System The Spinal Cord Serves as a sort of neural cable, connecting the brain with parts of the peripheral nervous system extending into the trunk and limbs. Does not connect the brain to internal organs. Responsible for simple reflexes. ...
Introduction to Sensory Systems
... In the dark, Na channels are open, causing depolarization and allowing Na influx and K efflux, counteracted by pump. In light, Rhodopsin ultimately closes these channels stopping the flow. ...
... In the dark, Na channels are open, causing depolarization and allowing Na influx and K efflux, counteracted by pump. In light, Rhodopsin ultimately closes these channels stopping the flow. ...
The Nervous System
... • All neural functions involve communication of neurons with one another and with other cells – Neuroglia: supporting cells with various functions: ...
... • All neural functions involve communication of neurons with one another and with other cells – Neuroglia: supporting cells with various functions: ...
Ativity 13 - PCC - Portland Community College
... weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “Flaccid Paralysis” ...
... weakness, twitching of muscle (fasciculation), and loss of muscle mass (muscle atrophy). “Flaccid Paralysis” ...
Sir Charles Scott Sherrington English Neurophysiologist 1857
... neuro-developmental deficits. Sherrington’s work relating to the dual protection effect of a reflex pattern in the face of dysfunction or pathology helps Dr. Masgutova explain why standard physical, occupational, and speech therapy methods often have difficulty imparting functional change, if not ta ...
... neuro-developmental deficits. Sherrington’s work relating to the dual protection effect of a reflex pattern in the face of dysfunction or pathology helps Dr. Masgutova explain why standard physical, occupational, and speech therapy methods often have difficulty imparting functional change, if not ta ...
BIO 218 F 2012 Ch 15 Martini Lecture Outline
... Sensory and Motor Tracts Naming the tracts If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract ...
... Sensory and Motor Tracts Naming the tracts If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy Lecture Outline Adapted from Martini
... Sensory and Motor Tracts Naming the tracts If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract ...
... Sensory and Motor Tracts Naming the tracts If the tract name begins with “spino” (as in spinocerebellar), the tract is a sensory tract delivering information from the spinal cord to the cerebellum (in this case) If the tract name ends with “spinal” (as in vestibulospinal), the tract is a motor tract ...
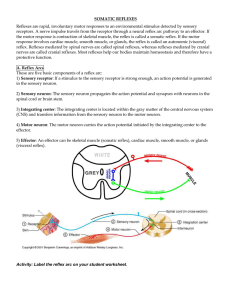
Reflex Activity/Lab
... Reflexes are rapid, involuntary motor responses to an environmental stimulus detected by sensory receptors. A nerve impulse travels from the receptor through a neural reflex arc pathway to an effector. If the motor response is contraction of skeletal muscle, the reflex is called a somatic reflex. If ...
... Reflexes are rapid, involuntary motor responses to an environmental stimulus detected by sensory receptors. A nerve impulse travels from the receptor through a neural reflex arc pathway to an effector. If the motor response is contraction of skeletal muscle, the reflex is called a somatic reflex. If ...
Historical analysis of the neural control of movement from the
... monosynaptic reflexes, with the incoming afferents directly contacting the outgoing motoneurons (MNs). The relevant afferent fibers were shown to be the fast Ia afferents from the primary endings of muscle spindles, which are exquisitely sensitive to dynamic stretching. Much later the slower group I ...
... monosynaptic reflexes, with the incoming afferents directly contacting the outgoing motoneurons (MNs). The relevant afferent fibers were shown to be the fast Ia afferents from the primary endings of muscle spindles, which are exquisitely sensitive to dynamic stretching. Much later the slower group I ...
Undulatory locomotion of polychaete annelids - FORTH-ICS
... with a rough one (as in the case of errant polychaete). In both cases, the body is assumed to be cylindrical in shape, with a small diameter compared to its overall length. The model used is a resistive one, whereby the local instantaneous force exerted on a segment of the undulating body depends (u ...
... with a rough one (as in the case of errant polychaete). In both cases, the body is assumed to be cylindrical in shape, with a small diameter compared to its overall length. The model used is a resistive one, whereby the local instantaneous force exerted on a segment of the undulating body depends (u ...
Eye Movements - Center for Neural Science
... Primates, for example, have a highly specialized central region of the retina known as the fovea. The fovea can gather visual information from only 18 of the visual world, but the photoreceptors in the fovea are packed at high density, permitting high resolution. High resolution would be useless, ho ...
... Primates, for example, have a highly specialized central region of the retina known as the fovea. The fovea can gather visual information from only 18 of the visual world, but the photoreceptors in the fovea are packed at high density, permitting high resolution. High resolution would be useless, ho ...
Cerebellum: The Brain for an Implicit Self
... The primary rationale for my writing this book is that I have been involved in research on the cerebellum for half a century and it seemed appropriate to share with younger generations of researchers how thrilling and dramatic this epoch has been, particularly since research on the cerebellum has ad ...
... The primary rationale for my writing this book is that I have been involved in research on the cerebellum for half a century and it seemed appropriate to share with younger generations of researchers how thrilling and dramatic this epoch has been, particularly since research on the cerebellum has ad ...
muscle stretch reflex
... muscle. As seen in Figure 4, the quadriceps and the hamstring muscles can be described as antagonistic. This means that the two muscles work together, in opposition, to produce movement. When the quadri ...
... muscle. As seen in Figure 4, the quadriceps and the hamstring muscles can be described as antagonistic. This means that the two muscles work together, in opposition, to produce movement. When the quadri ...
directional asymmetries of optokinetic nystagmus: developmental
... canals during head movements of high frequency and velocity and from the visual system during head movements of low frequency and velocity. The resulting eye movements are called the vestibulo-ocular reflex when only vestibular inputs are involved and are called optokinetic eye movements when only v ...
... canals during head movements of high frequency and velocity and from the visual system during head movements of low frequency and velocity. The resulting eye movements are called the vestibulo-ocular reflex when only vestibular inputs are involved and are called optokinetic eye movements when only v ...
Biomechanical and neurophysiological mechanisms related to
... tension variation, but only a combination of afferent inputs can provide the necessary information to control body equilibrium (Dietz, 1996). The role of proprioceptive information from ankle muscles has been highlighted in various studies (Fitzpatrick et al., 1994; Fitzpatrick et al., 1992a; Gatev ...
... tension variation, but only a combination of afferent inputs can provide the necessary information to control body equilibrium (Dietz, 1996). The role of proprioceptive information from ankle muscles has been highlighted in various studies (Fitzpatrick et al., 1994; Fitzpatrick et al., 1992a; Gatev ...
Auris Nasus Larynx 34 (2008) 1-10
... Sufficient morphologic, physiologic and clinical evidence has accumulated in the past few decades to indicate an organization in the vestibular system that may account for different forms of vertigo depending on the location of pathology in the vestibular nerve. The evidence supporting such a "place ...
... Sufficient morphologic, physiologic and clinical evidence has accumulated in the past few decades to indicate an organization in the vestibular system that may account for different forms of vertigo depending on the location of pathology in the vestibular nerve. The evidence supporting such a "place ...
29.4 Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems The
... The Nervous System :Components and Function (2m41s) • Add at least 5 additional notes to your tree map ...
... The Nervous System :Components and Function (2m41s) • Add at least 5 additional notes to your tree map ...
Grade 5 Life Science Unit (5.L.1)
... Describe each of the following joints and where they are located: hinge, pivot, and ball-and-socket. You may include other joints as well. Find five facts about your body system. You may list the facts as sentences or use them to create trivia questions. ...
... Describe each of the following joints and where they are located: hinge, pivot, and ball-and-socket. You may include other joints as well. Find five facts about your body system. You may list the facts as sentences or use them to create trivia questions. ...
Proprioceptive Eye Position Signals Are Still Missing a Sensory
... that connects to the orbit (orbital layer; Fig. 1). EOMs are also characterized by the presence of slow-contracting muscle fibers which do not propagate action potentials. Those fibers are innervated by multiple, “en grappe,” terminals and consequently are called multiply innervated muscle fibers (M ...
... that connects to the orbit (orbital layer; Fig. 1). EOMs are also characterized by the presence of slow-contracting muscle fibers which do not propagate action potentials. Those fibers are innervated by multiple, “en grappe,” terminals and consequently are called multiply innervated muscle fibers (M ...
Motor Systems - Neuroanatomy
... reflexes are a basic building block of movement. Dorsal root inputs provide the sensory input for spinal reflexes, and the LMNs provide the motor output pathway. One of the simplest and best studied reflexes is the stretch reflex - stretch a muscle and the reflex circuit leads to contraction of the ...
... reflexes are a basic building block of movement. Dorsal root inputs provide the sensory input for spinal reflexes, and the LMNs provide the motor output pathway. One of the simplest and best studied reflexes is the stretch reflex - stretch a muscle and the reflex circuit leads to contraction of the ...
2-Motor System2009-03-20 18:254.4 MB
... to perform a motor task into a series of motor command that will do the task. ...
... to perform a motor task into a series of motor command that will do the task. ...
f19c623c99fc721
... • Supplementary motor area (SMA) Note: All the three projects directly to the spinal cord via corticospinal tract. • Premotor and supplementary motor cortex also project to primary motor cortex and is involved in coordinating & planning complex sequences of movement (motor learning). ...
... • Supplementary motor area (SMA) Note: All the three projects directly to the spinal cord via corticospinal tract. • Premotor and supplementary motor cortex also project to primary motor cortex and is involved in coordinating & planning complex sequences of movement (motor learning). ...
bupropion and the autonomic nervous system
... hair follicles, eyes (the iris; smooth muscle) sphincters, etc. It also controls the following functions: heart rate, blood pressure, regional blood flow, breathing, cellular metabolism, gastrointestinal motility, stomach, intestines and bladder, secretion of exocrine glands, body temperature, empty ...
... hair follicles, eyes (the iris; smooth muscle) sphincters, etc. It also controls the following functions: heart rate, blood pressure, regional blood flow, breathing, cellular metabolism, gastrointestinal motility, stomach, intestines and bladder, secretion of exocrine glands, body temperature, empty ...
Reflexes - Sinoe Medical Association
... skeletal muscles, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, & glands). The spinal cord is also responsible for spinal reflexes. ...
... skeletal muscles, smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, & glands). The spinal cord is also responsible for spinal reflexes. ...
Neuroscience in space

Space neuroscience is the scientific study of the central nervous system (CNS) functions during spaceflight. Living systems can integrate the inputs from the senses to navigate in their environment and to coordinate posture, locomotion, and eye movements. Gravity has a fundamental role in controlling these functions. In weightlessness during spaceflight, integrating the sensory inputs and coordinating motor responses is harder to do because gravity is no longer sensed during free-fall. For example, the otolith organs of the vestibular system no longer signal head tilt relative to gravity when standing. However, they can still sense head translation during body motion. Ambiguities and changes in how the gravitational input is processed can lead to potential errors in perception, which affects spatial orientation and mental representation. Dysfunctions of the vestibular system are common during and immediately after spaceflight, such as space motion sickness in orbit and balance disorders after return to Earth.Adaptation to weightlessness involves not just the Sensory-motor coupling functions, but some autonomic nervous system functions as well. Sleep disorders and orthostatic intolerance are also common during and after spaceflight. There is no hydrostatic pressure in a weightless environment. As a result, the redistribution of body fluids toward the upper body causes a decrease in leg volume, which may affect muscle viscosity and compliance. An increase in intracranial pressure may also be responsible for a decrease in near visual acuity. In addition, muscle mass and strength both decrease as a result of the reduced loading in weightlessness. Moreover, approximately 70% of astronauts experience space motion sickness to some degree during the first days. The drugs commonly used to combat motion sickness, such as scopolamine and promethazine, have soporific effects. These factors can lead to chronic fatigue. The challenge of integrative space medicine and physiology is to investigate the adaptation of the human body to spaceflight as a whole, and not just as the sum of body parts because all body functions are connected and interact with each other.