Review sheet Atomic Structure, Electron Configuration, and Periodic
... Identify groups as vertical columns on the periodic table. Know that main group elements in the same group have similar properties, the same number of valence electrons and the same oxidation number. Understand that reactivity increases as you go down within a group for metals and decreases for nonm ...
... Identify groups as vertical columns on the periodic table. Know that main group elements in the same group have similar properties, the same number of valence electrons and the same oxidation number. Understand that reactivity increases as you go down within a group for metals and decreases for nonm ...
Physical Science 100 Chapter 18, The Periodic Table
... Metals and non-metals are separated by a red “staircase” Elements near this staircase are called semi-metals (or semi-conductors) The noble or inert gases are on the far right. ...
... Metals and non-metals are separated by a red “staircase” Elements near this staircase are called semi-metals (or semi-conductors) The noble or inert gases are on the far right. ...
File
... c. The elements at the far left of the periodic table are nonmetals d. Elements are arranged by increasing atomic number 16. _____ Which of the following statements about alkali metals is true? a. Alkali metals are generally found in their uncombined form b. Alkali metals are group 1 elements c. Alk ...
... c. The elements at the far left of the periodic table are nonmetals d. Elements are arranged by increasing atomic number 16. _____ Which of the following statements about alkali metals is true? a. Alkali metals are generally found in their uncombined form b. Alkali metals are group 1 elements c. Alk ...
Periodic Table Vocabulary Periodic Table – a chart that organizes
... Atomic Mass – the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of one atom of the element. Located under the elemental symbol (at the bottom of the element box on the periodic table). ...
... Atomic Mass – the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of one atom of the element. Located under the elemental symbol (at the bottom of the element box on the periodic table). ...
The Periodic Table Worksheet
... 4. a) What is the link between the group to which an element belongs in the periodic table and the number of electrons in an atom of the element’s outer shell? ...
... 4. a) What is the link between the group to which an element belongs in the periodic table and the number of electrons in an atom of the element’s outer shell? ...
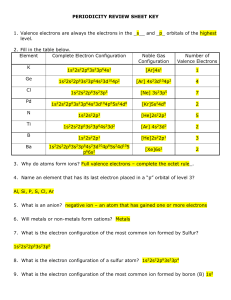
periodicity review sheet key
... __R___ 14. As the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element increases, its atomic number generally ________________ . __I___ 15. Going down a group of elements, the atomic radius (size)? __D___ 16. Going down a group of elements, the ionization energy? __D___ 17. Going left to right across a ...
... __R___ 14. As the number of neutrons in an atom of a given element increases, its atomic number generally ________________ . __I___ 15. Going down a group of elements, the atomic radius (size)? __D___ 16. Going down a group of elements, the ionization energy? __D___ 17. Going left to right across a ...
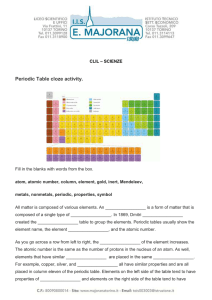
Periodic Table cloze activity.
... metals, nonmetals, periodic, properties, symbol All matter is composed of various elements. An _________________ is a form of matter that is composed of a single type of _________________. In 1869, Dmitri _________________ created the _________________ table to group the elements. Periodic tables us ...
... metals, nonmetals, periodic, properties, symbol All matter is composed of various elements. An _________________ is a form of matter that is composed of a single type of _________________. In 1869, Dmitri _________________ created the _________________ table to group the elements. Periodic tables us ...
sodium
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... The halogens are the nonmetals in Group 17. They are the most reactive nonmetals Reactivity in nonmetals increases as atomic number deceases, so fluorine is the most reactive nonmetal. Astatine is the least reactive. The halogens react with the alkali metals to form salts. Elements in the halogen fa ...
... The halogens are the nonmetals in Group 17. They are the most reactive nonmetals Reactivity in nonmetals increases as atomic number deceases, so fluorine is the most reactive nonmetal. Astatine is the least reactive. The halogens react with the alkali metals to form salts. Elements in the halogen fa ...
Periodic Table – an arrangement of the elements in order of their
... and a good conductor of heat and electricity; found on left side of periodic table. a Nonmetal – an element that has a low melting point and a dull surface, breaks easily, a poor conductor of heat and electricity and tends to gain electrons in a chemical reaction. Semimetal – an element that does no ...
... and a good conductor of heat and electricity; found on left side of periodic table. a Nonmetal – an element that has a low melting point and a dull surface, breaks easily, a poor conductor of heat and electricity and tends to gain electrons in a chemical reaction. Semimetal – an element that does no ...
2.2 The Periodic table and Chemical Properties
... • This is the average mass of an atom of an element. • It is always written as a decimal number and is measured in atomic mass unit (amu) ...
... • This is the average mass of an atom of an element. • It is always written as a decimal number and is measured in atomic mass unit (amu) ...
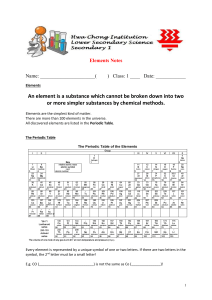
CHEMISTRY NOTES 9.1.1 ATOMS, ELEMENTS, PERIODIC TABLE
... e.g. hydrogen burns in air; hydrogen combines with oxygen to form water ATOMIC STRUCTURE Subatomic particles: components of atoms Some of these components can have a positive or negative charge. Particles with the same charge repel each other; particles with unlike charges are attracted to one anoth ...
... e.g. hydrogen burns in air; hydrogen combines with oxygen to form water ATOMIC STRUCTURE Subatomic particles: components of atoms Some of these components can have a positive or negative charge. Particles with the same charge repel each other; particles with unlike charges are attracted to one anoth ...
periodic table: quantum numbers
... about the student authors, visit http://www.ck12.org/about/about-us/team/ interns. ...
... about the student authors, visit http://www.ck12.org/about/about-us/team/ interns. ...
Test Review
... c.Most transition metals are hard _____ solids with high _____ melting points. d.Transition metal unpaired d-electrons have the ability to move into the s __ level. Because of this, many transition metals can form ...
... c.Most transition metals are hard _____ solids with high _____ melting points. d.Transition metal unpaired d-electrons have the ability to move into the s __ level. Because of this, many transition metals can form ...
ATOMIC NUMBER!!!
... outer energy levels: •Add electrons to a partially filled outer energy level •Lose all electrons in the outer energy level •Share electrons with another atom ...
... outer energy levels: •Add electrons to a partially filled outer energy level •Lose all electrons in the outer energy level •Share electrons with another atom ...
UNIT 3 –TEST REVIEW 1 Atoms of which of the
... Zinc IS IN SAME GROUP AS Cd F gold (Au) G zinc (Zn) H silver (Ag) J copper (Cu) ...
... Zinc IS IN SAME GROUP AS Cd F gold (Au) G zinc (Zn) H silver (Ag) J copper (Cu) ...
Periodic table
... table, with links labelled with numbers. Students are asked to supply sentences to match the links. Below are some suggested sentences that relate to each of the numbers on the diagram. They are not the only sentences that are valid. ...
... table, with links labelled with numbers. Students are asked to supply sentences to match the links. Below are some suggested sentences that relate to each of the numbers on the diagram. They are not the only sentences that are valid. ...
NAME: Unit 3 Test Review Arsenic (As), Selenium (Se), and
... 19. Below you need to draw Sodium, Oxygen, and Lithium. You must show the electron levels, draw the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons. You need to use “+” for protons, “-” for electrons, and “o” for neutrons. ...
... 19. Below you need to draw Sodium, Oxygen, and Lithium. You must show the electron levels, draw the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons. You need to use “+” for protons, “-” for electrons, and “o” for neutrons. ...
University Chemistry
... There is exception between O and N, because higher energy is required to remove an electron from the half-filled p orbital in nitrogen atom ...
... There is exception between O and N, because higher energy is required to remove an electron from the half-filled p orbital in nitrogen atom ...
The Chinese High School
... What is 12K/18K/24K gold? What is the difference between the different types of gold? All these questions can be answered with one key word – do you know what it is? ...
... What is 12K/18K/24K gold? What is the difference between the different types of gold? All these questions can be answered with one key word – do you know what it is? ...
Periodic Relationships Among the Elements
... which it is formed. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. ...
... which it is formed. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. ...
PERIODICITY
... • Anions are always larger than the atoms from which they form. – When an atom gains an electron, the attraction of the nucleus for any one electron decreases allowing the size to ...
... • Anions are always larger than the atoms from which they form. – When an atom gains an electron, the attraction of the nucleus for any one electron decreases allowing the size to ...
Noble gas

The noble gases make a group of chemical elements with similar properties. Under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six noble gases that occur naturally are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn).For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18 of the periodic table.It is possible that due to relativistic effects, the group 14 element flerovium exhibits some noble-gas-like properties, instead of the group 18 element ununoctium. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive except when under particular extreme conditions. The inertness of noble gases makes them very suitable in applications where reactions are not wanted. For example: argon is used in lightbulbs to prevent the hot tungsten filament from oxidizing; also, helium is breathed by deep-sea divers to prevent oxygen and nitrogen toxicity.The properties of the noble gases can be well explained by modern theories of atomic structure: their outer shell of valence electrons is considered to be ""full"", giving them little tendency to participate in chemical reactions, and it has been possible to prepare only a few hundred noble gas compounds. The melting and boiling points for a given noble gas are close together, differing by less than 10 °C (18 °F); that is, they are liquids over only a small temperature range.Neon, argon, krypton, and xenon are obtained from air in an air separation unit using the methods of liquefaction of gases and fractional distillation. Helium is sourced from natural gas fields which have high concentrations of helium in the natural gas, using cryogenic gas separation techniques, and radon is usually isolated from the radioactive decay of dissolved radium, thorium, or uranium compounds (since those compounds give off alpha particles). Noble gases have several important applications in industries such as lighting, welding, and space exploration. A helium-oxygen breathing gas is often used by deep-sea divers at depths of seawater over 55 m (180 ft) to keep the diver from experiencing oxygen toxemia, the lethal effect of high-pressure oxygen, and nitrogen narcosis, the distracting narcotic effect of the nitrogen in air beyond this partial-pressure threshold. After the risks caused by the flammability of hydrogen became apparent, it was replaced with helium in blimps and balloons.