* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.2 The Periodic table and Chemical Properties
Group 12 element wikipedia , lookup
Boron group wikipedia , lookup
Alkali metal wikipedia , lookup
Alkaline earth metal wikipedia , lookup
Dmitri Mendeleev wikipedia , lookup
Group 3 element wikipedia , lookup
Period 3 element wikipedia , lookup
Period 6 element wikipedia , lookup
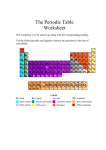
2.2 The Periodic Table and Chemical Properties History • Chemists began looking for a way to organize their observations of elements • In 1867, Dmitiri Mendeleev wrote down every element on a card • It included density, color, melting point, and boiling point • As Mendeleev did this he began to notice holes within the table and predict properties of other elements History • Born : 1834 Died : 1907 Nationality : Russian • Occupation : Chemist • Dmitri Mendeleev brought order to the chaos of chemistry by asserting his periodic law, which states that the elements arrange themselves according to their atomic number and their chemical properties The Periodic Table By the end of the lesson you should be able to • Know how the elements are listed in rows by increasing order of Atomic number • Rows are arranged in such a way that elements with similar properties line up in vertical columns • Each element in the table is recorded using its name, symbol, atomic number, atomic mass, and common ion charges The Periodic Table • Two families of metals are the alkali metals and the alkaline earth metals • Two families of non-metals are the halogens and the noble gases The Periodic Table • Is a chart that organizes the elements according to their physical and chemical properties. • The periodic table gives each element’s name, symbol, atomic number, atomic mass, and ion charges The Atomic Number • This is the number of protons in the nucleus of each atom of an element • It is always a whole number (they run in a pattern) Atomic Mass • This is the average mass of an atom of an element. • It is always written as a decimal number and is measured in atomic mass unit (amu) Ion Charge • This happens to an element when it gains or loses electrons • Any electrically charged atom is called an ion • The electrons make it more negative because they are negative Ion Charges • Some elements have multiple ion charges • These form in more than one way • Pattern: • Elements on the left hand side are usually positive ions • Elements on the right hand side, except for the last column, generally form negative ions • Elements that are in the same column often form ions with the same ion charge as other elements in that column How is it set up? • Elements are listed horizontally according to their atomic number (number of protons). • Periods are the horizontal rows of elements. How is it set up? • Elements are listed vertically according to their chemical properties. • Groups or Families are arranged vertically. • Non-Metals are found on the right side of the staircase • Metals are found on the left side of the staircase • Metalloids (have some properties of both metals and nonmetals) are on the staircase Metal, Non-Metals, and Metalloids Groups Alkali Alkaline Metals Earth Metals Noble Gases Halogens Alkali Metals • Highly reactive • Reactivity increases as you go down the group. • • • • React with both oxygen and water. Soft Low melting points Have a +1 ion charge Alkaline Earth Metals • • • • • Less reactive than alkali metals Burn in air if heated Produce bright flames and used in fireworks. Will react with water, but not as vigorously as alkali metals Have a +2 ion charge Halogens • • • • • • Non-metals Highly reactive F and Cl are gases at room temperature Br is a liquid and I is a solid F is the most reactive and I is the least Have a -1 ion charge Noble Gases • • • • • • Non-Metals Most stable and unreactive elements They are colourless, odourless gases Ar and Ne are used in light fixtures “Royal” Have a 0 ion charge (don’t make ions)