* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 3.08_Periodic Table and the Atom
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
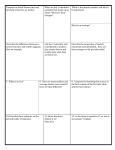
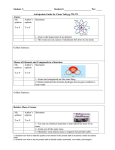
Periodic Table and the Atom Complete the table. Symbol Atomic # 23 Mass # # of Protons # of Electrons # of Neutrons Na K 40 19 38 38 F 10 20 41 50 131 26 52 18 50 72 I Mg 1. An element's or isotope's atomic number tells you _________________________________________. 2. An element's or isotope's mass number tells you ___________________________________________. 3. The heaviest part of an atom is the ________________, which contains both ________________and ________________. The ________________are found in a cloud surrounding the nucleus. 4. If an atom was a penny inside a football stadium, the penny would represent the ________________ and the football stadium would represent ________________________________________________. 5. Which has a higher atomic number? Helium or Hydrogen ____________________ Magnesium or Manganese ____________________ 6. Which has a lower atomic mass? Carbon or Calcium ____________________ Xenon or Radon ____________________ 7. Generally speaking, how does atomic mass change throughout the periodic table? ________________ Does it increases as you go across and down on the periodic table._____________ 8. Where are the most active metals located? ________________________________ 9. Where are the most active non-metals located? ________________________________ 10. As you go from left to right across a period, the atomic radius (increases/decreases). Why? _________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 11. As you travel down a group, the atomic radius (increases/decreases). Why? _____________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ 12. A negative ion is (larger/smaller) than its parent atom. 13. A positive ion is (larger/smaller) than its parent atom. 14. As you go from left to right across a period, the first ionization energy generally (increases/decreases). Why? ____________________________________________________________________________ 15. As you travel down a group, the first ionization energy generally (increases/decreases). Why? ______ __________________________________________________________________________________ 16. Where is the highest electronegative ion found? ________________ 17. Where is the lowest electronegative ion found? ________________ 18. Elements of Group 1 are called ________________________________________. . 19. Elements of Group 2 are called ___________________________________________. 20. Elements of Groups 3-12 are called ____________________________________________. . 21. As you go from left to right across the periodic table, the elements go from (metals/non-metals) to (metals/non-metals). 22. Elements of Groups 17 are called ________________________________. 23. The most active element in Group 17 is ________________________________. 24. Elements of Groups 18 are called ________________________________. 25. What sublevels are filling across the Transition Metals? ________________ 26. Elements within a group have a similar number of ________________________________. 27. Elements across a period have the same number of ________________________________. 28. A colored ion generally indicates a________________________________. 29. As you go down a group, the elements generally become (more/less) metallic. 30. The majority of elements in the periodic table are (metals/non-metals). 31. Elements in the periodic table are arranged according to their ________________________________. 32. An element with both metallic and non-metallic properties is called a _________________________. 33. Identify the following elements as metal, nonmetals, or metalloid. 1) Boron 2) Carbon 3) Gold 4) Lead 5) Hydrogen 34. Identify the following elements by which group they belong to on the periodic table. 1) Flourine 2) Argon 3) Calcium 4) Potassium 5) Carbon