periodicity
... • Ionization Energy - energy needed to remove 1 e- from a neutral atom • Increases from bottom to top in a group. • Increases from left to right across a period. ...
... • Ionization Energy - energy needed to remove 1 e- from a neutral atom • Increases from bottom to top in a group. • Increases from left to right across a period. ...
Chemistry Textbook Notes
... Elements in the same group tend to either gain or lose the same amount of electrons, giving it similar properties (except for Group 4) A covalent molecule is when an element shares electrons to obtain noble gas configuration Substances made from covalent molecules are called covalent molecular subst ...
... Elements in the same group tend to either gain or lose the same amount of electrons, giving it similar properties (except for Group 4) A covalent molecule is when an element shares electrons to obtain noble gas configuration Substances made from covalent molecules are called covalent molecular subst ...
Chapter 5 - Midway ISD
... Stanislao Cannizzaro (1860) proposed method for measuring atomic mass at First International Congress of Chemists Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) arranged elements by atomic mass & similar chemical properties; left blanks for undiscovered elements ...
... Stanislao Cannizzaro (1860) proposed method for measuring atomic mass at First International Congress of Chemists Dmitri Mendeleev (1869) arranged elements by atomic mass & similar chemical properties; left blanks for undiscovered elements ...
Periodic Table - MunterChemistry
... Ionization Energy (IE) Trends • IE generally increases across each period. – As the nuclear charge increases, the electrons are held more tightly ...
... Ionization Energy (IE) Trends • IE generally increases across each period. – As the nuclear charge increases, the electrons are held more tightly ...
Slide 1
... They have typical metal properties such as a very high luster and good conduction. They are so unreactive that they normally exist in nature as lone elements. Their normal state of matter is solid. ...
... They have typical metal properties such as a very high luster and good conduction. They are so unreactive that they normally exist in nature as lone elements. Their normal state of matter is solid. ...
Periodic Trends
... Increases moving down a group Decreases moving from left to right across a period ...
... Increases moving down a group Decreases moving from left to right across a period ...
The Periodic Law
... according to atomic mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same group Predicted the properties of elements that had not yet been discovered using his periodic table ...
... according to atomic mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same group Predicted the properties of elements that had not yet been discovered using his periodic table ...
1. Define: a. Period b. group or family
... 10. What are most elements: metals, non-metals or metalloids?_______________________________ 11. Complete the chart below: ...
... 10. What are most elements: metals, non-metals or metalloids?_______________________________ 11. Complete the chart below: ...
PT NOTES WEBSITE
... nucleus containing proton & neutron A. Shortly after that, (50 yrs after DM) Henry Moseley determined the atomic # of elements by using X rays ...
... nucleus containing proton & neutron A. Shortly after that, (50 yrs after DM) Henry Moseley determined the atomic # of elements by using X rays ...
Define the following: Electronegativity
... Electronegativity - The ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. Increases across periodic table, decreases going down Ionization energy – Energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom of an element. Increases across periodic tabl ...
... Electronegativity - The ability of an atom in a chemical compound to attract electrons from another atom in the compound. Increases across periodic table, decreases going down Ionization energy – Energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom of an element. Increases across periodic tabl ...
Name: Homeroom
... are called isotopes. An isotope can be identified by using a value called an atomic mass. Atomic mass is the sum of the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the nucleus. ...
... are called isotopes. An isotope can be identified by using a value called an atomic mass. Atomic mass is the sum of the number of neutrons and the number of protons in the nucleus. ...
Periodic trends - Cloudfront.net
... Ex: Which of the following elements has the highest 1st ionization energy? K, Rb, H, or Li? ...
... Ex: Which of the following elements has the highest 1st ionization energy? K, Rb, H, or Li? ...
Cations (positive ions) are smaller than their respective atoms.
... Is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gas phase. Each atom can have a series of ionization energies, since more than one electron can always be removed ...
... Is defined as the energy required to remove an electron from an atom in the gas phase. Each atom can have a series of ionization energies, since more than one electron can always be removed ...
PPT Periodic Families from Class
... What does it mean to be reactive? • We will be describing elements according to their reactivity. • Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. • Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. • What makes an element reactive? • An incomplete va ...
... What does it mean to be reactive? • We will be describing elements according to their reactivity. • Elements that are reactive bond easily with other elements to make compounds. • Some elements are only found in nature bonded with other elements. • What makes an element reactive? • An incomplete va ...
Ch 2 Test Review part 2
... 10. What is the group number for elements that have a stable number of electrons in their outer energy level? a. 17 b. 18 c. 2 d. 1 11. Why do the noble gases NOT form compounds readily? a. Their outer energy levels have 8 valence electrons. b. They have empty outer energy levels. c. T ...
... 10. What is the group number for elements that have a stable number of electrons in their outer energy level? a. 17 b. 18 c. 2 d. 1 11. Why do the noble gases NOT form compounds readily? a. Their outer energy levels have 8 valence electrons. b. They have empty outer energy levels. c. T ...
The Periodic Table Memorize which elements are gases and
... E. Some elements exist as two or more forms in the same phase called allotropes which have different properties; include O and C F. Chemistry of selected elements 1. Alkali metals – Group 1 elements; have silvery appearance; are soft; have low melting points; are too reactive to exist in nature as f ...
... E. Some elements exist as two or more forms in the same phase called allotropes which have different properties; include O and C F. Chemistry of selected elements 1. Alkali metals – Group 1 elements; have silvery appearance; are soft; have low melting points; are too reactive to exist in nature as f ...
Honors Chemistry- Chapter 5 Homework Packet The Periodic Law
... 4) (a) Which elements are designated at the alkali metals? (b) List four of their characteristic properties. ...
... 4) (a) Which elements are designated at the alkali metals? (b) List four of their characteristic properties. ...
AP Chemistry-Chapter 6 MC Questions
... ____ 22. A property that measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond is a. binding energy. b. mass defect. c. electron affinity. d. ionization energy. e. electronegativity. ____ 23. Which element has the highest electronegativity? a. N b. Si c. As d. P e. C ____ 24. Which ...
... ____ 22. A property that measures the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond is a. binding energy. b. mass defect. c. electron affinity. d. ionization energy. e. electronegativity. ____ 23. Which element has the highest electronegativity? a. N b. Si c. As d. P e. C ____ 24. Which ...
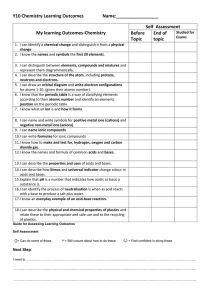
Y10 Chem SLOs 2016 File
... 4. I can describe the structure of the atom, including protons, neutrons and electrons. 5. I can draw an orbital diagram and write electron configurations for atoms 1-20. (given their atomic number). 6. I know that the periodic table is a way of classifying elements according to their atomic number ...
... 4. I can describe the structure of the atom, including protons, neutrons and electrons. 5. I can draw an orbital diagram and write electron configurations for atoms 1-20. (given their atomic number). 6. I know that the periodic table is a way of classifying elements according to their atomic number ...
Chapter 5 and 6 Notes 2015-2016 Models, Waves and Light Models
... • Sodium atom 1s22s22p63s1 • Sodium ion 1s22s22p6 (Sodium atom lost 1 electron) • Neon 1s22s22p6 • Sodium ion has the same electron configuration as neon • Octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of ___________________ valence electrons (to be like a noble g ...
... • Sodium atom 1s22s22p63s1 • Sodium ion 1s22s22p6 (Sodium atom lost 1 electron) • Neon 1s22s22p6 • Sodium ion has the same electron configuration as neon • Octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of ___________________ valence electrons (to be like a noble g ...
In the periodic table, the elements are placed from left to right in
... A group, or family, is a vertical column in the periodic table. Elements in the same group show patterns in atomic radius,ionization energy, and electronegativity. From top to bottom in a group, the atomic radii of the elements increase: since there are more filled energy levels, valence electrons a ...
... A group, or family, is a vertical column in the periodic table. Elements in the same group show patterns in atomic radius,ionization energy, and electronegativity. From top to bottom in a group, the atomic radii of the elements increase: since there are more filled energy levels, valence electrons a ...
U1 Periodic Trends - Alliance Ouchi-O`Donovan 6
... 12. Are elements with similar chemical properties more likely to be found in the same period or in the same group? A: The same group because the number of valence electrons determine the chemical properties. ...
... 12. Are elements with similar chemical properties more likely to be found in the same period or in the same group? A: The same group because the number of valence electrons determine the chemical properties. ...
ExamView - chemistry chapter 6 test.tst
... ____ 13. At room temperature, none of the metals are a. malleable. c. gases. b. soft. d. liquids. ____ 14. Mendeleev arranged the known chemical elements in a table according to increasing a. mass. c. atomic number. b. number of electrons. d. number of protons. ____ 15. What is the element with the ...
... ____ 13. At room temperature, none of the metals are a. malleable. c. gases. b. soft. d. liquids. ____ 14. Mendeleev arranged the known chemical elements in a table according to increasing a. mass. c. atomic number. b. number of electrons. d. number of protons. ____ 15. What is the element with the ...
Unit 3 Test Review – Periodic Table (Yes, this is worth a grade!) Fill
... A) Periodic trends in ionization energies are opposite those for atomic size. B) Periodic trends in ionization energies are opposite those for electronegativity. C) Periodic trends in ionization energies are opposite those for electron affinity. D) none of the above 9. The elements in the modern per ...
... A) Periodic trends in ionization energies are opposite those for atomic size. B) Periodic trends in ionization energies are opposite those for electronegativity. C) Periodic trends in ionization energies are opposite those for electron affinity. D) none of the above 9. The elements in the modern per ...
Noble gas

The noble gases make a group of chemical elements with similar properties. Under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six noble gases that occur naturally are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn).For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18 of the periodic table.It is possible that due to relativistic effects, the group 14 element flerovium exhibits some noble-gas-like properties, instead of the group 18 element ununoctium. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive except when under particular extreme conditions. The inertness of noble gases makes them very suitable in applications where reactions are not wanted. For example: argon is used in lightbulbs to prevent the hot tungsten filament from oxidizing; also, helium is breathed by deep-sea divers to prevent oxygen and nitrogen toxicity.The properties of the noble gases can be well explained by modern theories of atomic structure: their outer shell of valence electrons is considered to be ""full"", giving them little tendency to participate in chemical reactions, and it has been possible to prepare only a few hundred noble gas compounds. The melting and boiling points for a given noble gas are close together, differing by less than 10 °C (18 °F); that is, they are liquids over only a small temperature range.Neon, argon, krypton, and xenon are obtained from air in an air separation unit using the methods of liquefaction of gases and fractional distillation. Helium is sourced from natural gas fields which have high concentrations of helium in the natural gas, using cryogenic gas separation techniques, and radon is usually isolated from the radioactive decay of dissolved radium, thorium, or uranium compounds (since those compounds give off alpha particles). Noble gases have several important applications in industries such as lighting, welding, and space exploration. A helium-oxygen breathing gas is often used by deep-sea divers at depths of seawater over 55 m (180 ft) to keep the diver from experiencing oxygen toxemia, the lethal effect of high-pressure oxygen, and nitrogen narcosis, the distracting narcotic effect of the nitrogen in air beyond this partial-pressure threshold. After the risks caused by the flammability of hydrogen became apparent, it was replaced with helium in blimps and balloons.