The Periodic Table
... Periodic Properties 1. Atomic Radius: defined as one-half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms chemically bonded together. Trends: ...
... Periodic Properties 1. Atomic Radius: defined as one-half the distance between the nuclei of two identical atoms chemically bonded together. Trends: ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... 1. The noble gases were once called inert gases because they were thought to be unreactive. 2. No stable compounds of helium, neon and argon have ever been formed. 3. The other noble gases – xenon, krypton, and radon – have very low reactivity. They have been forced to form compounds. 4. Noble gases ...
... 1. The noble gases were once called inert gases because they were thought to be unreactive. 2. No stable compounds of helium, neon and argon have ever been formed. 3. The other noble gases – xenon, krypton, and radon – have very low reactivity. They have been forced to form compounds. 4. Noble gases ...
Coloring the Periodic Table
... Atomic Mass: The average mass of the atoms of an element. Group: the elements in a column of the periodic table Period: a horizontal row in the periodic table ...
... Atomic Mass: The average mass of the atoms of an element. Group: the elements in a column of the periodic table Period: a horizontal row in the periodic table ...
Chapter 6 review
... Unit 6 Review – Periodic Table and Trends 1. Fill in the blanks with increases or decreases. 1. As you move across a period, atomic radius ________________________________ 2. As you move down a group, atomic radius _______________________________ 3. As you move across a period from group 1 to 14 rea ...
... Unit 6 Review – Periodic Table and Trends 1. Fill in the blanks with increases or decreases. 1. As you move across a period, atomic radius ________________________________ 2. As you move down a group, atomic radius _______________________________ 3. As you move across a period from group 1 to 14 rea ...
File
... by the first element in the column. E.g. Group 10 is the nickel group because nickel is the first element at the top of that column. ...
... by the first element in the column. E.g. Group 10 is the nickel group because nickel is the first element at the top of that column. ...
Physical Science Chapters 4
... Physical Science Chapters 4-5 Study Guide 1. Know all vocabulary from chapters 4-5. ...
... Physical Science Chapters 4-5 Study Guide 1. Know all vocabulary from chapters 4-5. ...
THE PERIODIC TABLE TODAY
... by the first element in the column. ¢ E.g. Group 10 is the nickel group because nickel is the first element at the top of that column. ...
... by the first element in the column. ¢ E.g. Group 10 is the nickel group because nickel is the first element at the top of that column. ...
Periodic Table
... Form ionic compounds to forming covalent compounds Melting Points from relatively high to relatively low Form positive ions to form negative ions ...
... Form ionic compounds to forming covalent compounds Melting Points from relatively high to relatively low Form positive ions to form negative ions ...
Periodic Table Notes 2
... The atomic number increases, electrons increase, but fill the same orbit. The increase in number of protons, causes an increase in nuclear charge, pulling the valence electrons. This higher nuclear charge, causes a higher I.E. (more energy needed to remove electrons). Second I.E.- energy to remove s ...
... The atomic number increases, electrons increase, but fill the same orbit. The increase in number of protons, causes an increase in nuclear charge, pulling the valence electrons. This higher nuclear charge, causes a higher I.E. (more energy needed to remove electrons). Second I.E.- energy to remove s ...
Chapter 2 Atoms, Molecules, and Ions Section 2.1 The Atomic Theory
... Name common ionic compounds, molecular compounds, binary acids, oxoacids, bases, and hydrates given their respective chemical formulas. Predict the chemical formulas of common ionic compounds, molecular compounds, binary acids, oxoacids, bases, and hydrates given their respective names. ...
... Name common ionic compounds, molecular compounds, binary acids, oxoacids, bases, and hydrates given their respective chemical formulas. Predict the chemical formulas of common ionic compounds, molecular compounds, binary acids, oxoacids, bases, and hydrates given their respective names. ...
Structure of the Atom and Periodic Table Quiz 2016 Self
... When I compare the halogen group to the noble gases, one way they are different is that halogens are highly reactive and noble gases are not. A second property is that halogens have a missing an electron in their outer shell, but noble gases have out shells that full outer shells. 17. Which scientis ...
... When I compare the halogen group to the noble gases, one way they are different is that halogens are highly reactive and noble gases are not. A second property is that halogens have a missing an electron in their outer shell, but noble gases have out shells that full outer shells. 17. Which scientis ...
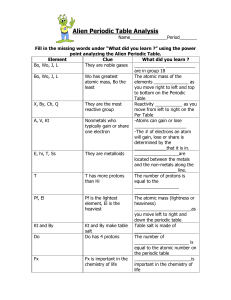
Alien Periodic Table Analysis
... They are the most Reactivity ___________ as you reactive group move from left to right on the Per Table A, V, Kt Nonmetals who -Atoms can gain or lose typically gain or share _____________________ one electron -The # of electrons an atom will gain, lose or share is determined by the _____________tha ...
... They are the most Reactivity ___________ as you reactive group move from left to right on the Per Table A, V, Kt Nonmetals who -Atoms can gain or lose typically gain or share _____________________ one electron -The # of electrons an atom will gain, lose or share is determined by the _____________tha ...
Document
... Know the definition of an isotope and be able to recognize if an element is an isotope or a different element. Recognize the definition for periodic law. Know how to read the symbol box on the periodic table (see the key) in our textbook. Recognize the most important properties of specific groups of ...
... Know the definition of an isotope and be able to recognize if an element is an isotope or a different element. Recognize the definition for periodic law. Know how to read the symbol box on the periodic table (see the key) in our textbook. Recognize the most important properties of specific groups of ...
periodic-data-and-trends-assign-2016
... The Periodic Table is arranged according to Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. These patterns can be discovered by examining the changes in properties of element ...
... The Periodic Table is arranged according to Periodic Law. The Periodic Law states that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, their physical and chemical properties show a periodic pattern. These patterns can be discovered by examining the changes in properties of element ...
The Periodic Table
... • Columns are also grouped into families. • Families may be one column, or several columns put together. • Families have names rather than numbers. (Just like your family has a common last name.) ...
... • Columns are also grouped into families. • Families may be one column, or several columns put together. • Families have names rather than numbers. (Just like your family has a common last name.) ...
Finals Review ans 2012sem 1
... Metallic bonding is similar to ionic bonding because there is an attraction between positively charged and negatively charged particles. ____ ...
... Metallic bonding is similar to ionic bonding because there is an attraction between positively charged and negatively charged particles. ____ ...
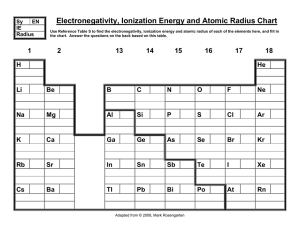
Electronegativity, Ionization Energy and Atomic Radius Chart
... - They are only found bonded to other elements in compounds in their natural state. - They can be separated from those compounds using electricity (electrolytic decomposition). - They combine with hydrogen, to form strong acids (like hydrochloric acid, HCl). Fluorine and chlorine are extremely corro ...
... - They are only found bonded to other elements in compounds in their natural state. - They can be separated from those compounds using electricity (electrolytic decomposition). - They combine with hydrogen, to form strong acids (like hydrochloric acid, HCl). Fluorine and chlorine are extremely corro ...
Objective - davis.k12.ut.us
... element. The bonding power of an element refers to the number of chemical bonds an element can form. This was determined by how each element formed bonds with oxygen. Mendeleev noticed that patterns appeared when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. As he put his cards in o ...
... element. The bonding power of an element refers to the number of chemical bonds an element can form. This was determined by how each element formed bonds with oxygen. Mendeleev noticed that patterns appeared when the elements were arranged in order of increasing atomic mass. As he put his cards in o ...
Noble gas

The noble gases make a group of chemical elements with similar properties. Under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six noble gases that occur naturally are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn).For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18 of the periodic table.It is possible that due to relativistic effects, the group 14 element flerovium exhibits some noble-gas-like properties, instead of the group 18 element ununoctium. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive except when under particular extreme conditions. The inertness of noble gases makes them very suitable in applications where reactions are not wanted. For example: argon is used in lightbulbs to prevent the hot tungsten filament from oxidizing; also, helium is breathed by deep-sea divers to prevent oxygen and nitrogen toxicity.The properties of the noble gases can be well explained by modern theories of atomic structure: their outer shell of valence electrons is considered to be ""full"", giving them little tendency to participate in chemical reactions, and it has been possible to prepare only a few hundred noble gas compounds. The melting and boiling points for a given noble gas are close together, differing by less than 10 °C (18 °F); that is, they are liquids over only a small temperature range.Neon, argon, krypton, and xenon are obtained from air in an air separation unit using the methods of liquefaction of gases and fractional distillation. Helium is sourced from natural gas fields which have high concentrations of helium in the natural gas, using cryogenic gas separation techniques, and radon is usually isolated from the radioactive decay of dissolved radium, thorium, or uranium compounds (since those compounds give off alpha particles). Noble gases have several important applications in industries such as lighting, welding, and space exploration. A helium-oxygen breathing gas is often used by deep-sea divers at depths of seawater over 55 m (180 ft) to keep the diver from experiencing oxygen toxemia, the lethal effect of high-pressure oxygen, and nitrogen narcosis, the distracting narcotic effect of the nitrogen in air beyond this partial-pressure threshold. After the risks caused by the flammability of hydrogen became apparent, it was replaced with helium in blimps and balloons.