Chapter 4-1 & 4-2: The Periodic Table
... radioactive. Generally less reactive than alkali and alkaline earth metals ...
... radioactive. Generally less reactive than alkali and alkaline earth metals ...
2.2 Periodic Chart
... The alkali metal elements are silvery, have a low density (float on water), react very strongly with water to form hydrogen gas and very strong bases (alkalis). ...
... The alkali metal elements are silvery, have a low density (float on water), react very strongly with water to form hydrogen gas and very strong bases (alkalis). ...
Metals and Non
... Metals generally are malleable, and ductile solids with a lustrous appearance and an ability to conduct heat and electricity. Found to the left of the “diagonal line” on the Periodic Table Nonmetals: elements whose atoms tend to gain small numbers of electrons to form negative ions (anions) with the ...
... Metals generally are malleable, and ductile solids with a lustrous appearance and an ability to conduct heat and electricity. Found to the left of the “diagonal line” on the Periodic Table Nonmetals: elements whose atoms tend to gain small numbers of electrons to form negative ions (anions) with the ...
Name Periodic Table Assignment Directions: Using your text (pgs
... Define Atomic Radius. What is its trend as you go across a period? What is its trend as you go down a group? When metals become ions, what happens to the size of their radius? Why? When nonmetals become ions, what happens to the size of their radius? Why? Define electronegativity. What is its trend ...
... Define Atomic Radius. What is its trend as you go across a period? What is its trend as you go down a group? When metals become ions, what happens to the size of their radius? Why? When nonmetals become ions, what happens to the size of their radius? Why? Define electronegativity. What is its trend ...
Name________________________ Period____ Date
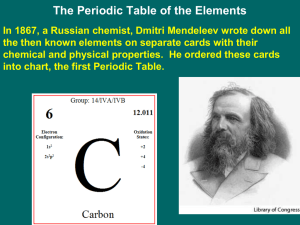
... C is the element symbol. Carbon is the element name. 6 is the atomic number (number of protons). 12.011 is the atomic mass (protons + neutrons) 9. Which group/family is highly reactive? Group 1 10. Which group/family doesn’t bond with other elements? Noble Gases (18) ...
... C is the element symbol. Carbon is the element name. 6 is the atomic number (number of protons). 12.011 is the atomic mass (protons + neutrons) 9. Which group/family is highly reactive? Group 1 10. Which group/family doesn’t bond with other elements? Noble Gases (18) ...
Name Chemistry Midterm Review Chapter # 2
... 6. What are the 4 types of sub orbitals? How many “rooms” does each have? How many electrons can each of the 4 suborbitals hold? (make a chart) ...
... 6. What are the 4 types of sub orbitals? How many “rooms” does each have? How many electrons can each of the 4 suborbitals hold? (make a chart) ...
Ch.6 Periodic Trends - MrsSavallisChemistry
... d. poor conductor of electric current e. shinny 5. In general, how are metalloids different from metals and nonmetals? 6. Elements in the same period have the same…? 7. Elements in the same group have similar…? 8. Based on their locations in the periodic table, would you expect carbon and silicon to ...
... d. poor conductor of electric current e. shinny 5. In general, how are metalloids different from metals and nonmetals? 6. Elements in the same period have the same…? 7. Elements in the same group have similar…? 8. Based on their locations in the periodic table, would you expect carbon and silicon to ...
Science Review Sheet: Periodic Table Test Name: ______ Study
... List the different properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids. Know how to find them on the periodic table. Also know that metals are to the left of the zigzag line, metalloids touch the zigzag line on both sides (exception Al), and that nonmetals are to the right of the zigzag line. Metals Non ...
... List the different properties of Metals, Nonmetals, and Metalloids. Know how to find them on the periodic table. Also know that metals are to the left of the zigzag line, metalloids touch the zigzag line on both sides (exception Al), and that nonmetals are to the right of the zigzag line. Metals Non ...
Chapter 13
... increasing atomic mass The columns were arranged so that elements with the most similar properties were side by side Dmitri ...
... increasing atomic mass The columns were arranged so that elements with the most similar properties were side by side Dmitri ...
Periodic Table and Elements Review
... 2.) Potassium, K, has a mass of 39.096 and Argon, Ar, has a mass of 39.944, which would indicate that that K would become before Ar. However, Mendeleev switched these around. Why did he do this? ...
... 2.) Potassium, K, has a mass of 39.096 and Argon, Ar, has a mass of 39.944, which would indicate that that K would become before Ar. However, Mendeleev switched these around. Why did he do this? ...
History of Chemistry PPT
... • Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms • All atoms of the same element are identical (later to be revised) • The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element • Elements combine to form compounds • Mass is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but ...
... • Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms • All atoms of the same element are identical (later to be revised) • The atoms of a given element are different from those of any other element • Elements combine to form compounds • Mass is neither created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, but ...
Chapter Test A
... ______16. Which of the following elements have full outer energy levels when they are in the ground state? a. alkali metals b. noble gases c. halogens d. transition metals ______ 17. In which period is an element that has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p1 when it is in its ground ...
... ______16. Which of the following elements have full outer energy levels when they are in the ground state? a. alkali metals b. noble gases c. halogens d. transition metals ______ 17. In which period is an element that has the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p1 when it is in its ground ...
Chapter 4 Notes - Riverton High School
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
Unit 2 Periodic Table
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
... Noble Gases are colorless gases that are extremely unreactive. One important property of the noble gases is their inactivity. They are inactive because their outermost energy level is full. Because they do not readily combine with other elements to form compounds, the noble gases are called inert. T ...
Periodic Relationships Among the Elements
... which it is formed. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. ...
... which it is formed. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. ...
The Periodic Table
... Hydrogen reacts violently with oxygen. The hot water vapor that forms as a result pushed the space shuttle into orbit. Placed above the group 1 elements because it has only 1 electron in it’s valance shell and can give one away Properties are more like atoms of alkali metals Hydrogen was involved in ...
... Hydrogen reacts violently with oxygen. The hot water vapor that forms as a result pushed the space shuttle into orbit. Placed above the group 1 elements because it has only 1 electron in it’s valance shell and can give one away Properties are more like atoms of alkali metals Hydrogen was involved in ...
Chapter 5
... • Left blank spots in table which predicted _________ of elements not yet discovered ...
... • Left blank spots in table which predicted _________ of elements not yet discovered ...
Ch. 7 Multiple Choice
... 42) In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first ionization energy __________. A) increases, increasingly, increases B) decreases, increasingly, decreases C) ...
... 42) In general, as you go across a period in the periodic table from left to right: (1) the atomic radius __________; (2) the electron affinity becomes __________ negative; and (3) the first ionization energy __________. A) increases, increasingly, increases B) decreases, increasingly, decreases C) ...
Name
... A compound is a substance made of atoms of two or more ________________ that are chemically combined. The chemical formula for a compound shows the _________________ that are in the compound. The chemical formula also compares the number of __________________ of the different elements within the com ...
... A compound is a substance made of atoms of two or more ________________ that are chemically combined. The chemical formula for a compound shows the _________________ that are in the compound. The chemical formula also compares the number of __________________ of the different elements within the com ...
PERIODIC TABLE - WordPress.com
... 3. What is atomic number? 4. What are the atomic numbers and relative atomic masses of Sodium and Chlorine? 5. What are d-block elements commonly known as? 6. Name three metalloids (semi-metals) from the Periodic Table. 7. Which block (s, p, d, f) does iron belong to in the Periodic Table? 8. Which ...
... 3. What is atomic number? 4. What are the atomic numbers and relative atomic masses of Sodium and Chlorine? 5. What are d-block elements commonly known as? 6. Name three metalloids (semi-metals) from the Periodic Table. 7. Which block (s, p, d, f) does iron belong to in the Periodic Table? 8. Which ...
Lab 18
... conduct heat and electricity, Malleable and ductile (flexible) as solids. Also, generally the melting points of non-metals are generally lower than metals. And finally compounds of metals with non-metals tend to be ionic in nature as opposed to non-metal’s being nonmetal oxides are acidic oxide. 4. ...
... conduct heat and electricity, Malleable and ductile (flexible) as solids. Also, generally the melting points of non-metals are generally lower than metals. And finally compounds of metals with non-metals tend to be ionic in nature as opposed to non-metal’s being nonmetal oxides are acidic oxide. 4. ...
4.1 Vocabulary
... An atom of iron contains 26 protons, so the atomic number of iron is 26. Atomic number is used in identifying atoms. element a pure substance made of only one type of atom Copper, helium, calcium, and neon are all types of elements. Each element is made up of one kind of atom. A copper atom is diffe ...
... An atom of iron contains 26 protons, so the atomic number of iron is 26. Atomic number is used in identifying atoms. element a pure substance made of only one type of atom Copper, helium, calcium, and neon are all types of elements. Each element is made up of one kind of atom. A copper atom is diffe ...
Noble gas

The noble gases make a group of chemical elements with similar properties. Under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low chemical reactivity. The six noble gases that occur naturally are helium (He), neon (Ne), argon (Ar), krypton (Kr), xenon (Xe), and the radioactive radon (Rn).For the first six periods of the periodic table, the noble gases are exactly the members of group 18 of the periodic table.It is possible that due to relativistic effects, the group 14 element flerovium exhibits some noble-gas-like properties, instead of the group 18 element ununoctium. Noble gases are typically highly unreactive except when under particular extreme conditions. The inertness of noble gases makes them very suitable in applications where reactions are not wanted. For example: argon is used in lightbulbs to prevent the hot tungsten filament from oxidizing; also, helium is breathed by deep-sea divers to prevent oxygen and nitrogen toxicity.The properties of the noble gases can be well explained by modern theories of atomic structure: their outer shell of valence electrons is considered to be ""full"", giving them little tendency to participate in chemical reactions, and it has been possible to prepare only a few hundred noble gas compounds. The melting and boiling points for a given noble gas are close together, differing by less than 10 °C (18 °F); that is, they are liquids over only a small temperature range.Neon, argon, krypton, and xenon are obtained from air in an air separation unit using the methods of liquefaction of gases and fractional distillation. Helium is sourced from natural gas fields which have high concentrations of helium in the natural gas, using cryogenic gas separation techniques, and radon is usually isolated from the radioactive decay of dissolved radium, thorium, or uranium compounds (since those compounds give off alpha particles). Noble gases have several important applications in industries such as lighting, welding, and space exploration. A helium-oxygen breathing gas is often used by deep-sea divers at depths of seawater over 55 m (180 ft) to keep the diver from experiencing oxygen toxemia, the lethal effect of high-pressure oxygen, and nitrogen narcosis, the distracting narcotic effect of the nitrogen in air beyond this partial-pressure threshold. After the risks caused by the flammability of hydrogen became apparent, it was replaced with helium in blimps and balloons.