a sentence which gives information. ( declarative )
... Complement: is a word/phrase/clause that completes the meaning of another word/phrase/clause. It is necessary for the meaning to be complete. Appositive: a noun phrase that describes the same person or thing as another noun phrase that came before it. Adjunct: is a word/phrase/clause that provides a ...
... Complement: is a word/phrase/clause that completes the meaning of another word/phrase/clause. It is necessary for the meaning to be complete. Appositive: a noun phrase that describes the same person or thing as another noun phrase that came before it. Adjunct: is a word/phrase/clause that provides a ...
Grammar: the rules that say how words are combined, arranged and
... Adjunct: is a word/phrase/clause that provides additional information about another noun/phrase/clause Adverbial: is a group of words that does the same job as an adverb. Adjectives: are words which we use to describe people, things, events… etc. Adjective phrases: are composed of an adjective which ...
... Adjunct: is a word/phrase/clause that provides additional information about another noun/phrase/clause Adverbial: is a group of words that does the same job as an adverb. Adjectives: are words which we use to describe people, things, events… etc. Adjective phrases: are composed of an adjective which ...
1A Parts of Speech
... [Answers the question, “How?” “When?” “Where?” “To what degree?” etc.] Modifying a verb: “He ate quickly.” “She slept soundly.” Modifying an adjective: “They were very smart.” Modifying another adverb: “He ate very quickly.” Examples of other adverbs: here, there, yesterday, often, only, undoubtedly ...
... [Answers the question, “How?” “When?” “Where?” “To what degree?” etc.] Modifying a verb: “He ate quickly.” “She slept soundly.” Modifying an adjective: “They were very smart.” Modifying another adverb: “He ate very quickly.” Examples of other adverbs: here, there, yesterday, often, only, undoubtedly ...
Phrases: 1.) Prepositional Phrases 2.) Appositives 3.) Gerund 4
... above the ocean's floor across the entire gymnasium after the game against her will along the long, winding, green, lush path amid the exhausting school year around the time ...
... above the ocean's floor across the entire gymnasium after the game against her will along the long, winding, green, lush path amid the exhausting school year around the time ...
The Phrase
... • a talented magician… • A talented magician, Mr.Betts often entertains his math students with his magic tricks. ...
... • a talented magician… • A talented magician, Mr.Betts often entertains his math students with his magic tricks. ...
English 430 - My Heritage
... elements into meaningful discourse: putting words together in a way that makes sense to other speakers of the same language. In English, the relationships among words and other elements, such as phrases and clauses, are the primary method for conveying meaning. Therefore, understanding these relatio ...
... elements into meaningful discourse: putting words together in a way that makes sense to other speakers of the same language. In English, the relationships among words and other elements, such as phrases and clauses, are the primary method for conveying meaning. Therefore, understanding these relatio ...
Spelling and Grammar Test Unit # 9
... 7. again 8. says Review Concept Words 9. cleaning 10. freeway ...
... 7. again 8. says Review Concept Words 9. cleaning 10. freeway ...
key vocabulary - Nutfield Church Primary School
... Pronouns- stand in for a noun (e.g. I, you, he, she, we, they, my, your, his, her, our, their) ...
... Pronouns- stand in for a noun (e.g. I, you, he, she, we, they, my, your, his, her, our, their) ...
Prepositions - MultiMediaPortfolio
... Common Prepositions • Aboard, about, above, across, after, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, into, like, of, off, on, over, past, since, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneath, until, up, ...
... Common Prepositions • Aboard, about, above, across, after, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, down, during, except, for, from, in, into, like, of, off, on, over, past, since, through, throughout, to, toward, under, underneath, until, up, ...
Glossary of Grammatical Terms
... Glossary of Grammatical Terms There are hundreds of words about words but, thankfully, most of them we don't all need to know. But a few are very helpful and well worth learning. Here is a list of essential grammatical terms. ...
... Glossary of Grammatical Terms There are hundreds of words about words but, thankfully, most of them we don't all need to know. But a few are very helpful and well worth learning. Here is a list of essential grammatical terms. ...
Noun Clause Practice
... place where she could eat ice cream everyday. The fact was (6)that she wanted to go to any store without white people`s eyes. In addition, she thought (7)that singing could take pain away. (8)What she wanted to do was to sing every time (9)that she faced problems. In the end, she wished (10)that she ...
... place where she could eat ice cream everyday. The fact was (6)that she wanted to go to any store without white people`s eyes. In addition, she thought (7)that singing could take pain away. (8)What she wanted to do was to sing every time (9)that she faced problems. In the end, she wished (10)that she ...
Name: Date: 6B- _____ Grammar: Nouns 1 Steps to Identify Case
... 4. Objective: Receives action. Take subject + verb, and then ask who / what. The answer is an objective noun. There may be more than one objective noun in a sentence, but sentences don’t have to have objective nouns. Ex: The batter hit the ball. (Question: The batter hit who or what? Answer: the bal ...
... 4. Objective: Receives action. Take subject + verb, and then ask who / what. The answer is an objective noun. There may be more than one objective noun in a sentence, but sentences don’t have to have objective nouns. Ex: The batter hit the ball. (Question: The batter hit who or what? Answer: the bal ...
What are nouns - WordPress.com
... Noun phrase which is broken discontinuous Example: Several Accidents have been reported involving passengers falling from trains. Several accidents involving passengers failing from trains have been reported. ...
... Noun phrase which is broken discontinuous Example: Several Accidents have been reported involving passengers falling from trains. Several accidents involving passengers failing from trains have been reported. ...
conjunctions - World of Teaching
... exceptions, is expressed with a certain definiteness (e.g., definite or indefinite), just as many languages express every noun with a certain grammatical number (e.g., singular or plural). Every noun must be accompanied by the article, if any, corresponding to its definiteness, and the lack of an ar ...
... exceptions, is expressed with a certain definiteness (e.g., definite or indefinite), just as many languages express every noun with a certain grammatical number (e.g., singular or plural). Every noun must be accompanied by the article, if any, corresponding to its definiteness, and the lack of an ar ...
Parts of Speech
... very, now, then, there, up, down, certainly, however, etc.) *Adverbs usually answer the questions: how? When? Where? To what extent? And many adverbs are formed by adding –ly to an adjective (e.g. Quickly) ...
... very, now, then, there, up, down, certainly, however, etc.) *Adverbs usually answer the questions: how? When? Where? To what extent? And many adverbs are formed by adding –ly to an adjective (e.g. Quickly) ...
Basic ideas of syntax
... Syntax deals with sentences—specifically, the phrases that combine to make up a sentence. When a sentence is ungrammatical, we use a * to indicate its syntax is “off”. Syntax is not about meaning. (See Noam Chomsky’s famous example “Colorless green ideas sleep furiously.”) Although we do use meaning ...
... Syntax deals with sentences—specifically, the phrases that combine to make up a sentence. When a sentence is ungrammatical, we use a * to indicate its syntax is “off”. Syntax is not about meaning. (See Noam Chomsky’s famous example “Colorless green ideas sleep furiously.”) Although we do use meaning ...
Grammar—Parts of Speech
... Adjective—adjectives describe, or modify, the noun. Usually, we place adjectives right before the noun they describe. Many people consider articles (a, an, the) to be a type of adjective. However, because they don’t actually modify anything, articles are really part of a category of words known as n ...
... Adjective—adjectives describe, or modify, the noun. Usually, we place adjectives right before the noun they describe. Many people consider articles (a, an, the) to be a type of adjective. However, because they don’t actually modify anything, articles are really part of a category of words known as n ...
Parts of Speech - Dayton Independent Schools
... write, or exhibit. The state of being verbs are words such as am, is, are, was, were, being, and been. Adverbs are used to describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They answer the questions: when, where, why, how, and to what extent or degree. Some examples of adverbs are absolutely, briefly, e ...
... write, or exhibit. The state of being verbs are words such as am, is, are, was, were, being, and been. Adverbs are used to describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They answer the questions: when, where, why, how, and to what extent or degree. Some examples of adverbs are absolutely, briefly, e ...
nouns, pronouns, and adjectives
... 2. When used after a linking verb or the verb to be, it is a predicate noun (or the predicate nominative) Ex: Mike will become chairperson of the committee. I am the boss. 3. As an appositive. An appositive is a word or phrase that identifies, explains, or gives information about the sentence. It is ...
... 2. When used after a linking verb or the verb to be, it is a predicate noun (or the predicate nominative) Ex: Mike will become chairperson of the committee. I am the boss. 3. As an appositive. An appositive is a word or phrase that identifies, explains, or gives information about the sentence. It is ...
Intro to Linguistics Syntax 2: A more perfect Tree
... For sentences without auxiliaries, we’ll think of Aux as still containing information about tense, which then somehow glums onto the verb in the shape of inflectional morphology: 8) a. John [past] run => John ran b. John [present] run => John runs ...
... For sentences without auxiliaries, we’ll think of Aux as still containing information about tense, which then somehow glums onto the verb in the shape of inflectional morphology: 8) a. John [past] run => John ran b. John [present] run => John runs ...
At which/what hotel will I be staying during the conference?
... I love to dance all night long. ...
... I love to dance all night long. ...
Grammar Pointers: Use of It in Subject Position Placement of
... • Fue una experiencia maravillosa. • It was a wonderful experience. ...
... • Fue una experiencia maravillosa. • It was a wonderful experience. ...
Pinker_ch7
... the mental “click” that signals that we have just heard a complete grammatical sentence.” ...
... the mental “click” that signals that we have just heard a complete grammatical sentence.” ...
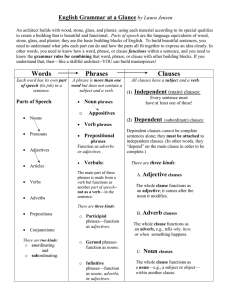
Words Phrases Clauses2
... English Grammar at a Glance by Laura Jensen An architect builds with wood, stone, glass, and plaster, using each material according to its special qualities to create a building that is beautiful and functional. Parts of speech are the language equivalents of wood, stone, glass, and plaster; they ar ...
... English Grammar at a Glance by Laura Jensen An architect builds with wood, stone, glass, and plaster, using each material according to its special qualities to create a building that is beautiful and functional. Parts of speech are the language equivalents of wood, stone, glass, and plaster; they ar ...
noun cluster - Blog Stikom
... notions, and groups of each. In a sentence, nouns execute and suffer the actions/states expressed by the verbs, and they may... Nouns are principal sentence elements. ...
... notions, and groups of each. In a sentence, nouns execute and suffer the actions/states expressed by the verbs, and they may... Nouns are principal sentence elements. ...
Determiner phrase

In linguistics, a determiner phrase (DP) is a type of phrase posited by some theories of syntax. The head of a DP is a determiner, as opposed to a noun. For example in the phrase the car, the is a determiner and car is a noun; the two combine to form a phrase, and on the DP-analysis, the determiner the is head over the noun car. The existence of DPs is a controversial issue in the study of syntax. The traditional analysis of phrases such as the car is that the noun is the head, which means the phrase is a noun phrase (NP), not a determiner phrase. Beginning in the mid 1980s, an alternative analysis arose that posits the determiner as the head, which makes the phrase a DP instead of an NP.The DP-analysis of phrases such as the car is the majority view in generative grammar today (Government and Binding and Minimalist Program), but is a minority stance in the study of syntax and grammar in general. Most frameworks outside of generative grammar continue to assume the traditional NP analysis of noun phrases. For instance, representational phrase structure grammars assume NP, e.g. Head-Driven Phrase Structure Grammar, and most dependency grammars such as Meaning-Text Theory, Functional Generative Description, Lexicase Grammar also assume the traditional NP-analysis of noun phrases, Word Grammar being the one exception. Construction Grammar and Role and Reference Grammar also assume NP instead of DP. Furthermore, the DP-analysis does not reach into the teaching of grammar in schools in the English-speaking world, and certainly not in the non-English-speaking world. Since the existence of DPs is a controversial issue that splits the syntax community into two camps (DP vs. NP), this article strives to accommodate both views. Some arguments supporting/refuting both analyses are considered.