1.5 physics beyond the Standard Model
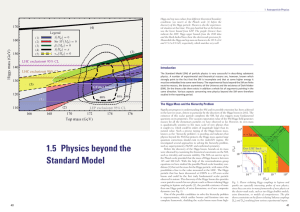
... known as the “hierarchy problem”, is puzzling and indicates that physics beyond the SM that protects the Higgs mass against large quantum corrections should exist in the multi-TeV regime. We investigated several approaches to solving the hierarchy problem, such as supersymmetry (SUSY) and conformal ...
... known as the “hierarchy problem”, is puzzling and indicates that physics beyond the SM that protects the Higgs mass against large quantum corrections should exist in the multi-TeV regime. We investigated several approaches to solving the hierarchy problem, such as supersymmetry (SUSY) and conformal ...
ParticleZoo
... particle-anti-particle pairs can be created out of collision energy, either via electromagnetic or weak interaction. collision energy (GeV) m+ ...
... particle-anti-particle pairs can be created out of collision energy, either via electromagnetic or weak interaction. collision energy (GeV) m+ ...
Particle physics tomorrow LHC
... phases of the fields as we like at any point of space-time and ascertain that the exchanged states still satisfy Dirac equation. It is not possible. • The way out is to introduce massless gauge vector bosons that compensate exactly for the effect. We need as many as there are generators in the excha ...
... phases of the fields as we like at any point of space-time and ascertain that the exchanged states still satisfy Dirac equation. It is not possible. • The way out is to introduce massless gauge vector bosons that compensate exactly for the effect. We need as many as there are generators in the excha ...
Symmetry breaking and the deconstruction of mass
... 3. The problem of mass in the standard model In the electroweak theory of Glashow, Weinberg and Salam, we have four agents transmitting forces, the vector bosons W + , W − , Z and the photon field γ . Their description is in terms of a gauge theory with group SU(2) × U(1), and it is not consistent t ...
... 3. The problem of mass in the standard model In the electroweak theory of Glashow, Weinberg and Salam, we have four agents transmitting forces, the vector bosons W + , W − , Z and the photon field γ . Their description is in terms of a gauge theory with group SU(2) × U(1), and it is not consistent t ...
Lecture 1
... Yukawa concludes that the mass of the conjectured particles (mesons) is about 200 electron masses. Beginning of the meson theory of nuclear forces. 1937 A particle of 200 electron masses is discovered in cosmic rays. While at first physicists thought it was Yukawa's pion, it was later discovered to ...
... Yukawa concludes that the mass of the conjectured particles (mesons) is about 200 electron masses. Beginning of the meson theory of nuclear forces. 1937 A particle of 200 electron masses is discovered in cosmic rays. While at first physicists thought it was Yukawa's pion, it was later discovered to ...
Introduction to Nuclear and Particle Physics
... These models are defined by their particle content of the theory and by the allowed interactions of these particles (i.e. what are the allowed vertices) ...
... These models are defined by their particle content of the theory and by the allowed interactions of these particles (i.e. what are the allowed vertices) ...
Particle accelerator goes boldly where none have gone before
... But it would be boring if only the Higgs is found. This would mean that, at least within the LHC's large range of energies, there's nothing new in the universe beyond the predictions of the standard model. There are several tantalizing hints that this won't happen. First, astronomers have discovered ...
... But it would be boring if only the Higgs is found. This would mean that, at least within the LHC's large range of energies, there's nothing new in the universe beyond the predictions of the standard model. There are several tantalizing hints that this won't happen. First, astronomers have discovered ...
Forces Fundamental interactions in particle physics
... Gravity, electromagnetic, strong and weak ...
... Gravity, electromagnetic, strong and weak ...