Document
... Isotropy of space time laws of physics are invariant under rotations in space time. In particular laws of physics are invariant under rotations in space Conservation of angular momentum. Invariant under rotation in space and time (Lorentz transformation), Lorentz Symmetry ...
... Isotropy of space time laws of physics are invariant under rotations in space time. In particular laws of physics are invariant under rotations in space Conservation of angular momentum. Invariant under rotation in space and time (Lorentz transformation), Lorentz Symmetry ...
The beginning of physics
... All ordinary matter made of up quark, down quark, electrons and electron neutrinos. All forces (except gravity) mediated by photon, Z boson, W boson and gluon. ...
... All ordinary matter made of up quark, down quark, electrons and electron neutrinos. All forces (except gravity) mediated by photon, Z boson, W boson and gluon. ...
higgs bison
... considerable time and data. But whatever form the Higgs particle takes, our knowledge of the fundamental structure of matter is about to take a major step forward.” Krassnigg continues his comparison of the Higgs boson with a car to explain what’s next: “Measurements and data analysis will continue ...
... considerable time and data. But whatever form the Higgs particle takes, our knowledge of the fundamental structure of matter is about to take a major step forward.” Krassnigg continues his comparison of the Higgs boson with a car to explain what’s next: “Measurements and data analysis will continue ...
Physics and the Search for Ultimate BuildingBlocks
... • …and there is more to physics than the Standard Model • There is gravity, whose description by the theory of general relativity has yet to be reconciled with quantum theory. • Only about 4% of the total energy density in the universe can be understood in terms of the Standard Model. • About 22% is ...
... • …and there is more to physics than the Standard Model • There is gravity, whose description by the theory of general relativity has yet to be reconciled with quantum theory. • Only about 4% of the total energy density in the universe can be understood in terms of the Standard Model. • About 22% is ...
ASEPS_Poster_Ishihara1_A0
... Abstract: Neutrinoless double beta decay (0) takes place only when neutrinos are Majorana neutrinos that have the nature of no distinction between particles and their own anti-particles. Majorana neutrino plays important role in the theory called Seesaw Mechanism, in which a left-handed Majorana ...
... Abstract: Neutrinoless double beta decay (0) takes place only when neutrinos are Majorana neutrinos that have the nature of no distinction between particles and their own anti-particles. Majorana neutrino plays important role in the theory called Seesaw Mechanism, in which a left-handed Majorana ...
The Standard Model of Particle Physics: An - LAPTh
... non-Abelian SU (2)L , which besides τ ± has also “a neutral” generator τ 3 . There will therefore be 3 compensating gauge fields: Wµ± , Wµ3 . SU (2)L symmetry predicts the coupling of W 3 : ĒL γµ Wµ3 τ 3 EL = ν̄e γµ Wµ3 νe − ēL γµ Wµ3 eL . Unfortunately this neutral current does not correspond to ...
... non-Abelian SU (2)L , which besides τ ± has also “a neutral” generator τ 3 . There will therefore be 3 compensating gauge fields: Wµ± , Wµ3 . SU (2)L symmetry predicts the coupling of W 3 : ĒL γµ Wµ3 τ 3 EL = ν̄e γµ Wµ3 νe − ēL γµ Wµ3 eL . Unfortunately this neutral current does not correspond to ...
Modified from College Physics, 8th Ed., Serway and Vuille. For the
... There are four fundamental forces of nature: the strong (hadronic), electromagnetic, weak, and gravitational forces. The strong force is the force between nucleons that keeps the nucleus together. The weak force is responsible for beta decay. The electromagnetic and weak forces are now considered to ...
... There are four fundamental forces of nature: the strong (hadronic), electromagnetic, weak, and gravitational forces. The strong force is the force between nucleons that keeps the nucleus together. The weak force is responsible for beta decay. The electromagnetic and weak forces are now considered to ...
particlephysics
... must = 2mc2 (at least) 1 photon producing electron-positron pair It also works the other way around – knowing the mass of the particle-antiparticle pair that annihilate you calculate the energy of the photons produced. ...
... must = 2mc2 (at least) 1 photon producing electron-positron pair It also works the other way around – knowing the mass of the particle-antiparticle pair that annihilate you calculate the energy of the photons produced. ...
Document
... particle which stopped in the emulsion, was absorbed by a nucleus, and then “exploded” into “stars” (D.H. Perkins was one who observed these!) • The positive particles seemed to stop and then decay into the previously-seen muons • These had a similar mass to the mesons, but clearly had different int ...
... particle which stopped in the emulsion, was absorbed by a nucleus, and then “exploded” into “stars” (D.H. Perkins was one who observed these!) • The positive particles seemed to stop and then decay into the previously-seen muons • These had a similar mass to the mesons, but clearly had different int ...
History of Particle Physics (lecture notes)
... Since then the Standard Model has gone from triumph to triumph. The Cabibbo-‐Kobayashi-‐Maskawa theory of CP violation anticipated the existence of a third family -‐ an anticipation eventually fulfilled ...
... Since then the Standard Model has gone from triumph to triumph. The Cabibbo-‐Kobayashi-‐Maskawa theory of CP violation anticipated the existence of a third family -‐ an anticipation eventually fulfilled ...
Screen-Based Graphic Design: Tips for non
... spin, same direction of spin) quarks occupying identical quantum states The only way for this to work is if each quark possesses a further property, color: ...
... spin, same direction of spin) quarks occupying identical quantum states The only way for this to work is if each quark possesses a further property, color: ...
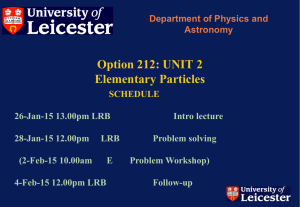
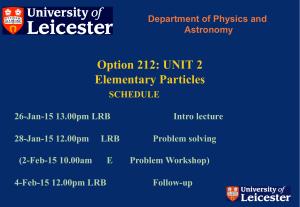
Option 212: UNIT 2 Elementary Particles - X
... spin, same direction of spin) quarks occupying identical quantum states The only way for this to work is if each quark possesses a further property, color: ...
... spin, same direction of spin) quarks occupying identical quantum states The only way for this to work is if each quark possesses a further property, color: ...
Field and gauge theories
... 1954 –Yang and Mills postulate a non-abelian theory for strong interactions 1958 – QED well understood and divergences addressed and accepted 1958-1960 – Glashow unifies electromagnetism and weak interactions 1960s and 70s – Propagation of the Standard Model as a unified gauge theory ...
... 1954 –Yang and Mills postulate a non-abelian theory for strong interactions 1958 – QED well understood and divergences addressed and accepted 1958-1960 – Glashow unifies electromagnetism and weak interactions 1960s and 70s – Propagation of the Standard Model as a unified gauge theory ...