Size & Distance Comparison (Powerpoint)
... the Earth in just over a second reach us from the next star ...
... the Earth in just over a second reach us from the next star ...
Chapter 7:
... visible frequencies, which can conceal objects of sizes of at least 3 orders of magnitude larger than the wavelength of light in all three dimensions, and works for a specific polarization of the incident light. ...
... visible frequencies, which can conceal objects of sizes of at least 3 orders of magnitude larger than the wavelength of light in all three dimensions, and works for a specific polarization of the incident light. ...
Modern Atomic Theory Notes Sheet
... different energy, and so produces different colors when the emitted light is passed through a prism the colors that appear are known as the element’s: Light as a Particle and Emission Spectra: Every element has a unique: The atomic emission spectra phenomenon is a key piece of evidence that li ...
... different energy, and so produces different colors when the emitted light is passed through a prism the colors that appear are known as the element’s: Light as a Particle and Emission Spectra: Every element has a unique: The atomic emission spectra phenomenon is a key piece of evidence that li ...
Chapter 4 Spectroscopy
... differences between allowed levels Modern model has electron “cloud” rather than orbit ...
... differences between allowed levels Modern model has electron “cloud” rather than orbit ...
pptx
... What fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? •Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polarizer, the light is now vertically polarized. Then, I2=I1cos26o= 1/4 I1 =1/8 I0. • Now the light i ...
... What fraction of the initial intensity emerges from the system? What is the polarization of the exiting light? •Through the first polarizer: unpolarized to polarized, so I1=½I0. • Into the second polarizer, the light is now vertically polarized. Then, I2=I1cos26o= 1/4 I1 =1/8 I0. • Now the light i ...
Absorption & Emission
... near 1.0 as they are “symmetry allowed”. McGarvey and Gaillard, Basic Photochemistry at ...
... near 1.0 as they are “symmetry allowed”. McGarvey and Gaillard, Basic Photochemistry at ...
Unit 1 VCE Physics: Sample Timeline, 2004
... this information” approach to teaching physics. It is, perhaps, more important to mix the supply of information with space for discussion of the “big questions” and mysteries surrounding physics. There should be room for the human stories and the dramatic clashes of philosophies. It is especially im ...
... this information” approach to teaching physics. It is, perhaps, more important to mix the supply of information with space for discussion of the “big questions” and mysteries surrounding physics. There should be room for the human stories and the dramatic clashes of philosophies. It is especially im ...
Name - Red Hook Central Schools
... the work function, φ. The kinetic energy of an ejected photon is the difference between the energy of the incident radiation and the work function, usually given in eV. The “eV” or electron-volt is an energy unit that results when one electron passes through a potential of one volt (Ue = qv). This i ...
... the work function, φ. The kinetic energy of an ejected photon is the difference between the energy of the incident radiation and the work function, usually given in eV. The “eV” or electron-volt is an energy unit that results when one electron passes through a potential of one volt (Ue = qv). This i ...
Optics and Optoelectronics
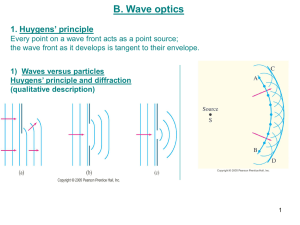
... ray and wave optics, physical optics phenomena, as well as raise understanding about the close connection between optics and electronics (1) Understanding of ray and and wave approximation used for description of optical phenomenon (2) Ability to solve problems in optics and optoelectronics using ma ...
... ray and wave optics, physical optics phenomena, as well as raise understanding about the close connection between optics and electronics (1) Understanding of ray and and wave approximation used for description of optical phenomenon (2) Ability to solve problems in optics and optoelectronics using ma ...