P316
... function of potassium and compute the value of Planck’s constant. If the angular momentum of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun were quantized what would the Earth’s quantum number be? How much energy would be released in a transition to the next lower quantum number? Would this amount of energy be de ...
... function of potassium and compute the value of Planck’s constant. If the angular momentum of the Earth’s orbit around the Sun were quantized what would the Earth’s quantum number be? How much energy would be released in a transition to the next lower quantum number? Would this amount of energy be de ...
Sample Problems for Final
... Two narrow slits are separated by 10 microns. Light that passes through the slits illuminates a screen 1 meter away. Two separate colors of light, of approximately equal intensity, are incident on the slit: yellow light of wavelength 480 nm and red light of wavelength 640 nm. The central (m=0) maxim ...
... Two narrow slits are separated by 10 microns. Light that passes through the slits illuminates a screen 1 meter away. Two separate colors of light, of approximately equal intensity, are incident on the slit: yellow light of wavelength 480 nm and red light of wavelength 640 nm. The central (m=0) maxim ...
Research Directions
... In the presence of a longitudinal magnetic field, the Zeeman sublevels of the ground state are shifted in energy by gmB×M. This leads to a difference in resonance frequencies for left- and right-circularly polarized light (s±). ...
... In the presence of a longitudinal magnetic field, the Zeeman sublevels of the ground state are shifted in energy by gmB×M. This leads to a difference in resonance frequencies for left- and right-circularly polarized light (s±). ...
Light Bulbs
... Electricity excites gas molecules in light bulb Most energy is converted into visible light instead of heat. Mercury is highly toxic chemical ...
... Electricity excites gas molecules in light bulb Most energy is converted into visible light instead of heat. Mercury is highly toxic chemical ...
Liad Elmelech 7.1-7.3 The Nature of Light, Atomic Spectroscopy
... A nitrogen gas laser pulse with a wavelength of 337 nm contains 3.83 mJ of energy. How many photons does it contain? (number of photons = Epulse / Ephoton) λ= 337nm*(10^-9m/1nm) = 3.37*10^-7m E Photon = hc / λ = ((6.626*10^-34 J*s)(3.00*10^8 m/s)) / (3.37*10^-7m) ...
... A nitrogen gas laser pulse with a wavelength of 337 nm contains 3.83 mJ of energy. How many photons does it contain? (number of photons = Epulse / Ephoton) λ= 337nm*(10^-9m/1nm) = 3.37*10^-7m E Photon = hc / λ = ((6.626*10^-34 J*s)(3.00*10^8 m/s)) / (3.37*10^-7m) ...
Crystal Optics with Intense Light Sources Exercise sheet #4
... (a) Think about the light you want and the light you do not want to measure. Which filter would you place behind the sample? Use the filter curves given on the next page. (1) (b) In addition, nonlinear optical processes can occur in the polarization optics before and after the light passes the sampl ...
... (a) Think about the light you want and the light you do not want to measure. Which filter would you place behind the sample? Use the filter curves given on the next page. (1) (b) In addition, nonlinear optical processes can occur in the polarization optics before and after the light passes the sampl ...
Biomolecular and cellular research devices.
... molecules can take place with no or very little change of wavelength. The intensity of the scattered light depends on molecular weight and also scattering angle which can be used for estimation of the macromolecule shape. Raman spectrometry. In scattering of photons a small change of wavelength oc ...
... molecules can take place with no or very little change of wavelength. The intensity of the scattered light depends on molecular weight and also scattering angle which can be used for estimation of the macromolecule shape. Raman spectrometry. In scattering of photons a small change of wavelength oc ...
SWIR (Short Wave Infrared) to Visible Image Up
... thus, full imaging capability is feasible. This wavelength up-conversion is carried out through a linear conversion and with relatively high conversion efficiency, where an external electric field is induced to supplement the energy difference between the SWIR energy absorbed and the visible light e ...
... thus, full imaging capability is feasible. This wavelength up-conversion is carried out through a linear conversion and with relatively high conversion efficiency, where an external electric field is induced to supplement the energy difference between the SWIR energy absorbed and the visible light e ...
5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom
... • The set of frequencies of light emitted by atoms of a given element • Each element has its own unique atomic emission spectrum (LIKE A FINGER PRINT) • Used to determine the composition of stars ...
... • The set of frequencies of light emitted by atoms of a given element • Each element has its own unique atomic emission spectrum (LIKE A FINGER PRINT) • Used to determine the composition of stars ...
Lecture 16 - Purdue Physics
... The changing magnetic field creates an electric field (which produces the EMF) It turns out that likewise, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. This process can continue indefinitely… Light is an oscillating electric-magnetic field propagating through free space. ...
... The changing magnetic field creates an electric field (which produces the EMF) It turns out that likewise, a changing electric field produces a magnetic field. This process can continue indefinitely… Light is an oscillating electric-magnetic field propagating through free space. ...
Wave Particle Duality Power Point NOTES
... Electronic structure (electron configurations) - base for many chemistry concepts. ex: molecular geometry & chemical reactivity. ...
... Electronic structure (electron configurations) - base for many chemistry concepts. ex: molecular geometry & chemical reactivity. ...
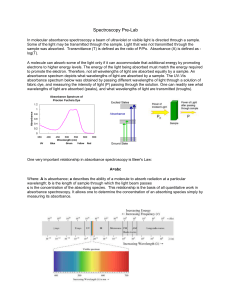
Introduction to Spectroscopy
... Interactions with matter • Ionizing – enough energy to liberate e• Non-ionizing – in general: reflection, transmission or absorption – Absorbed radiation may be re-radiated (scattered) at the original frequency (Rayleigh scattering) or at a different frequency (Raman, Brillouin, fluorescence, etc.) ...
... Interactions with matter • Ionizing – enough energy to liberate e• Non-ionizing – in general: reflection, transmission or absorption – Absorbed radiation may be re-radiated (scattered) at the original frequency (Rayleigh scattering) or at a different frequency (Raman, Brillouin, fluorescence, etc.) ...