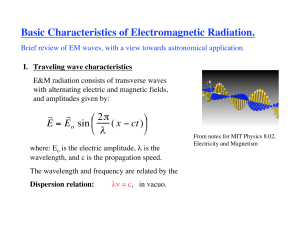
Chapter 29: Light Waves Interference Constructive Interference
... waves are in phase • Lasers also produce monochromatic light: all the same frequency (color)! • NOT sources of energy: laser pointers run on batteries ...
... waves are in phase • Lasers also produce monochromatic light: all the same frequency (color)! • NOT sources of energy: laser pointers run on batteries ...
Photoelectric Effect
... his work on the photoelectric effect. The emission of electrons from a metal irradiated by light was first noticed by Heinrich Hertz in 1887. In 1902 Phillipp Lenard observed that the energy of the emitted electrons increased as the frequency of the light increased. In 1905 Einstein published his th ...
... his work on the photoelectric effect. The emission of electrons from a metal irradiated by light was first noticed by Heinrich Hertz in 1887. In 1902 Phillipp Lenard observed that the energy of the emitted electrons increased as the frequency of the light increased. In 1905 Einstein published his th ...
optical pumping of rubidium
... -1 to –2 and in the F = 1 state from m F = -1 to 0, 0 to +1. As a result of this, the individual absorption signals appear in the corresponding order with increasing frequency of the HF irradiation. The relative position between the absorption transitions of the F = 2 state and those of the F = 1 st ...
... -1 to –2 and in the F = 1 state from m F = -1 to 0, 0 to +1. As a result of this, the individual absorption signals appear in the corresponding order with increasing frequency of the HF irradiation. The relative position between the absorption transitions of the F = 2 state and those of the F = 1 st ...
Study guide_2
... 16. Describe how images are formed in the eye and sent to the brain. 17. How is a camera like your eye? Compare the two and identify parts that have similar roles. 18. List two optical devices and how they work. 19. Define the following: a. Crest b. Trough c. Frequency d. Wavelength e. Amplitude 20. ...
... 16. Describe how images are formed in the eye and sent to the brain. 17. How is a camera like your eye? Compare the two and identify parts that have similar roles. 18. List two optical devices and how they work. 19. Define the following: a. Crest b. Trough c. Frequency d. Wavelength e. Amplitude 20. ...
Photoelectric Effect 1 Introduction 2 Experiment
... 5. The measurements of the tube voltage and current can be directly measured using the ammeter and voltmeter attached to the indicated banana jacks on the apparatus. Before directing the LED light onto the tube it is necessary to zero out the leakage current as much as possible. To do this make sur ...
... 5. The measurements of the tube voltage and current can be directly measured using the ammeter and voltmeter attached to the indicated banana jacks on the apparatus. Before directing the LED light onto the tube it is necessary to zero out the leakage current as much as possible. To do this make sur ...
Measuring Planck`s Constant Using Light Emitting Diodes - IFSC-USP
... The results yielded should give an accurate value for Planck’s constant. This method, depending on the results, can then be used in an entry level physics lab, such as that of a high school physics lab. ...
... The results yielded should give an accurate value for Planck’s constant. This method, depending on the results, can then be used in an entry level physics lab, such as that of a high school physics lab. ...
Physics Tute Sheet-6 - College of Engineering Roorkee
... Ans. 8.66x10-5cm & its odd multiple. 6. Calculate the thickness of a doubly refracting crystal plate which is required to convert a clockwise circularly polarized light to anticlockwise circularly polarized light. Given μe = 1.5388 and μo= 1.5212 for the wavelength 600nm. Ans. 1.7x10-3cm & its multi ...
... Ans. 8.66x10-5cm & its odd multiple. 6. Calculate the thickness of a doubly refracting crystal plate which is required to convert a clockwise circularly polarized light to anticlockwise circularly polarized light. Given μe = 1.5388 and μo= 1.5212 for the wavelength 600nm. Ans. 1.7x10-3cm & its multi ...
METO 621
... • The O2 molecule and atom can be left in several states if we consider energy alone, because any ‘extra’ energy can be used for kinetic energy of the products. • For wavelengths about 310 nm or less, spin conservation allows the transition O3 + hn → O2(1Dg) + O(1D) • The O(1D) atom formed in this r ...
... • The O2 molecule and atom can be left in several states if we consider energy alone, because any ‘extra’ energy can be used for kinetic energy of the products. • For wavelengths about 310 nm or less, spin conservation allows the transition O3 + hn → O2(1Dg) + O(1D) • The O(1D) atom formed in this r ...
Heat and Energy Review
... Closed Circuit is a loop with NO breaks through which electric current can flow (Hint: this is the meaning of closed) Series Circuit this is a simple circuit where there is only 1 path for the electricity to flow. Example Christmas tree lights..when one goes out they all go out ...
... Closed Circuit is a loop with NO breaks through which electric current can flow (Hint: this is the meaning of closed) Series Circuit this is a simple circuit where there is only 1 path for the electricity to flow. Example Christmas tree lights..when one goes out they all go out ...
Electron configuration of atoms
... external source, the electron moves to a higher energy orbit. • The atom is now in an excited state. • The electron then drops to a lower state and emits a photon corresponding to the difference between the energy levels of the two orbits. ...
... external source, the electron moves to a higher energy orbit. • The atom is now in an excited state. • The electron then drops to a lower state and emits a photon corresponding to the difference between the energy levels of the two orbits. ...
Photoreflectance of Semiconductors
... Majority of Defects on the Surface Defects cause strain on the surface Cracks form Periodicity lost ...
... Majority of Defects on the Surface Defects cause strain on the surface Cracks form Periodicity lost ...
optical illusions caused by the refracted light through the overheated
... The intense heat can cause a mirageoptical illusions caused by the refracted light through the overheated air layers near the ground. ...
... The intense heat can cause a mirageoptical illusions caused by the refracted light through the overheated air layers near the ground. ...
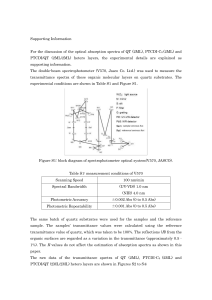
Supporting Information For the discussion of the optical absorption
... Figure S6: the UPS spectra of levels of QT (2ML), PTCDI-C8 (2ML), and QT/PTCDI-C8 (2ML/2ML). In contrast, the HOMO level is located around 5.9 eV, estimated by UPS measurements carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT ...
... Figure S6: the UPS spectra of levels of QT (2ML), PTCDI-C8 (2ML), and QT/PTCDI-C8 (2ML/2ML). In contrast, the HOMO level is located around 5.9 eV, estimated by UPS measurements carried out by the authors [Figure S6] and Forker [18]. This result indicates that the ex-situ measurement reveals the QT ...