Chapter8_notes
... the energy transitions in the atom that have a line width of zero. In reality, the lines are broadened due to a number of factors and will have a finite width. • Narrow line widths are crucial in atomic spectroscopy to reduce the possibility of overlapping lines in the spectra. • The effective line ...
... the energy transitions in the atom that have a line width of zero. In reality, the lines are broadened due to a number of factors and will have a finite width. • Narrow line widths are crucial in atomic spectroscopy to reduce the possibility of overlapping lines in the spectra. • The effective line ...
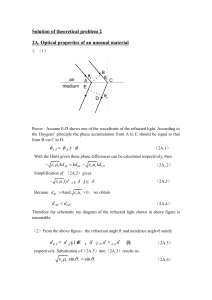
Solution of theoretical problem 2
... Further taking the symmetry about the y axis into consideration we obtain that if the following condition sin( / 8) ...
... Further taking the symmetry about the y axis into consideration we obtain that if the following condition sin( / 8) ...
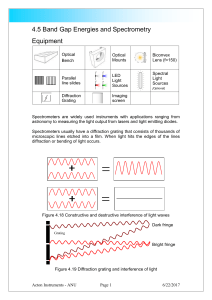
4.5 Band Gap Energies and Spectrometry
... The amount of bending depends on the spacing and size of the lines on the diffraction grating. Light can be produced in a number of different ways. The filament of a light bulb is heated by passing a current through it. This heat is radiated as visible and non-visible light. An LED or light emitting ...
... The amount of bending depends on the spacing and size of the lines on the diffraction grating. Light can be produced in a number of different ways. The filament of a light bulb is heated by passing a current through it. This heat is radiated as visible and non-visible light. An LED or light emitting ...
Besombes - International Conference on Quantum Dots (QD 2012)
... high energy state |Sz1=+5/2;Sz2=+5/2;J=+1> (Szi and J are the angular momentum of the Mn atom i and exciton respectively) and the emission of the same QD when a single mode laser is scanned around this high energy state E1 (top panel). One observes a power dependent and detuning dependent splitting ...
... high energy state |Sz1=+5/2;Sz2=+5/2;J=+1> (Szi and J are the angular momentum of the Mn atom i and exciton respectively) and the emission of the same QD when a single mode laser is scanned around this high energy state E1 (top panel). One observes a power dependent and detuning dependent splitting ...
plane-polarized
... A phase difference of 90° means that when one wave is at its peak then the other one is just crossing the zero line. Special electromagnetic wave. At any fixed point in space that is in the line of the propagation of this wave, the electric field vector rotates in a circle while its length remains c ...
... A phase difference of 90° means that when one wave is at its peak then the other one is just crossing the zero line. Special electromagnetic wave. At any fixed point in space that is in the line of the propagation of this wave, the electric field vector rotates in a circle while its length remains c ...
Atoms and Spectra Chapter 7 Guidepost
... Any object above the temperature of 0 Kelvin (absolute zero) will emit radiation of a particular wavelength / frequency. Temperature is a measure of the activity/agitation of the atoms and molecules making up a substance. The frequency is directly related to the temperature of the object. In the cas ...
... Any object above the temperature of 0 Kelvin (absolute zero) will emit radiation of a particular wavelength / frequency. Temperature is a measure of the activity/agitation of the atoms and molecules making up a substance. The frequency is directly related to the temperature of the object. In the cas ...
Introduction to spectroscopy
... Spectrum: A plot of the intensity as a function light or particle energy (frequency, wavelength) ...
... Spectrum: A plot of the intensity as a function light or particle energy (frequency, wavelength) ...
doc
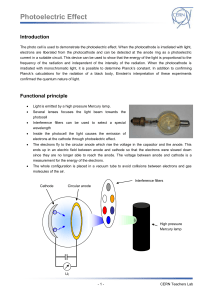
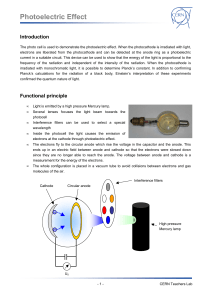
... electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the light is proportional to the frequency of the radiation and independent of the intensity of the radiation. When ...
... electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the light is proportional to the frequency of the radiation and independent of the intensity of the radiation. When ...
Photoelectric Effect
... electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the light is proportional to the frequency of the radiation and independent of the intensity of the radiation. When ...
... electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the light is proportional to the frequency of the radiation and independent of the intensity of the radiation. When ...
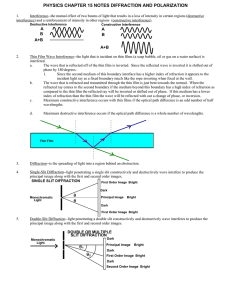
PHYSICS CHAPTER 15 NOTES DIFFRACTION AND
... compared to the thin film the reflected ray will be inverted or shifted out of phase. If this medium has a lower index of refraction than the thin film the wave will be reflected with out a change of phase, or inversion. ...
... compared to the thin film the reflected ray will be inverted or shifted out of phase. If this medium has a lower index of refraction than the thin film the wave will be reflected with out a change of phase, or inversion. ...
Document
... Until about 1900, the classical wave theory of light described most observed phenomenon. ...
... Until about 1900, the classical wave theory of light described most observed phenomenon. ...
absorbance, a - srmbiotech25
... – The incident radiation must consist of parallel rays, each traversing the same length in the absorbing medium; – The incident radiation should preferably be monochromatic, or have at least a width that is narrower than that of the absorbing transition; and – The incident flux must not influence th ...
... – The incident radiation must consist of parallel rays, each traversing the same length in the absorbing medium; – The incident radiation should preferably be monochromatic, or have at least a width that is narrower than that of the absorbing transition; and – The incident flux must not influence th ...
EE 566 - Optical Communications
... principles of photonic devices and their applications in optical communications systems. Topics covered include the waveguide theory, optical fibers, semiconductor lasers and detectors, noise, electrooptic modulation, acoutooptic effect, coupled mode analysis and grating, soliton, wavelength-divison ...
... principles of photonic devices and their applications in optical communications systems. Topics covered include the waveguide theory, optical fibers, semiconductor lasers and detectors, noise, electrooptic modulation, acoutooptic effect, coupled mode analysis and grating, soliton, wavelength-divison ...
doc
... the photocathode is irradiated with light, electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the light is proportional to the frequency of the radiation and independ ...
... the photocathode is irradiated with light, electrons are liberated from the photocathode and can be detected at the anode ring as a photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the light is proportional to the frequency of the radiation and independ ...
photoelectric-effect-qrg
... photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the light is proportional to the frequency of the radiation and independent of the intensity of the radiation. When the photocathode is irradiated with monochromatic light, it is possible to determine Pla ...
... photoelectric current in a suitable circuit. This device can be used to show that the energy of the light is proportional to the frequency of the radiation and independent of the intensity of the radiation. When the photocathode is irradiated with monochromatic light, it is possible to determine Pla ...
The electron! Speed and energy notes
... • When elements are given energy from a variety of sources (heat, light, electricity) the electrons absorb that energy, & jump up to a higher energy level, the excited state. The electrons can return to ground state by giving off the energy as a color of light, called photons of light. ...
... • When elements are given energy from a variety of sources (heat, light, electricity) the electrons absorb that energy, & jump up to a higher energy level, the excited state. The electrons can return to ground state by giving off the energy as a color of light, called photons of light. ...
Lecture 3: Specific Intensity, Flux and Optical Depth
... through a medium where the absorption and scattering (together often referred to as “extinction”) is important, but the emission is not. An example of this is the propagation of star light through the interstellar medium. At optical wavelengths the ISM adds nothing of importance to the beam because ...
... through a medium where the absorption and scattering (together often referred to as “extinction”) is important, but the emission is not. An example of this is the propagation of star light through the interstellar medium. At optical wavelengths the ISM adds nothing of importance to the beam because ...
UV and IR Spectra to Determine Simulated Astrophysical Species
... species, absorption spectra in IR and UV regions are measured. A Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer (Bruker, Vertex 80) equipped with a KBr beamsplitter and HgCdTe detector was utilized to record the IR spectra. To measure the UV spectra, UV light was dispersed using a 6-m monochromator on the ...
... species, absorption spectra in IR and UV regions are measured. A Fourier-transform infrared spectrometer (Bruker, Vertex 80) equipped with a KBr beamsplitter and HgCdTe detector was utilized to record the IR spectra. To measure the UV spectra, UV light was dispersed using a 6-m monochromator on the ...