PHYSICS CHAPTER 12 NOTES THE NATURE OF LIGHT
... electromagnetic waves is equally divided between and electric field and a magnetic field, each perpendicular to the other, and both perpendicular to the propagation of the wave. b. Electromagnetic Energy--can be converted to other energy forms such as thermal, electric, kinetic, potential, chemical. ...
... electromagnetic waves is equally divided between and electric field and a magnetic field, each perpendicular to the other, and both perpendicular to the propagation of the wave. b. Electromagnetic Energy--can be converted to other energy forms such as thermal, electric, kinetic, potential, chemical. ...
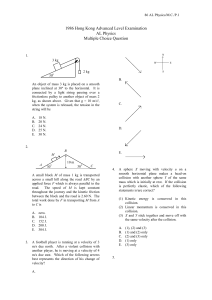
1. An object of mass 3 kg is placed on a smooth plane inclined at 30º
... A. were at rest until the switch was closed but now move along the wire with a drift velocity of a few millimetres per second. B. were at rest until the switch was closed but now move along the wire at a speed approaching the speed of light. C. had random motion onto which was imposed a drift veloci ...
... A. were at rest until the switch was closed but now move along the wire with a drift velocity of a few millimetres per second. B. were at rest until the switch was closed but now move along the wire at a speed approaching the speed of light. C. had random motion onto which was imposed a drift veloci ...
10. Molecules and Solids
... photons and make transitions to a higher vibrational state when electromagnetic radiation is incident upon a collection of a particular kind of molecule. ...
... photons and make transitions to a higher vibrational state when electromagnetic radiation is incident upon a collection of a particular kind of molecule. ...
Document
... A Scattering Picture of Optical Rotation A circularly polarized light wave ‘bouncing’ from one group to the other as it scatters from a simple two-group chiral molecular structure will sample the chirality. The scattered intensity of right- and left-circularly polarized waves will be slightly diffe ...
... A Scattering Picture of Optical Rotation A circularly polarized light wave ‘bouncing’ from one group to the other as it scatters from a simple two-group chiral molecular structure will sample the chirality. The scattered intensity of right- and left-circularly polarized waves will be slightly diffe ...
Lecture 7 - UIC Department of Chemistry
... for a compound. Check out the structures of amino acids and possible chemical shifts. ...
... for a compound. Check out the structures of amino acids and possible chemical shifts. ...
LED and ILED
... visible light. The junction in an LED is forward biased and when electrons cross the junction from the n- to the p-type material, the electron-hole recombination process produces some photons in the IR or visible in a process called electroluminescence. An exposed semiconductor surface can then emit ...
... visible light. The junction in an LED is forward biased and when electrons cross the junction from the n- to the p-type material, the electron-hole recombination process produces some photons in the IR or visible in a process called electroluminescence. An exposed semiconductor surface can then emit ...
Ray Box Lab - Iona Physics
... To locate the focus and measure the focal length several optical components. ...
... To locate the focus and measure the focal length several optical components. ...
Chem 2 AP Ch 7 MC Review
... all refer to gaseous atoms in their ground states. An atom may absorb a quantum of energy and promote one of its electrons to a higher-energy orbital. When this happens, we say that the atom is in an excited state. The electron configurations of some excited atoms are given. Identify the species. I. ...
... all refer to gaseous atoms in their ground states. An atom may absorb a quantum of energy and promote one of its electrons to a higher-energy orbital. When this happens, we say that the atom is in an excited state. The electron configurations of some excited atoms are given. Identify the species. I. ...
2 - BYU Physics and Astronomy
... (e) Draw to scale the appearance of the Zeeman-split spectral line in emission. Indicate the direction of increasing frequency. Label each of the Zeeman components as π or σ and indicate the transition(s), 1, 2, . . . , n, with which it is associated. Show for purposes of comparison: (2 points) (i) ...
... (e) Draw to scale the appearance of the Zeeman-split spectral line in emission. Indicate the direction of increasing frequency. Label each of the Zeeman components as π or σ and indicate the transition(s), 1, 2, . . . , n, with which it is associated. Show for purposes of comparison: (2 points) (i) ...
Optical Molasses
... Both use 3 pairs of counterpropagating laser beams Trap about the same amount of atoms Detection of atoms is easier in MOT because of higher density (less spatial extension) In MOT the magnetic field only acts on atoms as they fall from trap Optical molasses uses circularly polarized lasers Optical ...
... Both use 3 pairs of counterpropagating laser beams Trap about the same amount of atoms Detection of atoms is easier in MOT because of higher density (less spatial extension) In MOT the magnetic field only acts on atoms as they fall from trap Optical molasses uses circularly polarized lasers Optical ...
The Vibrating String
... A glowing, low density gas, such as a neon sign, produces a discrete emission spectrum. This type of spectra is seen as having individual lines of different colors. The colors that are emitted by an excited atom are characteristic of that particular kind of atom. They represent a unique set of ener ...
... A glowing, low density gas, such as a neon sign, produces a discrete emission spectrum. This type of spectra is seen as having individual lines of different colors. The colors that are emitted by an excited atom are characteristic of that particular kind of atom. They represent a unique set of ener ...
Towards a lattice based neutral magnesium optical frequency
... Magnesium is an interesting candidate for a future high performance neutral atom optical frequency standard. It offers low sensitivity to frequency shifts of the 1 S0 to 3 P0 clock transition by room temperature blackbody radiation and several isotopes of suitable abundance (two bosonic, one fermion ...
... Magnesium is an interesting candidate for a future high performance neutral atom optical frequency standard. It offers low sensitivity to frequency shifts of the 1 S0 to 3 P0 clock transition by room temperature blackbody radiation and several isotopes of suitable abundance (two bosonic, one fermion ...
Document
... 2. Rutherford’s model provided an explanation for the emission of light from atoms. What was this mechanism and why was it unsatisfactory? 3. Suppose you were a nineteenth-century scientist who had just discovered a new phenomenon known as Zeta rays. What experiment could you perform to define if Ze ...
... 2. Rutherford’s model provided an explanation for the emission of light from atoms. What was this mechanism and why was it unsatisfactory? 3. Suppose you were a nineteenth-century scientist who had just discovered a new phenomenon known as Zeta rays. What experiment could you perform to define if Ze ...
07_04_05.html
... A substance is optically active if it rotates the plane of polarized light. In order for a substance to exhibit optical activity, it must be chiral and one enantiomer must be present in excess of the other. ...
... A substance is optically active if it rotates the plane of polarized light. In order for a substance to exhibit optical activity, it must be chiral and one enantiomer must be present in excess of the other. ...