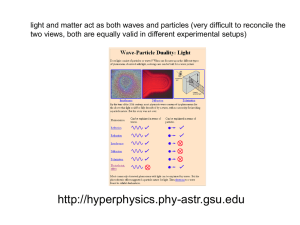
The Photoelectric Effect, work function
... 2. Light of a lower frequency (e.g. red light) has no effect.(recall: lower frequency = lower energy) 3. The minimum frequency of light necessary to produce photoelectrons is called the threshold frequency. (What is a threshold? Define) 4. Below the threshold frequency, no photoelectrons are produce ...
... 2. Light of a lower frequency (e.g. red light) has no effect.(recall: lower frequency = lower energy) 3. The minimum frequency of light necessary to produce photoelectrons is called the threshold frequency. (What is a threshold? Define) 4. Below the threshold frequency, no photoelectrons are produce ...
Light+and+Sound.+RM1
... A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium. A disturbance is a localized and temporary change is the properties of a particular medium. A wave transports energy; it ...
... A wave is a disturbance that travels through a medium. A disturbance is a localized and temporary change is the properties of a particular medium. A wave transports energy; it ...
Properties of Light and Visual Function
... In the above illustration, black dots appear to form and vanish at the intersections of the gray horizontal and vertical lines. When focusing attention on a single white dot, some gray dots nearby and some black dots a little further away also seem to appear. More black dots seem to appear as the e ...
... In the above illustration, black dots appear to form and vanish at the intersections of the gray horizontal and vertical lines. When focusing attention on a single white dot, some gray dots nearby and some black dots a little further away also seem to appear. More black dots seem to appear as the e ...
Electromagnetic waves
... l D) parallel to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave ...
... l D) parallel to each other and perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave ...
Problem Set 1 (due 2/21/06)
... directed into a monochromator for scanning the emission. A fluorescence excitation spectrum is collected by measuring the intensity of a single emitted wavelength over a scan of excitation wavelengths. Typically the source would be a continuous source with a monochrometer (or the harmonics of a tuna ...
... directed into a monochromator for scanning the emission. A fluorescence excitation spectrum is collected by measuring the intensity of a single emitted wavelength over a scan of excitation wavelengths. Typically the source would be a continuous source with a monochrometer (or the harmonics of a tuna ...
Taking fingerprints of stars
... • Emission lines from heavy ions -- atoms stripped of one or more electrons -- dominate the high-energy (X-ray) spectra of stars • Ions of certain heavier elements (for example, highly ionized neon and iron) behave just like “supercharged” H and He Wavelength (in Angstroms) ...
... • Emission lines from heavy ions -- atoms stripped of one or more electrons -- dominate the high-energy (X-ray) spectra of stars • Ions of certain heavier elements (for example, highly ionized neon and iron) behave just like “supercharged” H and He Wavelength (in Angstroms) ...
CCR 22: Scattering of Starlight
... Starlight, like all other kinds of electromagnetic (EM) radiation, is absorbed and scattered by the gas molecules and dust in the interstellar medium (ISM). These processes depend on the atomic and molecular composition of the ISM. In addition, the second process depends on the size of the dust part ...
... Starlight, like all other kinds of electromagnetic (EM) radiation, is absorbed and scattered by the gas molecules and dust in the interstellar medium (ISM). These processes depend on the atomic and molecular composition of the ISM. In addition, the second process depends on the size of the dust part ...
Hydrogen Spectral Lines
... up of all the colors of the visible spectrum. Passing it through a prism separates it. ...
... up of all the colors of the visible spectrum. Passing it through a prism separates it. ...
Name: Period: ______ Date: ______ Group Activity: Light Years
... star to the Earth other than the sun. Since Proxima Centauri is 4.3 light years away, it takes 4.3 years for the light from the star to travel the distance needed to reach the Earth. It is important to remember that a light year is a measure of distance, not of time. ...
... star to the Earth other than the sun. Since Proxima Centauri is 4.3 light years away, it takes 4.3 years for the light from the star to travel the distance needed to reach the Earth. It is important to remember that a light year is a measure of distance, not of time. ...
Nearly All the Clues Come From Light
... different wavelengths move at slightly different speeds (longer wavelengths travel at slower speeds) (this causes differential refraction) ...
... different wavelengths move at slightly different speeds (longer wavelengths travel at slower speeds) (this causes differential refraction) ...
Extinction Coefficient Measurements of Turbid Media
... a spectral range from 390 nm (UV) to 1150 nm (IR) . In order to avoid the optical noise we let the whole path of the laser beam be within black-walled cylindrical tubes until it entered the photodetector . This has eliminated the optical noise to about zero. To avoid the entrance of scattered light ...
... a spectral range from 390 nm (UV) to 1150 nm (IR) . In order to avoid the optical noise we let the whole path of the laser beam be within black-walled cylindrical tubes until it entered the photodetector . This has eliminated the optical noise to about zero. To avoid the entrance of scattered light ...
TTh HW05 key
... B) are always in the same pattern, characteristic of hydrogen gas, as seen in the laboratory. C) change systematically, depending on the distance from the source, starting with a laboratory pattern. D) are in the same pattern for solar and planetary sources but are very different for stars at larger ...
... B) are always in the same pattern, characteristic of hydrogen gas, as seen in the laboratory. C) change systematically, depending on the distance from the source, starting with a laboratory pattern. D) are in the same pattern for solar and planetary sources but are very different for stars at larger ...
Culver City H.S. • AP Chemistry Name Period ___ Date ___/___/___
... It takes more energy to ionize (completely remove) the electron from n=3 than from the ground state. The electron is farther from the nucleus on average in the n=3 state than in the n=1 state. The wavelength of light emitted if the electron drops from n=3 to n=2 will be shorter than the wavelength o ...
... It takes more energy to ionize (completely remove) the electron from n=3 than from the ground state. The electron is farther from the nucleus on average in the n=3 state than in the n=1 state. The wavelength of light emitted if the electron drops from n=3 to n=2 will be shorter than the wavelength o ...