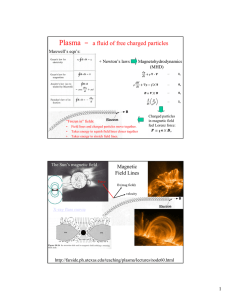
14. Elementary Particles
... theory that described the force between nucleons (protons and neutrons)—the strong force. To do this, he had to determine the carrier or mediator of the nuclear strong force analogous to the photon in the electromagnetic force, which he called a meson (derived from the ...
... theory that described the force between nucleons (protons and neutrons)—the strong force. To do this, he had to determine the carrier or mediator of the nuclear strong force analogous to the photon in the electromagnetic force, which he called a meson (derived from the ...
Most Precise Tests of the Standard Model, Its
... 680 Times Improved Comparision of the Antiproton and Proton Magnetic Moments ...
... 680 Times Improved Comparision of the Antiproton and Proton Magnetic Moments ...
subatomic particle
... radioactive decays would not conserve energy or momentum. • The 2002 Physics Nobel prize to Davis & Koshiba was for detecting neutrinos emitted by fusion in our sun. ...
... radioactive decays would not conserve energy or momentum. • The 2002 Physics Nobel prize to Davis & Koshiba was for detecting neutrinos emitted by fusion in our sun. ...