Chapter 1, Lecture 3 - University of Hawaii Physics and Astronomy
... Fixed target vs CM conceptual question For making new particles, which kind of experiment/accelerator is most effective ? Is there any tradeoff ? ...
... Fixed target vs CM conceptual question For making new particles, which kind of experiment/accelerator is most effective ? Is there any tradeoff ? ...
Chapter 17 - Probing Deep into Matter
... Starter: SAQ 30S 'Creation and annihilation' A new way to look at fields: The forces between things are due to exchange of particles: SoftAct 30S 'Interactions in particle physics' Book page 177/178 and discuss Feynmann diagrams There is a difference Dis 90O 'Identical particles - bosons and fermion ...
... Starter: SAQ 30S 'Creation and annihilation' A new way to look at fields: The forces between things are due to exchange of particles: SoftAct 30S 'Interactions in particle physics' Book page 177/178 and discuss Feynmann diagrams There is a difference Dis 90O 'Identical particles - bosons and fermion ...
Information
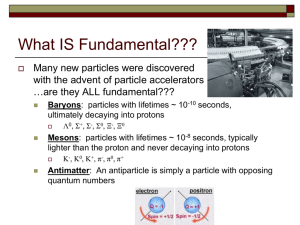
... and an equal but opposite (positive) charge. proton – an elementary particle having a rest mass of about 1.673 × 10–27 kg, slightly less than that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal and opposite to that of the electron. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic nu ...
... and an equal but opposite (positive) charge. proton – an elementary particle having a rest mass of about 1.673 × 10–27 kg, slightly less than that of a neutron, and a positive electric charge equal and opposite to that of the electron. The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom is the atomic nu ...
Slide 1 - StCPhysicsDept
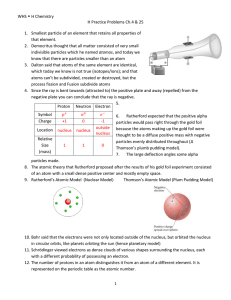
... accelerator) 2. beam pipes (a guide along which the particles will travel whilst being accelerated) 3. accelerating structures (a method of accelerating the particles) 4. a system of magnets (either electromagnets or superconducting magnets as in the LHC) 5. a target (in the LHC the target is a pack ...
... accelerator) 2. beam pipes (a guide along which the particles will travel whilst being accelerated) 3. accelerating structures (a method of accelerating the particles) 4. a system of magnets (either electromagnets or superconducting magnets as in the LHC) 5. a target (in the LHC the target is a pack ...
Natural Sciences
... The Search for the Dark Matter particle • The supersymmetric partners of quarks and gluons are expected to be produced with high rates • They decay into the lightest SUSY particle (LSP) • Weakly interacting à leaves the detector, carries away momentum and energy à characteristic signature: missi ...
... The Search for the Dark Matter particle • The supersymmetric partners of quarks and gluons are expected to be produced with high rates • They decay into the lightest SUSY particle (LSP) • Weakly interacting à leaves the detector, carries away momentum and energy à characteristic signature: missi ...
SCOP Subatomic Particles Cheat Sheet
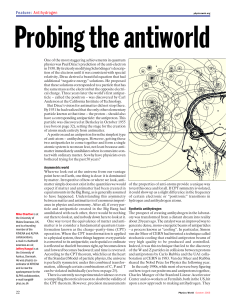
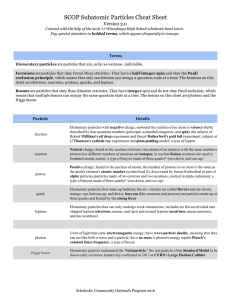
... Fermions are particles that obey FermiDirac statistics. They have a halfinteger spin and obey the Pauli exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are ...
... Fermions are particles that obey FermiDirac statistics. They have a halfinteger spin and obey the Pauli exclusion principle , which means that only one fermion can occupy a quantum state at a time. The fermions on this sheet are ...