Chapter 14
... When a neutron is converted into a proton, this is an example of _________. This is the process by which one element changes into another element. Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons are called _. The atomic number of an element is equal to _____________. This is the smalle ...
... When a neutron is converted into a proton, this is an example of _________. This is the process by which one element changes into another element. Atoms of the same element with a different number of neutrons are called _. The atomic number of an element is equal to _____________. This is the smalle ...
e - X-ray and Observational Astronomy Group
... by many other particles (muon, pion etc) We will discover that the electron and photon are indeed fundamental, elementary particles, but protons and neutrons are made of even smaller elementary particles called quarks ...
... by many other particles (muon, pion etc) We will discover that the electron and photon are indeed fundamental, elementary particles, but protons and neutrons are made of even smaller elementary particles called quarks ...
6. Divisibility of atoms: from radioactivity to particle physics
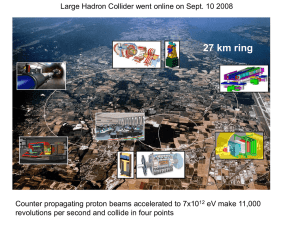
... • Higgs particle is required to account for finite mass of W+,W-,Z bosons; Dec. 2011: “tantalising hints” of new particle (mass about 125 GeV); 2013: Nobel prize for Higgs and Englert • Gravity is not included in standard model ...
... • Higgs particle is required to account for finite mass of W+,W-,Z bosons; Dec. 2011: “tantalising hints” of new particle (mass about 125 GeV); 2013: Nobel prize for Higgs and Englert • Gravity is not included in standard model ...
Atomic (proton) number = is the number of protons found in the
... decay by emitting a gamma ray(s) and/or subatomic particles. Radionuclides may occur naturally, but can also be artificially produced. Isotopes = nuclides that have the same proton number but different mass numbers. Radioisotope = radioactive species of a given element Isomers = two nuclides that di ...
... decay by emitting a gamma ray(s) and/or subatomic particles. Radionuclides may occur naturally, but can also be artificially produced. Isotopes = nuclides that have the same proton number but different mass numbers. Radioisotope = radioactive species of a given element Isomers = two nuclides that di ...
Chapter 4 Assessment Key: 83, 85-89, 106
... , mass number decreases by 4; , no change in mass number; , no change in mass number 86. What is the primary factor determining whether a nucleus is stable or unstable? the neutron-to-proton ratio 87. Explain how energy loss and nuclear stability are related to radioactive decay. Radioactivity re ...
... , mass number decreases by 4; , no change in mass number; , no change in mass number 86. What is the primary factor determining whether a nucleus is stable or unstable? the neutron-to-proton ratio 87. Explain how energy loss and nuclear stability are related to radioactive decay. Radioactivity re ...
Lecture 3 - Purdue Physics
... Observing Fundamental Particles • Ultimately, all particles are detected by means of the electromagnetic interaction: – A charged particle moving at high speed produces an electric field that can ionize matter or excite atomic electrons – The rate of energy loss depends on the velocity but not on t ...
... Observing Fundamental Particles • Ultimately, all particles are detected by means of the electromagnetic interaction: – A charged particle moving at high speed produces an electric field that can ionize matter or excite atomic electrons – The rate of energy loss depends on the velocity but not on t ...