Training
... bony structure It is formed by two sets of bones, the 8 cranial bones and the 14 facial bones These 22 bones combine to form the cranial cavity and the facial features In addition, there are 3 bones in each inner ear to assist in sound transmission ...
... bony structure It is formed by two sets of bones, the 8 cranial bones and the 14 facial bones These 22 bones combine to form the cranial cavity and the facial features In addition, there are 3 bones in each inner ear to assist in sound transmission ...
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION III FORMAT “K
... B. The medium umbilical ligament is attached to its apex C. Its neck leads into the urethra D. When distended, it becomes lower in position E. Its body shows superior and inferolateral surfaces 14. Correct relationships of the female ureters include which of the following? A. The ureters pass latera ...
... B. The medium umbilical ligament is attached to its apex C. Its neck leads into the urethra D. When distended, it becomes lower in position E. Its body shows superior and inferolateral surfaces 14. Correct relationships of the female ureters include which of the following? A. The ureters pass latera ...
Unit 4 - Skeletal System Review
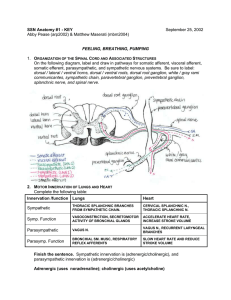
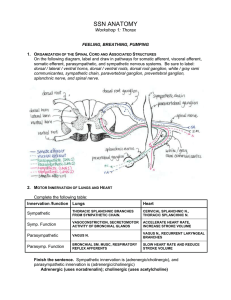
... Name______________________________________________________________Section___ __ Unit 4 - Skeletal System Review The five functions of the skeletal system are 1. ...
... Name______________________________________________________________Section___ __ Unit 4 - Skeletal System Review The five functions of the skeletal system are 1. ...
06 MUSCLES OF BACK
... Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare between groups of back muscles as regard their nerve supply and action. List the back muscles of each group. Describe the attachments of each muscle of the superficial group, as well as, its nerve supply and action. Describe ...
... Distinguish between the different groups of back muscles. Compare between groups of back muscles as regard their nerve supply and action. List the back muscles of each group. Describe the attachments of each muscle of the superficial group, as well as, its nerve supply and action. Describe ...
Slide 1
... the most posterior part of the vault and the base of the skull and the middle of the posterior edge of the foramen magnum ...
... the most posterior part of the vault and the base of the skull and the middle of the posterior edge of the foramen magnum ...
The Skeletal System
... Vertebral Anatomy: body- more massive, weight bearing portion of the vertebrae, transverse process- projecting laterally or dorsolaterall from the pidicles serve as sites for muscle attachments, vertebral arch- form the lateral and posterior walls of the vertebral foramen, intervertebral discfibroca ...
... Vertebral Anatomy: body- more massive, weight bearing portion of the vertebrae, transverse process- projecting laterally or dorsolaterall from the pidicles serve as sites for muscle attachments, vertebral arch- form the lateral and posterior walls of the vertebral foramen, intervertebral discfibroca ...
The Skeleton: Skull
... • It consists of anterior and posterior arches, and two lateral masses • The superior surfaces of lateral masses articulate with the occipital condyles Cervical Vertebrae: The Axis (C2) • The axis has a body, spine, and vertebral arches as do other cervical vertebrae • Unique to the axis is the dens ...
... • It consists of anterior and posterior arches, and two lateral masses • The superior surfaces of lateral masses articulate with the occipital condyles Cervical Vertebrae: The Axis (C2) • The axis has a body, spine, and vertebral arches as do other cervical vertebrae • Unique to the axis is the dens ...
1 - Circle of Docs
... The atlas axis articulation is considered to be which type of joint: a. Pivot b. Condyloid c. Planar d. Ginglymus Flexion and extension of the atlas in relation to the occiput occurs in which of the following planes: a. Transverse b. Sagittal c. Coronal d. Frontal Which ligament makes up the posteri ...
... The atlas axis articulation is considered to be which type of joint: a. Pivot b. Condyloid c. Planar d. Ginglymus Flexion and extension of the atlas in relation to the occiput occurs in which of the following planes: a. Transverse b. Sagittal c. Coronal d. Frontal Which ligament makes up the posteri ...
Chapter 7 Axial Skeleton
... d. pair posteriolateral (mastoid) - between temporal, occipital, and parietals C.. Spinal column 1. regions a. cervical 1-7 have transverse foramina C1 – atlas, no centrum, articulates w/ occipital bone superiorly and axis inferiorly. C2- axis – has a superior process, the dens, around which the atl ...
... d. pair posteriolateral (mastoid) - between temporal, occipital, and parietals C.. Spinal column 1. regions a. cervical 1-7 have transverse foramina C1 – atlas, no centrum, articulates w/ occipital bone superiorly and axis inferiorly. C2- axis – has a superior process, the dens, around which the atl ...
Cervical Spine joints
... superiorly; with spinous four through & lumbar spine subject seated palpate processes of the eight (C4-C8) Center Over spinous process of in posterior triangle 7th cervical and C7 of neck between the upper three Proximal Spinous processes of Special notes upper trapezius and or four thoracic Arm tho ...
... superiorly; with spinous four through & lumbar spine subject seated palpate processes of the eight (C4-C8) Center Over spinous process of in posterior triangle 7th cervical and C7 of neck between the upper three Proximal Spinous processes of Special notes upper trapezius and or four thoracic Arm tho ...
Anatomy Workshop #1
... How can you diagnose a breast tumor by observation only? Breast will dimple due to compression of suspensory ligaments of Cooper, which connect skin to Scarpa’s fascia and separate lobes. What happens to the costal groove with coarcation with the aorta? Narrowing of descending aorta leads to decreas ...
... How can you diagnose a breast tumor by observation only? Breast will dimple due to compression of suspensory ligaments of Cooper, which connect skin to Scarpa’s fascia and separate lobes. What happens to the costal groove with coarcation with the aorta? Narrowing of descending aorta leads to decreas ...
Hip External Rotators
... The obvious movement is hip extension, the rearward movement of the leg at the hip. This movement is driven by famous gluteus maximus, known affectionately as glute max. This is the big butt muscle that connects the pelvis to the femur. When it contracts, it drives the leg back as it propels the bo ...
... The obvious movement is hip extension, the rearward movement of the leg at the hip. This movement is driven by famous gluteus maximus, known affectionately as glute max. This is the big butt muscle that connects the pelvis to the femur. When it contracts, it drives the leg back as it propels the bo ...
Chapter 7 Part I Additional Slides
... Annulus fibrosus – surrounds the nucleus pulposus with a collar composed of collagen fibers (superficially) and ...
... Annulus fibrosus – surrounds the nucleus pulposus with a collar composed of collagen fibers (superficially) and ...
Directional Terms Practice Complete the following statements by
... Complete the following statements by circling the correct term in brackets. a. The toes are [proximal or distal] to the ankles. b. The scalp is [superficial or deep] to the skull. c. The diaphragm is [superior or inferior] to the lungs. d. The heart is [superior or inferior] to the diaphragm. e. The ...
... Complete the following statements by circling the correct term in brackets. a. The toes are [proximal or distal] to the ankles. b. The scalp is [superficial or deep] to the skull. c. The diaphragm is [superior or inferior] to the lungs. d. The heart is [superior or inferior] to the diaphragm. e. The ...
muscles involved in respiration
... 2. Twelve pairs of ribs: laterally 3. Twelve thoracic vertebrae: posteriorly ...
... 2. Twelve pairs of ribs: laterally 3. Twelve thoracic vertebrae: posteriorly ...
Chapter 3 - Victoria College
... • C1 & C2 are different from other cervical vertebrae • Atlas (C1) – Lacks spinous process & body – Articulates with occipital condyles of skull • Allows for nodding “yes” movement – Inferior surface articulates with C2 • Axis (C2) – Odontoid process: projects superiorly thru vertebral foramen of at ...
... • C1 & C2 are different from other cervical vertebrae • Atlas (C1) – Lacks spinous process & body – Articulates with occipital condyles of skull • Allows for nodding “yes” movement – Inferior surface articulates with C2 • Axis (C2) – Odontoid process: projects superiorly thru vertebral foramen of at ...
Hip bone - WordPress.com
... The Hyoid Bone The only bone that does not articulate with another bone ...
... The Hyoid Bone The only bone that does not articulate with another bone ...
The Skeletal System
... • Lamellae - concentric rings of bone • Central Canal - contains artery, vein and lymphatics ...
... • Lamellae - concentric rings of bone • Central Canal - contains artery, vein and lymphatics ...
Thorax Worksheet
... How can you diagnose a breast tumor by observation only? Breast will dimple due to compression of suspensory ligaments of Cooper, which connect skin to Scarpa’s fascia and separate lobes. What happens to the costal groove with coarctation with the aorta? Narrowing of descending aorta leads to decrea ...
... How can you diagnose a breast tumor by observation only? Breast will dimple due to compression of suspensory ligaments of Cooper, which connect skin to Scarpa’s fascia and separate lobes. What happens to the costal groove with coarctation with the aorta? Narrowing of descending aorta leads to decrea ...
Vertebrae
... There are twelve vertebrae (T1-T12) all of which articulate with ribs Major markings include two facets and two demifacets on the heart-shaped body, the circular vertebral foramen, transverse processes, and a long spinous process The location of the articulate facets prevents flexion and exten ...
... There are twelve vertebrae (T1-T12) all of which articulate with ribs Major markings include two facets and two demifacets on the heart-shaped body, the circular vertebral foramen, transverse processes, and a long spinous process The location of the articulate facets prevents flexion and exten ...
Neck
... vertebral artery. (B) Corresponding coronally reformatted CT angiogram shows the course and morphology of the right vertebral artery. The complexity of the fracture (arrow) is also visible. (C) Axial CT angiogram through C2 shows the course of the left vertebral artery. (D) Corresponding oblique cor ...
... vertebral artery. (B) Corresponding coronally reformatted CT angiogram shows the course and morphology of the right vertebral artery. The complexity of the fracture (arrow) is also visible. (C) Axial CT angiogram through C2 shows the course of the left vertebral artery. (D) Corresponding oblique cor ...
CNS
... CNS: Spinal Cord Anatomy • Central canal with gray matter surrounded by white matter. • The central canal contains cerebrospinal fluid. • Portions of sensory and motor neurons reside in the gray matter as do interneurons. The posterior root of a spinal nerve enters here and the anterior root (conta ...
... CNS: Spinal Cord Anatomy • Central canal with gray matter surrounded by white matter. • The central canal contains cerebrospinal fluid. • Portions of sensory and motor neurons reside in the gray matter as do interneurons. The posterior root of a spinal nerve enters here and the anterior root (conta ...
Thoracic cage Diaphragm
... Posterior intercostal arteries are direct branches of the thoracic aorta, while the anterior intercostal arteries arise from the internal thoracic artery, a branch of the subclavian artery. Supreme intercostal arteries of the two upper intercostal spaces also come from the subclavian artery. Poster ...
... Posterior intercostal arteries are direct branches of the thoracic aorta, while the anterior intercostal arteries arise from the internal thoracic artery, a branch of the subclavian artery. Supreme intercostal arteries of the two upper intercostal spaces also come from the subclavian artery. Poster ...
Low Back Bracing Study Bernstein
... in flexion. The capsule of the facets, the supraspinatus ligaments, and the inter-transverse ligaments add further stability to the spine. The iliolumbar ligaments are major stabilizers of the L4, L5 lumbar vertebrae on the sacrum. The intervertebral disc is the most important structure between vert ...
... in flexion. The capsule of the facets, the supraspinatus ligaments, and the inter-transverse ligaments add further stability to the spine. The iliolumbar ligaments are major stabilizers of the L4, L5 lumbar vertebrae on the sacrum. The intervertebral disc is the most important structure between vert ...
Vertebra

In the vertebrate spinal column, each vertebra is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, the proportions of which vary according to the segment of the backbone and the species of vertebrate animal.The basic configuration of a vertebra varies; the large part is the body, and the central part is the centrum. The upper and lower surfaces of the vertebra body give attachment to the intervertebral discs. The posterior part of a vertebra forms a vertebral arch, in eleven parts, consisting of two pedicles, two laminae, and seven processes. The laminae give attachment to the ligamenta flava. There are vertebral notches formed from the shape of the pedicles, which form the intervertebral foramina when the vertebrae articulate. These foramina are the entry and exit conducts for the spinal nerves. The body of the vertebra and the vertebral arch form the vertebral foramen, the larger, central opening that accommodates the spinal canal, which encloses and protects the spinal cord.Vertebrae articulate with each other to give strength and flexibility to the spinal column, and the shape at their back and front aspects determines the range of movement. Structurally, vertebrae are essentially alike across the vertebrate species, with the greatest difference seen between an aquatic animal and other vertebrate animals. As such, vertebrates take their name from the vertebrae that compose the vertebral column.