* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION III FORMAT “K
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
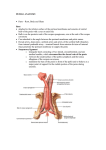
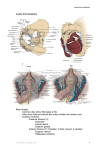
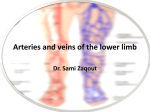
GROSS ANATOMY EXAMINATION III FORMAT “K-2” SELECT THE ONE BEST ANSWER OR COMPLETION: 1. Among the coverings of the cord and testis, which of the following represents the internal oblique muscle layer? A. B. C. D. E. Tunica dartos External spermatic fascla Cremaster muscle and fascia Internal spermatic fascia Subcutaneous layer 2. The second portion of the duodenum is crossed by which of the following structures? A. B. C. D. E. Right renal artery Transverse colon Right ureter Portal vein Superior mesenteric vein 3. Perinephric hematomas, perinephric urinomas, and perinephric abscesses are located between A. B. C. D. E. The kidney parenchyma and the renal capsule The kidney capsule and Gerota’s fascia The kidney capsule and the peritoneum Gerota’s fascia and the peritoneum Gerota’s fascia and the lumbodorsal fascia 4. Regarding the posterior cruciate ligament of the knee A. B. C. D. E. The popliteus muscle is attached to it It is located within the synovial cavity of the knee It is no named because it is attached to the posterior part of the femur It prevents forward displacement of the femur relative to the tibia It prevents forward displacement of the tibia relative to the femur 5. Which of the following nerves traverses the superficial Inguinal ring? A. B. C. D. E. IIlohypogastric Subcostal Illoinguinal Pudendal Obturator 6. The musculophrenic artery is a branch of which of the following arteries? A. B. C. D. E. Internal thoracic Inferior epigastric Superficial epigastric Superficial circumflex Deep external pudendal 7. Both the vagal parasympathetic innervation and the throracic splanchnic sympathetic innervation of the gastrointestinal tract terminate at which of the following? A. Duodenojejunal junction B. Junction of the middle and left thirds of the transverse colon C. Jejunoileal junction D. Ileocecal junction E. Distal one third of the sigmoid colon 8. The right suprarenal vein drains into which of the following veins? A. Right renal B. C. D. E. Inferior mesenteric Superior mesenteric Portal Inferior vena cava 9. Which of the nerves is formed by posterior divisions of the sacral plexus? A. B. C. D. E. Common peroneal Anococcygeal Pudendal Nerve to the quadrates femoris Nerve to the obturator internus and superior gemellus 10. These statements about pevic splanchnic nerves are correct EXPECT for which of the following? A. They contain pregangllonic parasympathetic fibers B. They convey visceral afferents from the pelvic plexus to sacral segments of the spinal cord C. They contribute to formation of the interior hypogastric plexus D. They are branches of the sciatic nerve E. They are known as nervi erigentes 11. Infection may reach the ischiorectal fossa from all EXPECT which one of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Inflammation of the anal sinuses Downward extension of a perirectal abscess Following a tear in the anal mucous membrane A penetrating wound in the anal region A ruptured urethra 12. In the female, the deep perineal space consists all EXCEPT which one of the following structures? A. B. C. D. E. The greater vestibular glands Part of the urethra The inferior part of the vagina The deep transverse perineal muscles The sphincter urethrae 13. All of these are true about the urinary bladder EXCEPT that A. Its base is the superior posterior surface B. The medium umbilical ligament is attached to its apex C. Its neck leads into the urethra D. When distended, it becomes lower in position E. Its body shows superior and inferolateral surfaces 14. Correct relationships of the female ureters include which of the following? A. The ureters pass lateral to the vagina B. The ureters are not in close proximity to the vesical nerve plexus C. At the base of the broad ligament the uterine artery crosses above and in front of the ureters D. The ureters enter the anterior aspect of the bladder. E. At the pelvic brim the ovarian vessels cross medial to the ureters 15. Territories supplied by the prudendal nerve include all the following EXCEPT the A. Pelvic surface of the levator ani B. Anal triangle C. Urogenital triangle D. Labium majus E. Scrotum 16. The pelvic diagram is composed of all the following muscles EXCEPT the A. Coccygeus B. Iliococcgeus C. Piriformis D. Pubococcygeus E. Puborectalis 17. Which of the following arteries is a terminal branch of the popliteal artery? A. Anterior tibial B. Dorsalis pedis C. Peroneal D. Medial superior genicular E. Sural 18. Clinicians often refer to which of the following articulations as “facet joints”? A. Opposing articular processes of adjacent vertebral arches B. Ribs and transverse ventral processes C. Vertebrae and adjacent intervertebral discs D. Adjacent vertebral bodies E. Adjacent vertebral spinous processes 19. The chief of the gluteus medlus is A. Extension at the hip joint B. Flexion at the hip joint C. Medial rotation of the femur D. Abduction at the hip joint E. Abduction at the hip joint 20. Which of the following muscles can extend the thigh at the hip without at the same time producing flexion at the knee? A. Biceps femoris, long head B. Semitendinosus C. Biceps femoris, short head D. Adductor magnus E. Semimembranosus 21. The seminal colliculus A. Is also known as the perineal membrane B. Contains the openings of the prostate glandular ducts C. Is within the membranous urethra D. Contains the ostia of the ejaculatory ducts E. None of the above 22. With regard to the contents of Alcock’s Canal A. A pudendal nerve block would completely anesthetize the scrotum B. The artery would terminate as the perineal artery and inferior rectal artery C. They travel in fascia on the surface of the obturator externus D. They enter the lesser sciatic foramen E. No afferent fibers travel in the pudendal nerve 23. The common peroneal nerve is most easily injured at which of the following locations? A. Where it leaves the sciatic nerve in the popliteal fossa B. As it branches into the short head of the biceps femoris C. Just behind the head of the fibula D. Where it emerges below the piriformis muscle E. At the place its divides into the superficial and deep peroneal nerves 24. Which of the following muscles is NOT a plantar flexor at the ankle? A. Gastrocnemius B. Soleus C. Peroneus longus D. Peroneus tertius E. Posterior tibial 25. An L2 transverse process fracture caused by major trauma should prompt consideration of which of the following? A. Doudenal hematoma B. Renal pedicle injury C. Pancreatic injury D. Ruptured spleen E. None of the above 26. Fracture of the base of the tibial intercondylar eminence implies detachment of which one of the following? A. B. C. D. E. Anterior cruciate ligament Posterior cruciate ligament Medial collateral ligament Lateral collateral ligament Infrapatellar tendon 27. At vertebral level A. L5 is the umbilical plane B. L4 is the vena cava forms C. L1 is the subscostal plane D. L4 the aorta bifurcates E. None of the above 28. Intrinsic back muscles A. Are innervated by anterior primary rami of spinal nerves B. Include the erector spinae and serratus posterior muscle groups C. Include the splenius capitis, even though it attaches to the cranium D. Anteriority flex the vertebral column E. Include the lastissimus since it originates from the thoracodorsal aponeurosis 29. A dissection of the spinal cord will indicate A. The filum terminate internum consists of dura mater B. An extension of the subarachnoid space surrounds the posterior root ganglia C. A potential, not actual , epidural space D. A vertebral venous plexus only in the pelvic region E. Equal segmental arterial supply of the cord at all levels 30. The uterus is normally A. Anteflexed and anteverted B. Anteflexed and retroverted C. Retroflexed and anterverted D. Retroflexed and retroverted 31. With regard to the fascias of the perineum A. Dartos fascia of the scrotum is the same layer as Camper’s fascia B. Colles fascia encloses the contents of the superficial pouch C. Buck’s fascia encloses the contents of the deep pouch D. Scarpa’s fascia is the same layer as Buck’s fascia E. None of the above 32. The ureter A. Is supplied by a solitary and artery B. Enters the pelvis at the origin of the internal iliac artery C. Enters the pelvis at the pectin pubis D. Normally has but one constriction of its diameter E. Is of uniform caliber along its length 33. Traumatic spondyiollsthesis of C2, e.g; the hangman’s fracture, involves which of the following parts of the axis vertebra? A. Pedicle B. Articular mass C. Pars Interarticularis D. Laminae E. Body FOR THE FOLLOWING QUESTIONS ANSWER A. If choices 1, 2 and 3 are correct B. If choices 1 and 3 are correct C. If choices 2 and 4 are correct D. If only choice 4 is correct E. If all choices are correct 34. Which of the following statements correctly apply to the spinal dura mater? 1. It forms dural sleeves that continue into the intervertebral foramina 2. It becomes continuous with the epineurium 3. It is continuous with the cranial dura mater 4. It is usually ends at the level of the lower border of S2 in adults 35. Which of the following statements correctly apply to the spinal dura mater? 1. Together the pia mater and the arachnoid are called the leptomeninges 2. The subarachnoid space is a potential space 3. The subarachnoid space contains cerebrospinal fluid 4. The subarachnoid space extending from L2 to S2 is known as the cerebellomedullary cistern 36. Which of the following structures may be observed on the visceral surface of the liver? 1. Porta hepatis 2. Gallbladder 3. Fissure for the ligamentum teres 4. Fissure for the ligamentum venosum 37. Regarding the femoral triangle 1. The apex is the beginning of the adductor canal 2. The femoral vein is lateral to the femoral artery in the femoral sheath 3. A femoral hernia would be located medial to the femoral artery 4. The vastus laterals muscles forms the lateral border of the triangle 38. Which of the following is true of the foot? 1. The talus transmits the body weight to the plantar surface 2. The deltoid ligament courses from the fibula to the navicular bone 3. The calcaneonavicular or “spring” ligament supports the talus 4. The peroneal muscles are related to the medial malleolus 39. The lymph vessels from the anal canal superior to the pecinate line drain into which of the following? 1. Internal iliac nodes 2. Common iliac nodes 3. Aortic lymph nodes 4. Superficial inguinal nodes 40. The first layer of plantar muscles includes the 1. Flexor digitorum longus 2. quadratus plantae 3. Flexor hallucis brevis 4. Flexor digitorum brevis 41. With regard to the hip joint 1. A Cruciate anastomosis will found on the anterior surface of the joint capsule 2. The ligaments of the hip joint particularly strengthen the joint in flexion 3. An illopsoas bursa is present on the inferior aspect of the joint capsule 4. Development of an avascular necrosis of the femoral head may be a possible complication of a femoral neck fracture 42. The anal pectin is 1. A feature of the ischiorectal fossa 2. A feature of the cutaneous portion of the anal canal 3. Synonymous with the anal verge 4. A smooth, hairiess band in the anal canal 43. With regard to fascias of the anterior abdominal wall 1. The posterior rectus sheath below the linea arcuata is composed only of transversalis fascia 2. Transversalis fascia is synonymous with fascia of the transverses abdominous 3. The sac of an indirect inguinal hernia is composed of all the fascial layers of the spermatic cord 4. The median umbilical fold of peritoneum covers the inferior epigastric artery 44. During normal gait 1. The pelvis rotates and tiits 2. action of the gluteus medius is crucial 3. the knee flexes during swing 4. the foot dorsiflexes during swing 45. Arterial supply of the 2nd and 3rd portions of the duodenum 1. Is derived from the celiac artery 2. Arises from the Marginal artery of Drummond 3. Is derived from the superior mesenteric artery 4. Is anastomotic with the right renal artery 46. Which are true with regard to vertebrae? 1. Lumbar vertebrae have mammiliary processes 2. Thoracic vertebrae have a physiological kyphosis 3. The Atias has no body 4. There are 4 lumbar vertebrae in the case of lumbar sacralizaiton 47. Abdominal structures with NO mesentery include the 1. 2nd or descending portion of the duodenum 2. Appendix 3. Rectum 4. Sigmoid colon MATCHING : A. Male B. Female C. Both A and B D. Neither A nor B 48. Cowper’s Glands 49. Alcock’s Canal 50. Cardinal Ligament ( of Mackinrodt )