* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Penile Anatomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
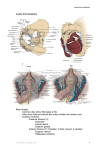
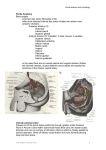
PENILE ANATOMY Parts – Root, Body and Glans Root attached to the inferior surface of the perineal membrane and consists of central bulb of the penis with a crus on each side Bulb is on the posterior end of the corpus spongiosum, crus at the end of the corpus cavernosa Crus attached to the angle between the perineal membrane and pubic ramus. Dorsal artery, deep artery, urethral artery and artery of the urethral bulb (branches from internal pudendal artery – terminal branch from anterior division of internal iliac) penetrate the perineal membrane to supply the penis Suspensory ligament o triangular sheet consisting of two lateral, circumferential, and one median bundles, which circumscribes the dorsal vein of the penis o between the undersurface of the pubis symphysis and the tunica albuginea of the corpora cavernosa. o maintains the base of the penis in front of the pubis and to behave as a major point of support for the mobile portion of the penis during erection. Suspensory ligament Body/Shaft of Penis Fascial layers 1. Superficial (Dartos) fascia - Continuous with Colles fascia (=Scarpa’s fascia) 2. Buck’s fascia 3. Tunica albuginea of penis a. Tough fibrous membrane b. Surrounds each corpora c. That of the corpus spongiosum enlarges distally to surround the glans superficial perineal fascia (Colles' fascia) is attached o laterally to the pubic rami and fascia lata of the thighs o posteriorly to the urogenital diaphragm and perineal membrane. Blood Supply (Cormack and Lamberty) Superficial Supply The arterial supply of the superficial fascia and skin of the shaft of the penis to the corona comes from the superficial and deep external pudendal arteries (branches from common femoral artery) o DEPA is usually dominant with SEPA contributing to the dorsal base. o Distally DEPA anastamoses with branches of the deep arteries at the level of the prepuce o Prepuce predominantly supplied by small perforators from the corpora cavernosum/spongiosum The venous supply of the skin drains to the superficial dorsal vein which empties into the superficial external pudendal and great saphenous veins Deep Supply From the internal pudendal artery (anterior division internal iliac artery) Pierces the perineal membrane medial to the dorsal nerve Sends artery to the buld and urethral artery to the corpus spongiosum Deep artery to the penis travels in corpus carvenosum Smaller dorsal artery traverses through the suspensory ligament under Buck’s fascia medial to the nerve to supply deep fascia and glans Lymphatic Drainage Glans and Corpora drain to the internal iliac nodes Penile shaft skin drain to the superficial inguinal nodes (medial group) Nerve supply Skin Shaft (S2) from posterior scrotal and dorsal nerves (pudendal branches) Glans from dorsal nerve Bulbocavernosus and ischiocavernosus From perineal nerve (from the pudendal S2,3) Contracts during ejaculation Sympathetics L1 spinal cord via superior and inferior hypogastric plexus Required for initial stages of ejaculation Parasympathetic Pelvic splanchnic nerves (S2,3) Allows increased blood flow for erection