Ch. 16: Solutions - Quynh Nguyen Official Website
... Amides are derivative of carboxylic acids, in which a nitrogen group replaces the hydroxyl group. Amide is formed when a salt of carboxylic with ammonia or amine is heated; a molecule of water is eliminated. Amide can be hydrolyzed back to carboxylic acid and ammonium salt in acidic solution, or t ...
... Amides are derivative of carboxylic acids, in which a nitrogen group replaces the hydroxyl group. Amide is formed when a salt of carboxylic with ammonia or amine is heated; a molecule of water is eliminated. Amide can be hydrolyzed back to carboxylic acid and ammonium salt in acidic solution, or t ...
HSE Chemistry Questions
... NaCl ? ( mol. Wt. of NaCl=58.5 ) ( c ) For complete oxidation 60 ml of a ferrous sulphate solution with KMnO4 in acid medium the amount of 0.01 M K2Cr2O7 required for the same oxidation. ( d ) An aqueous solution is 0.01 M CH3OH. The concentration of the solution ...
... NaCl ? ( mol. Wt. of NaCl=58.5 ) ( c ) For complete oxidation 60 ml of a ferrous sulphate solution with KMnO4 in acid medium the amount of 0.01 M K2Cr2O7 required for the same oxidation. ( d ) An aqueous solution is 0.01 M CH3OH. The concentration of the solution ...
Esters - chymist.com
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
... In contrast to inorganic reactions, which usually involve metals combining with non-metals or polyatomic ions, organic reactions occur as additions or substitutions into a compound or as a condensation-type reaction where removal of certain atoms or groups cause two molecules to combine. One type of ...
4.4 Formation of Esters from Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols
... process. Note that a water molecule is removed in the process of forming the ester from the carboxylic acid and the alcohol. The water comes from removing an OH group on the carboxylic acid and combining it with a H. One can show this using “lasso” chemistry as shown ...
... process. Note that a water molecule is removed in the process of forming the ester from the carboxylic acid and the alcohol. The water comes from removing an OH group on the carboxylic acid and combining it with a H. One can show this using “lasso” chemistry as shown ...
Topic 8.4 Acids and Bases The pH Scale
... power of hydrogen’, the scale provides a simple and universal measurement of the amount of hydrogen ions in a solution, which affects its acidity and how it reacts chemically. ...
... power of hydrogen’, the scale provides a simple and universal measurement of the amount of hydrogen ions in a solution, which affects its acidity and how it reacts chemically. ...
Acid Spill - Rosshall Academy
... 16 Which of the following is the best description of a salt? A. An acid with the hydrogen replaced by a metal B. An acid with the hydrogen ions replaced by metal ions or ammonium ions C. An acid that has been neutralised by an alkali D. An acid with the hydrogen ions replaced by ammonium ions 17 The ...
... 16 Which of the following is the best description of a salt? A. An acid with the hydrogen replaced by a metal B. An acid with the hydrogen ions replaced by metal ions or ammonium ions C. An acid that has been neutralised by an alkali D. An acid with the hydrogen ions replaced by ammonium ions 17 The ...
Incompatible Chemicals
... for corrosives, and a fifth color for less hazardous materials. The following tables are provided to assist laboratories with storage of reactive chemicals when container labels do not include segregation colors. In each table, chemicals listed on the left may react with chemicals listed on the righ ...
... for corrosives, and a fifth color for less hazardous materials. The following tables are provided to assist laboratories with storage of reactive chemicals when container labels do not include segregation colors. In each table, chemicals listed on the left may react with chemicals listed on the righ ...
Part1. Acid rain formation. 1. Discovery of acid rain.
... Acid rain today is produced mainly from emissions of sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) generated by human activities, which are oxidized in the atmosphere to form sulfuric and nitric acids, respectively. However, various species can be found in rainwater. ...
... Acid rain today is produced mainly from emissions of sulfur oxides (SOx) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) generated by human activities, which are oxidized in the atmosphere to form sulfuric and nitric acids, respectively. However, various species can be found in rainwater. ...
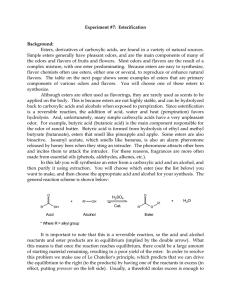
102 Lab 7 Esters Fall05
... and/or ease of purification at the end of the reaction. In this reaction we will add an excess of the acid. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, ...
... and/or ease of purification at the end of the reaction. In this reaction we will add an excess of the acid. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, ...
ACID AND BASES
... Bases react with acids to produce a salt and water The pH level of bases ranges from 8 to 14 A base with a pH of 8 is a weak base A base with a pH of 14 is a strong base Examples of bases: baking soda, ...
... Bases react with acids to produce a salt and water The pH level of bases ranges from 8 to 14 A base with a pH of 8 is a weak base A base with a pH of 14 is a strong base Examples of bases: baking soda, ...
ACID AND BASES
... Bases react with acids to produce a salt and water The pH level of bases ranges from 8 to 14 A base with a pH of 8 is a weak base A base with a pH of 14 is a strong base Examples of bases: baking soda, ...
... Bases react with acids to produce a salt and water The pH level of bases ranges from 8 to 14 A base with a pH of 8 is a weak base A base with a pH of 14 is a strong base Examples of bases: baking soda, ...
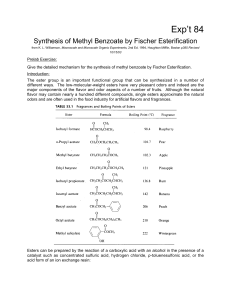
Synthesis of Methyl Benzoate by Fisher Esterification
... concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester is only about 8°C higher than the boiling points o ...
... concentration of either the alcohol or acid, as noted above. If either one is doubled, the theoretical yield increases to 85%. When one is tripled, it goes to 90%. But note that in the example cited the boiling point of the relatively nonpolar ester is only about 8°C higher than the boiling points o ...
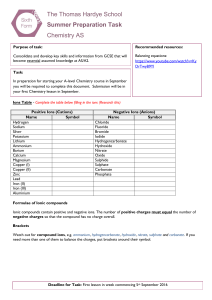
The Thomas Hardye School Summer Preparation Task Chemistry AS
... Moles – 3 significant figures Concentrations – 3 significant figures Temperatures – 1 decimal place Masses - 2 decimal places Common Acids and Bases (alkali’s) -Complete the table below Acids Name Sulphuric acid ...
... Moles – 3 significant figures Concentrations – 3 significant figures Temperatures – 1 decimal place Masses - 2 decimal places Common Acids and Bases (alkali’s) -Complete the table below Acids Name Sulphuric acid ...
carboxylic acids
... • Carboxylic acids have significantly higher boiling points than their corresponding alcohols or alkanes. ...
... • Carboxylic acids have significantly higher boiling points than their corresponding alcohols or alkanes. ...
Document
... Students will be able to describe the difference between a strong and weak acid or base Students will be able to articulate the conceptual and mathematical relationships between pH, Ka and Keq Students will be able to describe the solution of the equation for Ka given initial conditions Exerci ...
... Students will be able to describe the difference between a strong and weak acid or base Students will be able to articulate the conceptual and mathematical relationships between pH, Ka and Keq Students will be able to describe the solution of the equation for Ka given initial conditions Exerci ...
Chapter 07
... • Sodium hydroxide removes a proton to form the salt. • Adding a strong acid, like HCl, regenerates the carboxylic acid. ...
... • Sodium hydroxide removes a proton to form the salt. • Adding a strong acid, like HCl, regenerates the carboxylic acid. ...
Ethers and Epoxides
... Ethers and Their Relatives • An ether has two organic groups (alkyl, aryl, or vinyl) bonded to the same oxygen atom, R–O–R • Diethyl ether is used industrially as a solvent • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether • Thiols (R–S–H) and sulfides (R–S–R) are sulfur (for oxygen) an ...
... Ethers and Their Relatives • An ether has two organic groups (alkyl, aryl, or vinyl) bonded to the same oxygen atom, R–O–R • Diethyl ether is used industrially as a solvent • Tetrahydrofuran (THF) is a solvent that is a cyclic ether • Thiols (R–S–H) and sulfides (R–S–R) are sulfur (for oxygen) an ...
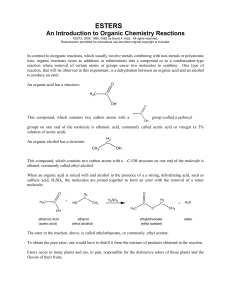
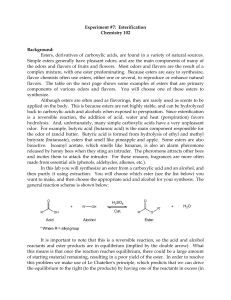
ESTERIFICATION
... and/or ease of purification at the end of the reaction. In this reaction we will add an excess of the acid. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, ...
... and/or ease of purification at the end of the reaction. In this reaction we will add an excess of the acid. Sulfuric acid (H2SO4) is used as a catalyst for this reaction in order to accelerate the rate at which the product is formed. Since a catalyst is not consumed during the course of a reaction, ...
AP Chemistry - Partners4results
... d. A buffer solution is prepared by dissolving some solid NaOCl in a soluliotn of HOCl at 298K. The pH of the buffer solution is determined to be 6.48. (i) Calculate the value of [H+] in the buffer solution. ...
... d. A buffer solution is prepared by dissolving some solid NaOCl in a soluliotn of HOCl at 298K. The pH of the buffer solution is determined to be 6.48. (i) Calculate the value of [H+] in the buffer solution. ...
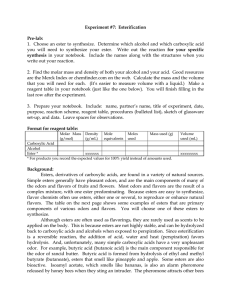
Lab 7_Esterification
... of starting material remaining, resulting in a poor yield of the ester. In order to resolve this problem we make use of Le Chatelier's principle, which predicts that we can drive the equilibrium to the right (to the products) by having one of the reactants in excess (in effect, putting pressure on t ...
... of starting material remaining, resulting in a poor yield of the ester. In order to resolve this problem we make use of Le Chatelier's principle, which predicts that we can drive the equilibrium to the right (to the products) by having one of the reactants in excess (in effect, putting pressure on t ...
The Buffer Equation
... compounds, such as boron trifluoride and aluminum chloride, although not containing hydrogen and consequently not serving as proton donors, are nevertheless acids in this scheme. Many substances that do not contain hydroxyl ions, including amines, ethers, and carboxylic acid anhydrides, are classifi ...
... compounds, such as boron trifluoride and aluminum chloride, although not containing hydrogen and consequently not serving as proton donors, are nevertheless acids in this scheme. Many substances that do not contain hydroxyl ions, including amines, ethers, and carboxylic acid anhydrides, are classifi ...
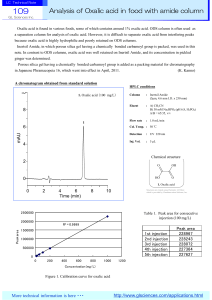
Analysis of Oxalic acid in food with amide column
... because oxalic acid is highly hydrophilic and poorly retained on ODS columns. Inertsil Amide, in which porous silica gel having a chemically bonded carbamoyl group is packed, was used in this note. In contrast to ODS columns, oxalic acid was well retained on Inertsil Amide, and its concentration in ...
... because oxalic acid is highly hydrophilic and poorly retained on ODS columns. Inertsil Amide, in which porous silica gel having a chemically bonded carbamoyl group is packed, was used in this note. In contrast to ODS columns, oxalic acid was well retained on Inertsil Amide, and its concentration in ...
reactions of functional groups of organic compounds with
... alcohol (which is oxidized to acetaldehyde). For aldehyde detection is used Schiff’s reagent (Exercise 1.1). This reagent form colored compound in presence of aldehydes to gives so called Schiff’s bases (aldimine; exercise 1.2) The aldehyde group is present in the entire spectrum of biologically sig ...
... alcohol (which is oxidized to acetaldehyde). For aldehyde detection is used Schiff’s reagent (Exercise 1.1). This reagent form colored compound in presence of aldehydes to gives so called Schiff’s bases (aldimine; exercise 1.2) The aldehyde group is present in the entire spectrum of biologically sig ...
Sulfuric acid
Sulfuric acid (alternative spelling sulphuric acid) is a highly corrosive strong mineral acid with the molecular formula H2SO4 and molecular weight 98.079 g/mol. It is a pungent-ethereal, colorless to slightly yellow viscous liquid which is soluble in water at all concentrations. Sometimes, it is dyed dark brown during production to alert people to its hazards. The historical name of this acid is oil of vitriol.Sulfuric acid is a diprotic acid and shows different properties depending upon its concentration. Its corrosiveness on other materials, like metals, living tissues or even stones, can be mainly ascribed to its strong acidic nature and, if concentrated, strong dehydrating and oxidizing properties. Sulfuric acid at a high concentration can cause very serious damage upon contact, since not only does it cause chemical burns via hydrolysis, but also secondary thermal burns through dehydration. It can lead to permanent blindness if splashed onto eyes and irreversible damage if swallowed. Accordingly, safety precautions should be strictly observed when handling it. Moreover, it is hygroscopic, readily absorbing water vapour from the air.Sulfuric acid has a wide range of applications including domestic acidic drain cleaner, electrolyte in lead-acid batteries and various cleaning agents. It is also a central substance in the chemical industry. Principal uses include mineral processing, fertilizer manufacturing, oil refining, wastewater processing, and chemical synthesis. It is widely produced with different methods, such as contact process, wet sulfuric acid process and some other methods.