Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 076101 - APS Link Manager
... latter holds the key for recovering the object and determines the ultimate image resolution. If one knows the amplitude and phase of either the non-R or the R part, the object structure can be directly calculated by Fourier inversion. In practice, this will typically not be the case. Therefore, the ...
... latter holds the key for recovering the object and determines the ultimate image resolution. If one knows the amplitude and phase of either the non-R or the R part, the object structure can be directly calculated by Fourier inversion. In practice, this will typically not be the case. Therefore, the ...
Michelson Lab Guide UTSA
... Adjust Slowly: As you align the mirrors to observe the ring pattern or interference walk the mirror left and right and up and down slowly. If you pass through alignment quickly you will not observe the effect. Air Cell: DO NOT exceed a pressure of 100 kPa over atmosphere. Interference occurs when tw ...
... Adjust Slowly: As you align the mirrors to observe the ring pattern or interference walk the mirror left and right and up and down slowly. If you pass through alignment quickly you will not observe the effect. Air Cell: DO NOT exceed a pressure of 100 kPa over atmosphere. Interference occurs when tw ...
Calculation of Complete Absorption and Intensity of Optical
... effective thickness of the absorbing layer at the moment of time t, x is the length of the absorbent, and L is the cavity base. It must pointed out here that, in the particular case where a laser pulse can be approximated by a ...
... effective thickness of the absorbing layer at the moment of time t, x is the length of the absorbent, and L is the cavity base. It must pointed out here that, in the particular case where a laser pulse can be approximated by a ...
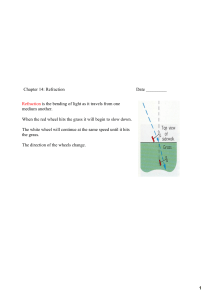
1 Chapter 14: Refraction
... When light moves from one medium to another, part of it is reflected and part is refracted. When light moves from a material in which its speed is higher (air) to a material in which its speed is lower (glass), the ray is bent _________ the normal. When light moves from material in which its speed ...
... When light moves from one medium to another, part of it is reflected and part is refracted. When light moves from a material in which its speed is higher (air) to a material in which its speed is lower (glass), the ray is bent _________ the normal. When light moves from material in which its speed ...
Chapter 1 - Liceo Crespi
... oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation. Unlike a wave on a string or a sound wave, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium in which to propagate. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or through substances (depending on the absorptio ...
... oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation. Unlike a wave on a string or a sound wave, electromagnetic waves do not require a medium in which to propagate. Electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum or through substances (depending on the absorptio ...
Refractive Index Measurement Principle - K
... The measuring prism provides the interface between the instrument and the medium which is measured. The geometry of the optical system is such that light rays at a certain selection of angles α are projected onto the prism surface. The actual angles are chosen so that the desired refractive index ra ...
... The measuring prism provides the interface between the instrument and the medium which is measured. The geometry of the optical system is such that light rays at a certain selection of angles α are projected onto the prism surface. The actual angles are chosen so that the desired refractive index ra ...
Modified copy of Flame Tests 2013
... is considerably different from that seen in the laboratory. This effect is primarily due to the presence of oxidizers and fuels that produce unwanted colors or otherwise mask the light given off by the coloring agents. Sodium is often viewed as an impurity because a small amount of sodium can cause ...
... is considerably different from that seen in the laboratory. This effect is primarily due to the presence of oxidizers and fuels that produce unwanted colors or otherwise mask the light given off by the coloring agents. Sodium is often viewed as an impurity because a small amount of sodium can cause ...
File
... 14. Unpolarised or ordinary light :In such light oscillation of electric field occur in all directions in a plane perpendicular to the direction of light propogation. 15. Polarisation : It is the phenomenon in which electric vectors of light restricted to a particular plane after passing through a n ...
... 14. Unpolarised or ordinary light :In such light oscillation of electric field occur in all directions in a plane perpendicular to the direction of light propogation. 15. Polarisation : It is the phenomenon in which electric vectors of light restricted to a particular plane after passing through a n ...
Chemistry - Unit 6 What do you need to know?? This chapter is on
... bell. It doesn't matter if you have an army of 10 year olds (intensity) lined up to take their turn none of them will ever hit it hard enough to ring the bell. However, Arnold (being Arnold) will have no problem ringing the bell. Thus, if a light shining on a metal does not have enough photons with ...
... bell. It doesn't matter if you have an army of 10 year olds (intensity) lined up to take their turn none of them will ever hit it hard enough to ring the bell. However, Arnold (being Arnold) will have no problem ringing the bell. Thus, if a light shining on a metal does not have enough photons with ...
Waves and Energy
... In 1913, Niels Bohr, a young Danish physicist proposed a quantum model for the hydrogen atom that seemed to answer this question. Impressively, Bohr's model also correctly predicted the frequencies of the lines in hydrogen's atomic emission spectrum. Bohr proposed that the hydrogen atom has only cer ...
... In 1913, Niels Bohr, a young Danish physicist proposed a quantum model for the hydrogen atom that seemed to answer this question. Impressively, Bohr's model also correctly predicted the frequencies of the lines in hydrogen's atomic emission spectrum. Bohr proposed that the hydrogen atom has only cer ...
Total Internal Reflection Microscopy
... Total Internal Reflection Microscopy TIRM is a optical technique for monitoring the instantaneous separation distance between a microscopic sphere and a flat plate. Changes in distance as small as 1 nm can be detected. To determine the instantaneous separation distance, we measure the intensity of l ...
... Total Internal Reflection Microscopy TIRM is a optical technique for monitoring the instantaneous separation distance between a microscopic sphere and a flat plate. Changes in distance as small as 1 nm can be detected. To determine the instantaneous separation distance, we measure the intensity of l ...
2. Spectral Stray Light
... The results of the spectral stray light characterisation measurements (Damm 2007) are illustrated in fig. 3. It can be seen that the spectral stray light can span 60 or more channels. The gap around channel 0 is due to the fact that only the out-of-band channels are shown (Damm 2007). While this met ...
... The results of the spectral stray light characterisation measurements (Damm 2007) are illustrated in fig. 3. It can be seen that the spectral stray light can span 60 or more channels. The gap around channel 0 is due to the fact that only the out-of-band channels are shown (Damm 2007). While this met ...
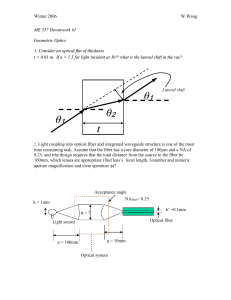
ME 557 Howmwork #1
... Light coupling into optical fiber and integrated waveguide structure is one of the most time consuming task. Assume that the fiber has a core diameter of 100m and a NA of 0.25, and trhe design requires that the total distance from the source to the fiber be 100mm, which lenses are appropriate (find ...
... Light coupling into optical fiber and integrated waveguide structure is one of the most time consuming task. Assume that the fiber has a core diameter of 100m and a NA of 0.25, and trhe design requires that the total distance from the source to the fiber be 100mm, which lenses are appropriate (find ...
Solved Problems in the Quantum Theory of Light
... Given here are solutions to 7 problems in the Quantum Theory of Light. The solutions were used as a learning-tool for students in the introductory undergraduate course Physics 200 Relativity and Quanta given by Malcolm McMillan at UBC during the 1998 and 1999 Winter Sessions. The solutions were prep ...
... Given here are solutions to 7 problems in the Quantum Theory of Light. The solutions were used as a learning-tool for students in the introductory undergraduate course Physics 200 Relativity and Quanta given by Malcolm McMillan at UBC during the 1998 and 1999 Winter Sessions. The solutions were prep ...
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy

Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy or ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry (UV-Vis or UV/Vis) refers to absorption spectroscopy or reflectance spectroscopy in the ultraviolet-visible spectral region. This means it uses light in the visible and adjacent (near-UV and near-infrared [NIR]) ranges. The absorption or reflectance in the visible range directly affects the perceived color of the chemicals involved. In this region of the electromagnetic spectrum, molecules undergo electronic transitions. This technique is complementary to fluorescence spectroscopy, in that fluorescence deals with transitions from the excited state to the ground state, while absorption measures transitions from the ground state to the excited state.