* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1 Chapter 14: Refraction
Night vision device wikipedia , lookup
Harold Hopkins (physicist) wikipedia , lookup
Nonimaging optics wikipedia , lookup
Surface plasmon resonance microscopy wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Bioluminescence wikipedia , lookup
Nonlinear optics wikipedia , lookup
Magnetic circular dichroism wikipedia , lookup
Speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Ray tracing (graphics) wikipedia , lookup
Ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Refractive index wikipedia , lookup
Birefringence wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Young (scientist) wikipedia , lookup
Transparency and translucency wikipedia , lookup
Atmospheric optics wikipedia , lookup
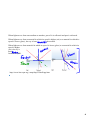
Chapter 14: Refraction Date _________ Refraction is the bending of light as it travels from one medium another. When the red wheel hits the grass it will begin to slow down. The white wheel will continue at the same speed until it hits the grass. The direction of the wheels change. 1 2 The wave front represents the trough of the light wave. The distance between to wave fronts is a _____________ The light ray is the direction of the motion of the wave front. As light enters a different medium, (water in this case) the wave front slows down, but the wave fronts in the air continue to travel at the speed of light in air. The slower wave fronts in water travel a smaller distance than the wave fronts in air so the entire wave front changes direction. The wavelength decreases in water, so the speed of the light in water decreases. The frequency doesn't change. Refraction occurs when light's _________ changes. 3 When light moves from one medium to another, part of it is reflected and part is refracted. When light moves from a material in which its speed is higher (air) to a material in which its speed is lower (glass), the ray is bent _________ the normal. When light moves from material in which its speed is lower (glass) to a material in which its speed is higher (air), the ray is bent ________ from the normal. http://www.loncapa.org/~mmp/kap25/Snell/app.htm 4 Index of refraction for a substance is the ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in that substance. The index of refraction is a dimensionless number that is always greater than one. The larger the index of refraction the slower light travels in that substance. The amount that light bends when entering a medium depends on the wavelength of the light as well as the speed. That is why a color spectrum is produced when white light passes through a prism. Each color has a different wavelength so each color is refracted a different amount. 5 Objects appear to be in different places due to refraction. The cat looks at the fish, but because of refraction the fish looks like it is closer to the surface than it really is. The fish looks at the cat, but because of refraction, the cat looks like it is farther from the surface than it really is. 6 Black Board Optics When the incident light ray enters the block parallel to the normal __________________________________________. As the angle of incidence increases, what happens to the angle of refraction? When light moves into a different medium with a higher index of refraction, in what direction does the light ray bend? When light moves into a different medium with a lower index of refraction, in what direction does the light ray bend? 7 Label the incident light ray. Which is greater the angle of refraction or the angle of incidence? Is the refracted light ray bent towards or away from the normal? Light travels faster in which substance? 1 or 2 Which substance has a greater index of refraction 1 or 2 Snell's Law can determine the angle of refraction: ni sin θi = nr sin θr 8 Attachments 70657.html 70657.swf