Support Systems of the Nervous System
... • On surface of cerebral hemispheres • Most empty into superior sagittal sinus – Some connect to other sinuses located between the two layers of the dura ...
... • On surface of cerebral hemispheres • Most empty into superior sagittal sinus – Some connect to other sinuses located between the two layers of the dura ...
Pig Dissection - Milton
... so that the legs are spread eagle and not in your way. Use scissors to cut through the skin and muscles according to the diagram. Do not remove the umbilical cord. In the first section, you will only examine the abdominal cavity (the area below the ribcage). After completing the cuts, locate the umb ...
... so that the legs are spread eagle and not in your way. Use scissors to cut through the skin and muscles according to the diagram. Do not remove the umbilical cord. In the first section, you will only examine the abdominal cavity (the area below the ribcage). After completing the cuts, locate the umb ...
Peripheral nervous system
... • 2. Ventral roots form by convergence of rootlets exiting from the ventral surface • 3. Dorsal Root Ganglion - found on the dorsal root just before it joins the ventral root ...
... • 2. Ventral roots form by convergence of rootlets exiting from the ventral surface • 3. Dorsal Root Ganglion - found on the dorsal root just before it joins the ventral root ...
Children The Early Years by Anita Decker
... Items Needed 4 large bags of marshmallow toothpicks ...
... Items Needed 4 large bags of marshmallow toothpicks ...
ductus venosus
... becomes the medial umbilical ligament as the adult remnant. o These arteries carry deoxygenated blood back to the placenta. 8. Explain what happens to the formaen ovale and the ductus arteriosus at birth? ...
... becomes the medial umbilical ligament as the adult remnant. o These arteries carry deoxygenated blood back to the placenta. 8. Explain what happens to the formaen ovale and the ductus arteriosus at birth? ...
Chapter 29
... • Mesoderm—a more loosely organized tissue which differentiates into a loose fetal connective tissue, called mesenchyme – Gives rise to muscle, bone, and blood – Composed of a loose network of wispy mesenchymal cells embedded in a gelatinous ground substance ...
... • Mesoderm—a more loosely organized tissue which differentiates into a loose fetal connective tissue, called mesenchyme – Gives rise to muscle, bone, and blood – Composed of a loose network of wispy mesenchymal cells embedded in a gelatinous ground substance ...
Chapter 29 *Lecture PowerPoint Human Development
... • Mesoderm—a more loosely organized tissue which differentiates into a loose fetal connective tissue, called mesenchyme – Gives rise to muscle, bone, and blood – Composed of a loose network of wispy mesenchymal cells embedded in a gelatinous ground substance ...
... • Mesoderm—a more loosely organized tissue which differentiates into a loose fetal connective tissue, called mesenchyme – Gives rise to muscle, bone, and blood – Composed of a loose network of wispy mesenchymal cells embedded in a gelatinous ground substance ...
Extraembryonic membranes
... The chorion cushions the embryo against mechanical shocks. The allantois functions as a disposal sac for uric acid. ...
... The chorion cushions the embryo against mechanical shocks. The allantois functions as a disposal sac for uric acid. ...
Pig
... the esophagus. The stomach is responsible for producing pepsinogen, HCl acid and mucus. 5. At each end of the stomach are valves that regulate food entering and leaving the stomach. At the esophagus is the cardiac sphincter valve, and at the duodenum is the pyloric sphincter valve. View the inside o ...
... the esophagus. The stomach is responsible for producing pepsinogen, HCl acid and mucus. 5. At each end of the stomach are valves that regulate food entering and leaving the stomach. At the esophagus is the cardiac sphincter valve, and at the duodenum is the pyloric sphincter valve. View the inside o ...
Human Embryology Development
... • The embryo remains an embryo for 8 weeks, then it will be referred to as a fetus. • The ‘yolk sac’ is another key element which acts as the circulatory system for the embryo. ...
... • The embryo remains an embryo for 8 weeks, then it will be referred to as a fetus. • The ‘yolk sac’ is another key element which acts as the circulatory system for the embryo. ...
Extraembryonic blood vessels form during the early 3rd week
... Proximal portions of both umbilical veins, and entire RIGHT umbilical vein degenerate. The caudal, LEFT umbilical vein is the only remaining path from placenta to liver. The left umbilical vein forms an anastomosis with the ductus venosus (a transient shunt that develops in the liver, channeling blo ...
... Proximal portions of both umbilical veins, and entire RIGHT umbilical vein degenerate. The caudal, LEFT umbilical vein is the only remaining path from placenta to liver. The left umbilical vein forms an anastomosis with the ductus venosus (a transient shunt that develops in the liver, channeling blo ...
clinical signs of arnold-chiari ii malformation in neonate/infant
... determining whether associated spinal abnormalities, such as diastematomyelia or syringomyelia, are present. The most important thing, of course, is whether or not the baby develops any clinical symptoms to suggest brainstem and/or cranial nerve dysfunction, which are the most serious and potentiall ...
... determining whether associated spinal abnormalities, such as diastematomyelia or syringomyelia, are present. The most important thing, of course, is whether or not the baby develops any clinical symptoms to suggest brainstem and/or cranial nerve dysfunction, which are the most serious and potentiall ...
SPINAL CORD -1
... Grey matter contains neural cell bodies, in contrast to white matter, which does not and mostly contains myelinated axon tracts In a transverse section each half of the gray substance is shaped like a comma or crescent, the concavity of which is directed laterally; and these, together with the inter ...
... Grey matter contains neural cell bodies, in contrast to white matter, which does not and mostly contains myelinated axon tracts In a transverse section each half of the gray substance is shaped like a comma or crescent, the concavity of which is directed laterally; and these, together with the inter ...
Blood Vessels
... Serve as conduits through which blood is circulated to every cell in the body. Tunica interna (intima) – -inner most layer of vessel wall. Lined with endothelial cells overlying a sparse layer of loose CT. Tunica media – -middle layer and thickest in arteries. Contains smooth muscle, collagen and in ...
... Serve as conduits through which blood is circulated to every cell in the body. Tunica interna (intima) – -inner most layer of vessel wall. Lined with endothelial cells overlying a sparse layer of loose CT. Tunica media – -middle layer and thickest in arteries. Contains smooth muscle, collagen and in ...
Lab Procedure (External and Internal Anatomy)
... 1. Trace the abominal aorta (also called the dorsal aorta) to the lower part of the body, careful tweezing of the tissue will reveal several places where it branches, though some of the arteries may have been cut when you removed organs of the digestive system. 2. The hepatic artery leads to the liv ...
... 1. Trace the abominal aorta (also called the dorsal aorta) to the lower part of the body, careful tweezing of the tissue will reveal several places where it branches, though some of the arteries may have been cut when you removed organs of the digestive system. 2. The hepatic artery leads to the liv ...
anterior, posterior, dorsal, ventral. In addition, you`ll need to know
... subclavian (10) The subclavians supply blood to the arms and follow the clavicle bone 7. The common carotid (4), which will branch into the left (7) and right carotid arteries (8). The carotid arteries supply blood to the head and neck. 8. Observe the coronary artery (6) on the outside of the heart ...
... subclavian (10) The subclavians supply blood to the arms and follow the clavicle bone 7. The common carotid (4), which will branch into the left (7) and right carotid arteries (8). The carotid arteries supply blood to the head and neck. 8. Observe the coronary artery (6) on the outside of the heart ...
Mesh Repair of Inguinal Hernia
... (If male: The vas deferens and testicular vessels were identified and protected during the remainder of the operation). The sac was/was not opened [and the contents were reduced into the peritoneal cavity]. The sac was twisted and suture ligated with 2-0 silk suture. Any redundant sac was excised u ...
... (If male: The vas deferens and testicular vessels were identified and protected during the remainder of the operation). The sac was/was not opened [and the contents were reduced into the peritoneal cavity]. The sac was twisted and suture ligated with 2-0 silk suture. Any redundant sac was excised u ...
Chapter 29 - Palm Beach State College
... – Trophoblasts on attachment side separate into two layers • Superficial layer is in contact with the endometrium – The plasma membranes break down – Trophoblastic cells fuse into a multinucleate mass: ...
... – Trophoblasts on attachment side separate into two layers • Superficial layer is in contact with the endometrium – The plasma membranes break down – Trophoblastic cells fuse into a multinucleate mass: ...
Pig Dissection
... so that the legs are spread eagle and not in your way. Use scissors to cut through the skin and muscles according to the diagram. Do not remove the umbilical cord. In the first section, you will only examine the abdominal cavity (the area below the ribcage). After completing the cuts, locate the umb ...
... so that the legs are spread eagle and not in your way. Use scissors to cut through the skin and muscles according to the diagram. Do not remove the umbilical cord. In the first section, you will only examine the abdominal cavity (the area below the ribcage). After completing the cuts, locate the umb ...
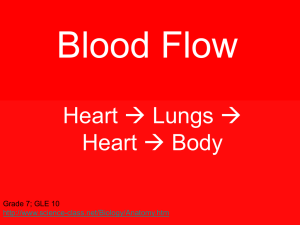
Blood Flow - WBR Teacher Moodle
... heart through the left atrium. The mitral valve is closed to keep the blood from going into the ventricle. ...
... heart through the left atrium. The mitral valve is closed to keep the blood from going into the ventricle. ...
Heart Physiology /Circulatory System Review
... 5. The first audible beats are produced by the forceful opening of an artery. This is considered to the systole 6. Explain why an athlete must exercise harder or longer to achieve a maximum heart rate than a person who is not as physically fit. Like any muscle, a well-conditioned heart beats more ef ...
... 5. The first audible beats are produced by the forceful opening of an artery. This is considered to the systole 6. Explain why an athlete must exercise harder or longer to achieve a maximum heart rate than a person who is not as physically fit. Like any muscle, a well-conditioned heart beats more ef ...
Chapter 21 - Circulatory
... Serve as conduits through which blood is circulated to every cell in the body. Tunica interna (intima) – -inner most layer of vessel wall. Lined with endothelial cells overlying a sparse layer of loose CT. Tunica media – -middle layer and thickest . Contains smooth muscle, collagen and in larger ves ...
... Serve as conduits through which blood is circulated to every cell in the body. Tunica interna (intima) – -inner most layer of vessel wall. Lined with endothelial cells overlying a sparse layer of loose CT. Tunica media – -middle layer and thickest . Contains smooth muscle, collagen and in larger ves ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Power Point
... • Do NOT cut out the intestines to dissect the urinary system! • Push the intestines to one side and use a scalpel or blunt probe to remove the connective ...
... • Do NOT cut out the intestines to dissect the urinary system! • Push the intestines to one side and use a scalpel or blunt probe to remove the connective ...
Spinal nerves
... Flexor Withdrawal Reflexes • Flexor(withdrawal) reflex occurs during withdrawal of foot from pain – polysynaptic reflex arc – neural circuitry in spinal cord controls sequence and duration of muscle contractions ...
... Flexor Withdrawal Reflexes • Flexor(withdrawal) reflex occurs during withdrawal of foot from pain – polysynaptic reflex arc – neural circuitry in spinal cord controls sequence and duration of muscle contractions ...
Chapter 34 - TeacherWeb
... Mammals generally have a larger brain than other vertebrates of equivalent size Monotremes Monotremes are a small group of egg-laying mammals consisting of echidnas and the platypus Marsupials Marsupials include opossums, kangaroos, and koalas A marsupial is born very early in its development I ...
... Mammals generally have a larger brain than other vertebrates of equivalent size Monotremes Monotremes are a small group of egg-laying mammals consisting of echidnas and the platypus Marsupials Marsupials include opossums, kangaroos, and koalas A marsupial is born very early in its development I ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.