embryology PAP 2 Fertilization and implantation
... • Rapid increase in the number of cells • These smaller embryonic cells are called Blastomeres • Normally occurs in the uterine tube • Zygote divides first into 2 then 4 & 8 cells • Zygote lies within the thick zona pellucida during cleavage Prof. Saeed Makare ...
... • Rapid increase in the number of cells • These smaller embryonic cells are called Blastomeres • Normally occurs in the uterine tube • Zygote divides first into 2 then 4 & 8 cells • Zygote lies within the thick zona pellucida during cleavage Prof. Saeed Makare ...
THE NEURAL TUBE AND ITS SUBDIVISIONS
... underlying ventricular cavity in the region of the pontine flexure, forming the choroid plexus. • At about month 4, areas of the roof plate of the rhombencephalon thin out, bulge outward, and finally disappear. The apertures formed are the 2 lateral foramina of Luschka and a median foramen of Magend ...
... underlying ventricular cavity in the region of the pontine flexure, forming the choroid plexus. • At about month 4, areas of the roof plate of the rhombencephalon thin out, bulge outward, and finally disappear. The apertures formed are the 2 lateral foramina of Luschka and a median foramen of Magend ...
Cardiovascular System_Lecture III - Medical
... arteries and veins, and most closely interact with tissues. Capillaries have walls composed of a single layer of cells, the endothelium. This layer is so thin that molecules such as oxygen, water and lipids can pass through them by diffusion and enter the tissues. Waste products such as carbon dioxi ...
... arteries and veins, and most closely interact with tissues. Capillaries have walls composed of a single layer of cells, the endothelium. This layer is so thin that molecules such as oxygen, water and lipids can pass through them by diffusion and enter the tissues. Waste products such as carbon dioxi ...
Flow of Blood and Vessel Structure and Location
... Vena Cava – The superior and inferior vena cava are collectively called the venae cavae. They are the veins that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. They both empty into the right atrium Aorta – The largest artery in the body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and ...
... Vena Cava – The superior and inferior vena cava are collectively called the venae cavae. They are the veins that return deoxygenated blood from the body into the heart. They both empty into the right atrium Aorta – The largest artery in the body, originating from the left ventricle of the heart and ...
Phylum Chordata
... The name Chordata comes from the notochord; a rodlike, semirigid tissue enclosed in a sheath. The chordates have five basic characteristics: ...
... The name Chordata comes from the notochord; a rodlike, semirigid tissue enclosed in a sheath. The chordates have five basic characteristics: ...
The walls of the veins consist also of three layers, but there is very
... The walls of the veins consist also of three layers, but there is very little elastic and muscular tissue in these and more of the connective tissue outer coating than the arteries possess. S o when a vein is cut across, the vessel collapses and closes its opening, the thin walls falling together. B ...
... The walls of the veins consist also of three layers, but there is very little elastic and muscular tissue in these and more of the connective tissue outer coating than the arteries possess. S o when a vein is cut across, the vessel collapses and closes its opening, the thin walls falling together. B ...
File
... the renal arteries. The renal veins take blood away from the kidneys. They are located just below the renal arteries. Remove these blood vessels very carefully. B. Environmentalist: Coming from the posterior end of the kidney is the ureter. This is the tube that drains urine from the kidney into the ...
... the renal arteries. The renal veins take blood away from the kidneys. They are located just below the renal arteries. Remove these blood vessels very carefully. B. Environmentalist: Coming from the posterior end of the kidney is the ureter. This is the tube that drains urine from the kidney into the ...
Pregnancy and development File
... • Pregnancy: events that occur from fertilization until the infant is born • Conceptus: the developing offspring • Gestation period: time from the last menstrual ...
... • Pregnancy: events that occur from fertilization until the infant is born • Conceptus: the developing offspring • Gestation period: time from the last menstrual ...
Gross Anatomy: Spinal Cord and Meninges
... • contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood vessels and connective tissue • surrounds the cord and spinal nerves, ends at the level of S2 ...
... • contains cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), blood vessels and connective tissue • surrounds the cord and spinal nerves, ends at the level of S2 ...
7.Development of mid..
... Hernia protrudes during crying, straining, or coughing It can easily be reduced through the fibrous ring at the umbilicus Surgery is not usually performed until it persists to the age of 3 to 5 years ...
... Hernia protrudes during crying, straining, or coughing It can easily be reduced through the fibrous ring at the umbilicus Surgery is not usually performed until it persists to the age of 3 to 5 years ...
unit 4. dissection: vertebral column and spinal cord
... part of the sacrum. Save a few dorsal rami of the thoracic nerves, so that they may later be traced to the main trunk of the nerves from which they arise. 2. Now perform a laminectomy from the level of C3 to the sacrum. The successive laminae and spines are held together by the ligamenta flava and t ...
... part of the sacrum. Save a few dorsal rami of the thoracic nerves, so that they may later be traced to the main trunk of the nerves from which they arise. 2. Now perform a laminectomy from the level of C3 to the sacrum. The successive laminae and spines are held together by the ligamenta flava and t ...
Protection Of The Spinal Cord
... • 31 Pairs of spinal nerves • Named & numbered by the cord level of their origin – 8 pairs of cervical nerves (C1 to C8) – 12 pairs of thoracic nerves (T1 to T12) – 5 pairs of lumbar nerves (L1 to L5) – 5 pairs of sacral nerves (S1 to S5) – 1 pair of coccygeal nerves ...
... • 31 Pairs of spinal nerves • Named & numbered by the cord level of their origin – 8 pairs of cervical nerves (C1 to C8) – 12 pairs of thoracic nerves (T1 to T12) – 5 pairs of lumbar nerves (L1 to L5) – 5 pairs of sacral nerves (S1 to S5) – 1 pair of coccygeal nerves ...
Prenatal Development - Southern Illinois University School
... • PLACENTA - mass of tissue, supplies oxygen and nutrients to the embryo and carries away waste products • Effectively filters out most substances, such as bacteria, which could be harmful to the embryo • However, certain substances, such as some viruses, alcohol, and many other drugs, can pass thro ...
... • PLACENTA - mass of tissue, supplies oxygen and nutrients to the embryo and carries away waste products • Effectively filters out most substances, such as bacteria, which could be harmful to the embryo • However, certain substances, such as some viruses, alcohol, and many other drugs, can pass thro ...
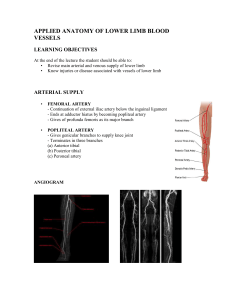
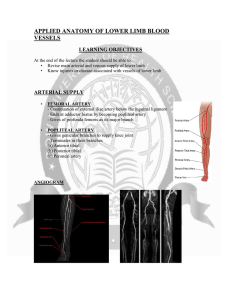
applied anatomy of lower limb blood vessels
... At the end of the lecture the student should be able to: • Revise main arterial and venous supply of lower limb • Know injuries or disease associated with vessels of lower limb ...
... At the end of the lecture the student should be able to: • Revise main arterial and venous supply of lower limb • Know injuries or disease associated with vessels of lower limb ...
APPLIED ANATOMY OF LOWER LIMB BLOOD VESSELS
... At the end of the lecture the student should be able to: • Revise main arterial and venous supply of lower limb • Know injuries or disease associated with vessels of lower limb ...
... At the end of the lecture the student should be able to: • Revise main arterial and venous supply of lower limb • Know injuries or disease associated with vessels of lower limb ...
Anatomical Position, etc. Notes Handout
... Area between hips ________________________ Shoulder blade region ________________________ Posterior surface of leg (calf) ________________________ Area of spinal column ...
... Area between hips ________________________ Shoulder blade region ________________________ Posterior surface of leg (calf) ________________________ Area of spinal column ...
ABDOMEN 1
... Surface anatomy of anterolateral abdominal wall Boundaries of the anterolateral abdominal wall Fascia of the anterolateral abdominal wall External oblique abdominis muscle – anatomy, attachments, actions, innervation Internal oblique abdominis muscle – anatomy, attachments, actions, innervation Tran ...
... Surface anatomy of anterolateral abdominal wall Boundaries of the anterolateral abdominal wall Fascia of the anterolateral abdominal wall External oblique abdominis muscle – anatomy, attachments, actions, innervation Internal oblique abdominis muscle – anatomy, attachments, actions, innervation Tran ...
Chapter 4 prenatal ppt
... Lining of uterus is thick enough for the zygote to attach itself and continue to grow Zygote implants in the uterus Size of the head of a pin ...
... Lining of uterus is thick enough for the zygote to attach itself and continue to grow Zygote implants in the uterus Size of the head of a pin ...
chapter 4 prenatal ppt
... Lining of uterus is thick enough for the zygote to attach itself and continue to grow Zygote implants in the uterus Size of the head of a pin ...
... Lining of uterus is thick enough for the zygote to attach itself and continue to grow Zygote implants in the uterus Size of the head of a pin ...
Fetal Pig Dissection Introduction: Today, we begin a new chapter in
... ix. ____ Vulva: Fleshy protuberance found at the covering/opening of the urogenital system. ...
... ix. ____ Vulva: Fleshy protuberance found at the covering/opening of the urogenital system. ...
PDF - Rosenblum Newfield
... segmented nucleus, and are called bands, or “stabs” (German for because of an insufficient number of older cells to deliver needed “sword”). Many immature neutrophils compared to mature cells oxygen. Therefore, an increased number of immature (nucleated) (the immature to total neutrophils ratio) ref ...
... segmented nucleus, and are called bands, or “stabs” (German for because of an insufficient number of older cells to deliver needed “sword”). Many immature neutrophils compared to mature cells oxygen. Therefore, an increased number of immature (nucleated) (the immature to total neutrophils ratio) ref ...
Spinal Cord Structure and Spinal Nerves
... A needle inserted into the subarachnoid space for the purpose of withdrawing CSF (for diagnosis or to reduce pressure) or to introduce a drug or contrast agent is called a lumbar puncture. CSF is often collected to diagnose meningitis or some other disease of the CNS. Agents injected into the ...
... A needle inserted into the subarachnoid space for the purpose of withdrawing CSF (for diagnosis or to reduce pressure) or to introduce a drug or contrast agent is called a lumbar puncture. CSF is often collected to diagnose meningitis or some other disease of the CNS. Agents injected into the ...
Development and Inheritance
... the organ decreases in size. Usually within an hour after delivery, the placental stage ends with the ejection of the placenta, or after birth. There could be as much as 500-600ml of blood lost, but the increase of maternal blood through pregnancy helps out. See page 629. ...
... the organ decreases in size. Usually within an hour after delivery, the placental stage ends with the ejection of the placenta, or after birth. There could be as much as 500-600ml of blood lost, but the increase of maternal blood through pregnancy helps out. See page 629. ...
File - Miss Williams Science Warriors
... increasing the volume of substances which can be absorbed by diffusion. The villi have a very GOOD BLOOD SUPPLY as each contains a capillary, which leads to the main blood supply, so when substances diffuse, they can go straight to the bloodstream. Attached to each villi are thousands and thousands ...
... increasing the volume of substances which can be absorbed by diffusion. The villi have a very GOOD BLOOD SUPPLY as each contains a capillary, which leads to the main blood supply, so when substances diffuse, they can go straight to the bloodstream. Attached to each villi are thousands and thousands ...
Document
... bearing some chordate characteristics. Both have similar ciliated bands in loops, sensory cilia at the anterior end, and a complete digestive system of ventral mouth and posterior anus. Both echinoderm and chordate embryos show indeterminate cleavage These characteristics are shared by brachiopods a ...
... bearing some chordate characteristics. Both have similar ciliated bands in loops, sensory cilia at the anterior end, and a complete digestive system of ventral mouth and posterior anus. Both echinoderm and chordate embryos show indeterminate cleavage These characteristics are shared by brachiopods a ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.