chapter 12-the central nervous system
... cervical enlargement. b. Lumbar Enlargement-in the lower back, nerves to/from the legs extend from this enlargement. 3. The Conus Medullaris-the tapered, cone-shaped end of the spinal cord. It is near the ...
... cervical enlargement. b. Lumbar Enlargement-in the lower back, nerves to/from the legs extend from this enlargement. 3. The Conus Medullaris-the tapered, cone-shaped end of the spinal cord. It is near the ...
Brachial plexus
... specifically from above the fifth cervical vertebra to underneath the first thoracic vertebra (C5-T1). It proceeds through the neck, the axilla (armpit region) and into the arm. Function The brachial plexus is responsible for cutaneous and muscular innervation of the entire upper limb, with two exce ...
... specifically from above the fifth cervical vertebra to underneath the first thoracic vertebra (C5-T1). It proceeds through the neck, the axilla (armpit region) and into the arm. Function The brachial plexus is responsible for cutaneous and muscular innervation of the entire upper limb, with two exce ...
Blood types
... blood protein was discovered. This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood does contain the protein, your blood is said to be Rh po ...
... blood protein was discovered. This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood does contain the protein, your blood is said to be Rh po ...
Document
... blood protein was discovered. This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood does contain the protein, your blood is said to be Rh po ...
... blood protein was discovered. This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood does contain the protein, your blood is said to be Rh po ...
Click Here for Spinal Cord Chapter
... The spinal cord and spinal nerves (as well as the cranial nerves) contain neural circuits bringing sensory information up to the brain (afferent) and motor signals out, away from the brain to the body (efferent). The CNS is protected by bone (skull and vertebral column); the meninges; and finally it ...
... The spinal cord and spinal nerves (as well as the cranial nerves) contain neural circuits bringing sensory information up to the brain (afferent) and motor signals out, away from the brain to the body (efferent). The CNS is protected by bone (skull and vertebral column); the meninges; and finally it ...
PNS/ANS Overview (Morton)
... Overview of the ANS • Sensory: monitor changes in viscera • Motor: innervate smooth and cardiac muscle/glands • Pre-ganglionic ANS neuron: cell body in CNS • Post-ganglionic ANS neuron: cell body in periph. gang. ...
... Overview of the ANS • Sensory: monitor changes in viscera • Motor: innervate smooth and cardiac muscle/glands • Pre-ganglionic ANS neuron: cell body in CNS • Post-ganglionic ANS neuron: cell body in periph. gang. ...
Gross anatomy, and terms for directions and sections
... • Superior / inferior ; anterior / posterior – System referenced to anatomical neuraxis, which is straight in many animals, and curved in humans. • Rostral / caudal; ventral / dorsal ...
... • Superior / inferior ; anterior / posterior – System referenced to anatomical neuraxis, which is straight in many animals, and curved in humans. • Rostral / caudal; ventral / dorsal ...
Conceptus – anything developed from fertilized egg
... and fold in to become the notochord and the endoderm grows back in place. The notochord is responsible for defining the longitudinal axis and provides signals to develop the axial musculoskeletal structures and central nervous system, as well as contributing to the intervertebral discs. As the notoc ...
... and fold in to become the notochord and the endoderm grows back in place. The notochord is responsible for defining the longitudinal axis and provides signals to develop the axial musculoskeletal structures and central nervous system, as well as contributing to the intervertebral discs. As the notoc ...
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves
... • Transmission of impulse from sensory receptors to brain and from brain to effectors Protection and Coverings • Passes through the vertebral foramina of vertebrae • Enclosed by spinal meninges - three layers – Dura mater - dense, irregular connective tissue layer • Epidural space contains cushionin ...
... • Transmission of impulse from sensory receptors to brain and from brain to effectors Protection and Coverings • Passes through the vertebral foramina of vertebrae • Enclosed by spinal meninges - three layers – Dura mater - dense, irregular connective tissue layer • Epidural space contains cushionin ...
The Spinal Cord and Spinal Nerves General Function • Reflex
... • Transmission of impulse from sensory receptors to brain and from brain to effectors Protection and Coverings • Passes through the vertebral foramina of vertebrae • Enclosed by spinal meninges - three layers – Dura mater - dense, irregular connective tissue layer • Epidural space contains cushionin ...
... • Transmission of impulse from sensory receptors to brain and from brain to effectors Protection and Coverings • Passes through the vertebral foramina of vertebrae • Enclosed by spinal meninges - three layers – Dura mater - dense, irregular connective tissue layer • Epidural space contains cushionin ...
The Nervous System
... Self-propagating wave of electrical disturbance that travels along the surface of a neuron’s plasma membrane. Initiated by a stimulus – a change in the neuron’s environment, pressure, temp. and chemical changes are common stimuli. Saltatory conduction – traveling impulse encounters a section of memb ...
... Self-propagating wave of electrical disturbance that travels along the surface of a neuron’s plasma membrane. Initiated by a stimulus – a change in the neuron’s environment, pressure, temp. and chemical changes are common stimuli. Saltatory conduction – traveling impulse encounters a section of memb ...
Branches of Internal Iliac Artery Posterior Division iliolumbar lateral
... 2. lateral sacral 3. superior gluteal a. largest branch of the internal iliac. b. usually passes between the lumbosacral trunk and the first sacral nerve to leave the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen above the piriformis. Anterior Division 1. inferior gluteal a. passes between the 2nd and ...
... 2. lateral sacral 3. superior gluteal a. largest branch of the internal iliac. b. usually passes between the lumbosacral trunk and the first sacral nerve to leave the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen above the piriformis. Anterior Division 1. inferior gluteal a. passes between the 2nd and ...
a notochord, a dorsal hollow nerve cord, pharyngeal slits
... pharyngeal slits allow for the exit of water that enters the mouth during feeding. Some invertebrate chordates use the pharyngeal slits to filter food out of the water that enters the mouth. In vertebrate fishes, the pharyngeal slits develop into gill arches, the bony or cartilaginous gill supports. ...
... pharyngeal slits allow for the exit of water that enters the mouth during feeding. Some invertebrate chordates use the pharyngeal slits to filter food out of the water that enters the mouth. In vertebrate fishes, the pharyngeal slits develop into gill arches, the bony or cartilaginous gill supports. ...
Kaan Yücel M.D., Ph.D. http://fhs122.org
... the spinal cord and, through the three foramina in its roof, with the subarachnoid space. The connection between subarachnoid space & the 4th ventricle 1 hole in the middle: median aperture (of Magendi),two holes lateral apertures (of Luschka) There are two large lateral ventricles, and one is pre ...
... the spinal cord and, through the three foramina in its roof, with the subarachnoid space. The connection between subarachnoid space & the 4th ventricle 1 hole in the middle: median aperture (of Magendi),two holes lateral apertures (of Luschka) There are two large lateral ventricles, and one is pre ...
Patient Preparation
... tug on testicle to return it to scrotal sac Postoperative Care: home same day on: vicodin 5/500 #35 1 refill dulcolax prn valium 5mg po BID x10d ibuprofen 600mg po TID x5d Intraop questions/pearls: What is the most important structure to protect in the cord? Artery-> ischemia.But this is wrong. Isch ...
... tug on testicle to return it to scrotal sac Postoperative Care: home same day on: vicodin 5/500 #35 1 refill dulcolax prn valium 5mg po BID x10d ibuprofen 600mg po TID x5d Intraop questions/pearls: What is the most important structure to protect in the cord? Artery-> ischemia.But this is wrong. Isch ...
Worksheet - Nervous System II Lecture Notes Page
... before the spinal cord D. Cerebellum Located _______________________ (anterior/posterior) to the brainstem and ____________________________(inferior/superior) to the cerebrum. It consists of outer ___________________(gray/white) matter and inner, branching ____________________(gray/white) matter. Th ...
... before the spinal cord D. Cerebellum Located _______________________ (anterior/posterior) to the brainstem and ____________________________(inferior/superior) to the cerebrum. It consists of outer ___________________(gray/white) matter and inner, branching ____________________(gray/white) matter. Th ...
Laparoscopic Anatomy of the Pelvis - Beck-Shop
... along the side of the bladder and runs upward on the back of the anterior abdominal wall to converge at the umbilicus with the hypogastric artery of the opposite side. Having passed through the umbilical opening, the two arteries, now termed umbilical, enter the umbilical cord, where they are coiled ...
... along the side of the bladder and runs upward on the back of the anterior abdominal wall to converge at the umbilicus with the hypogastric artery of the opposite side. Having passed through the umbilical opening, the two arteries, now termed umbilical, enter the umbilical cord, where they are coiled ...
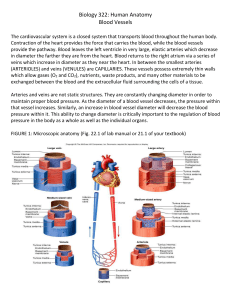
Blood Vessels (Exercise 22, 23, 24)
... ENDOTHELIUM atop a basement membrane (like all epithelia). The endothelium secretes many factors that regulate blood clotting, leukocyte migration, and blood vessel diameter. 2. TUNICA MEDIA – the middle layer. This is the thickest layer of the blood vessel and contains a great deal of connective ti ...
... ENDOTHELIUM atop a basement membrane (like all epithelia). The endothelium secretes many factors that regulate blood clotting, leukocyte migration, and blood vessel diameter. 2. TUNICA MEDIA – the middle layer. This is the thickest layer of the blood vessel and contains a great deal of connective ti ...
11-4_Spinothalamic_KajtsaDora
... pressure; thermal nociceptors, showing selective responses to burning heat or extreme cold; and chemical nociceptors, showing selective responses to histamine and other chemicals. Nociceptors are present in most body tissues, including skin, bone, muscle, most internal organs, blood vessels, and the ...
... pressure; thermal nociceptors, showing selective responses to burning heat or extreme cold; and chemical nociceptors, showing selective responses to histamine and other chemicals. Nociceptors are present in most body tissues, including skin, bone, muscle, most internal organs, blood vessels, and the ...
Thorax Forum Questions 2010ish
... 2. You have to perform a pericardiocentesis, what landmarks are you going to use to guide the needle? What is your approach? (not in your text) Infrasternal angle under the xiphoid process may be the safest; follow the bottom of the ribs upward to locate the xiphoid process 3. What is a stent and ho ...
... 2. You have to perform a pericardiocentesis, what landmarks are you going to use to guide the needle? What is your approach? (not in your text) Infrasternal angle under the xiphoid process may be the safest; follow the bottom of the ribs upward to locate the xiphoid process 3. What is a stent and ho ...
APSpring14_142E1Aans..
... The image was colored and was seen by the right eye The image was colored and focused on the left retina The nasal part of the image activated layer 4 & 6 of the LGN parvo-cellular layer Axons carrying information about this object projected through the right optic tract to the LGN A&C ...
... The image was colored and was seen by the right eye The image was colored and focused on the left retina The nasal part of the image activated layer 4 & 6 of the LGN parvo-cellular layer Axons carrying information about this object projected through the right optic tract to the LGN A&C ...
1. CNS tissue is enclosed within the vertebral column from the
... There are 31 pairs of mixed nerves that arise from the spinal cord and supply all parts of the body except the head, all named according to their point of issue. 8 cervical nerves (C1-C8) 12 thoracic (T1-T12) 5 Lumbar (L1-L5) 5 Sacral (S1-S5) 1 Coccygeal (C0) All ventral rami except T2-T12 form int ...
... There are 31 pairs of mixed nerves that arise from the spinal cord and supply all parts of the body except the head, all named according to their point of issue. 8 cervical nerves (C1-C8) 12 thoracic (T1-T12) 5 Lumbar (L1-L5) 5 Sacral (S1-S5) 1 Coccygeal (C0) All ventral rami except T2-T12 form int ...
Blood types - churchillcollegebiblio
... • While studying Rhesus monkeys, a certain blood protein was discovered. • This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood does contai ...
... • While studying Rhesus monkeys, a certain blood protein was discovered. • This protein is also present in the blood of some people. Other people, however, do not have the protein. • The presence of the protein, or lack of it, is referred to as the Rh (for Rhesus) factor. • If your blood does contai ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.