PowerPoint Slides
... enlargements • cauda equina (horse’s tail) – thin nerve fibers that exit at different level than they arise (note that spinal cord does not extend into this area of the lumbar spine). Begins around L2 and extends to S5. Good area for lumbar puncture and collection of CSF. ...
... enlargements • cauda equina (horse’s tail) – thin nerve fibers that exit at different level than they arise (note that spinal cord does not extend into this area of the lumbar spine). Begins around L2 and extends to S5. Good area for lumbar puncture and collection of CSF. ...
Spine/Back Vocabulary - Liberty Union High School District
... 19. Lumbar Vertebrae: 5 vertebrae associated with the lower back 20. Lordosis: “Sway Back”, exaggerated lumbar curve 21. Meninges: Any of 3 membranes that enclose brain & spinal cord 22. Mixed Nerve: Nerve composed of efferent and afferent fibers 23. Motor Nerve: Carries impulses from CNS, also know ...
... 19. Lumbar Vertebrae: 5 vertebrae associated with the lower back 20. Lordosis: “Sway Back”, exaggerated lumbar curve 21. Meninges: Any of 3 membranes that enclose brain & spinal cord 22. Mixed Nerve: Nerve composed of efferent and afferent fibers 23. Motor Nerve: Carries impulses from CNS, also know ...
Conception to Birth
... the zygote into the uterine wall. • Implantation usually occurs ten days after conception and if it does not occur, the zygote is flushed out of the woman’s system in her menstrual cycle. • Not every zygote will implant, so medically speaking a woman becomes pregnant when implantation occurs. By the ...
... the zygote into the uterine wall. • Implantation usually occurs ten days after conception and if it does not occur, the zygote is flushed out of the woman’s system in her menstrual cycle. • Not every zygote will implant, so medically speaking a woman becomes pregnant when implantation occurs. By the ...
No Slide Title
... Crossed Extensor Reflexes • Maintains balance by extending other leg • Intersegmental reflex extends up and down the spinal cord • Contralateral reflex arcs explained by pain at one foot causes muscle contraction in other leg ...
... Crossed Extensor Reflexes • Maintains balance by extending other leg • Intersegmental reflex extends up and down the spinal cord • Contralateral reflex arcs explained by pain at one foot causes muscle contraction in other leg ...
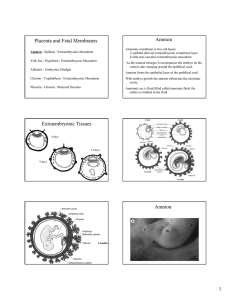
PLACENTA & FETAL MEMBRANES
... 15~25 cm, is approximately 3 cm thick, & weighs about 500~600 g. Sources: fetal part + maternal part. Has 2 surfaces: 1)fetal surface – smooth, coverd by amnion, umb. Cord attached to its centre. 2)Maternal surface – irregular, divided into 15 – 20 lobes or cotyledons separted by placental septa. ...
... 15~25 cm, is approximately 3 cm thick, & weighs about 500~600 g. Sources: fetal part + maternal part. Has 2 surfaces: 1)fetal surface – smooth, coverd by amnion, umb. Cord attached to its centre. 2)Maternal surface – irregular, divided into 15 – 20 lobes or cotyledons separted by placental septa. ...
EmbryoVent tablet dent 2010.jnt
... Third Ventricle –boundaries of the “box” best studied from midsagittal section, which we will do in Lab 2 (=HyperBrain Ch 2). Think of it as a narrow slit trapped between the two halves of the brain with many nooks and crannies. This ventricle is associated with the thalamus and hypothalamus. Aquedu ...
... Third Ventricle –boundaries of the “box” best studied from midsagittal section, which we will do in Lab 2 (=HyperBrain Ch 2). Think of it as a narrow slit trapped between the two halves of the brain with many nooks and crannies. This ventricle is associated with the thalamus and hypothalamus. Aquedu ...
VEINS - ANTERIOR REGION
... stance of the liver within which it receives the veins which drain the liver, the hepatic veins . Ductus Venosus - Within the body of liver the inferior vena cava then receives the ductus venosus. This vessel is a continuation of the umbilical vein which you 0 bserved earlier in the dissection. As y ...
... stance of the liver within which it receives the veins which drain the liver, the hepatic veins . Ductus Venosus - Within the body of liver the inferior vena cava then receives the ductus venosus. This vessel is a continuation of the umbilical vein which you 0 bserved earlier in the dissection. As y ...
Chapter 3
... Presence or absence of certain reflexes is useful in diagnosing disorders/injuries in nervous tissue • Patellar reflex: extension of knee results from tapping patellar ligament – blocked by damage to L2-L4 segment of spinal cord – absent in some cases of diabetes mellitus – exaggerated in certain br ...
... Presence or absence of certain reflexes is useful in diagnosing disorders/injuries in nervous tissue • Patellar reflex: extension of knee results from tapping patellar ligament – blocked by damage to L2-L4 segment of spinal cord – absent in some cases of diabetes mellitus – exaggerated in certain br ...
Placenta and Fetal Membranes
... The villi continue to enlarge during most of gestation. The villi project into a blood filled intervillous space resulting from the erosion of the decidua basalis. Endometrial vessels - spiral arteries and endometrial veins Villi associated with the decidua capsularis degenerate this region is calle ...
... The villi continue to enlarge during most of gestation. The villi project into a blood filled intervillous space resulting from the erosion of the decidua basalis. Endometrial vessels - spiral arteries and endometrial veins Villi associated with the decidua capsularis degenerate this region is calle ...
08 Placenta and Fetal Membranes total
... The villi continue to enlarge during most of gestation. The villi project into a blood filled intervillous space resulting from the erosion of the decidua basalis. Endometrial vessels - spiral arteries and endometrial veins Villi associated with the decidua capsularis degenerate this region is calle ...
... The villi continue to enlarge during most of gestation. The villi project into a blood filled intervillous space resulting from the erosion of the decidua basalis. Endometrial vessels - spiral arteries and endometrial veins Villi associated with the decidua capsularis degenerate this region is calle ...
Appendix A - UCLA Linguistics
... fibrous tissue securing a muscle to its attachment (adj. tendinous) that which draws tight the inside of the rib cage; region of the heart and lungs tube connecting the pharynx with the lungs at right angles to long axis (also horizontal) small bump (can be felt with finger) the navel pertaining to ...
... fibrous tissue securing a muscle to its attachment (adj. tendinous) that which draws tight the inside of the rib cage; region of the heart and lungs tube connecting the pharynx with the lungs at right angles to long axis (also horizontal) small bump (can be felt with finger) the navel pertaining to ...
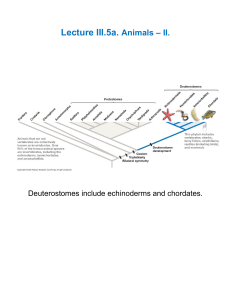
Lecture III.5a. Animals II.
... Below. Transverse sections through the tail (A and C) and trunk (B and D). The animal is a filter feeder, with water entering through the mouth and exiting through gill slits in the pharyngeal wall. Locomotion is via contraction of dorsal and ventral (epaxial and hypaxial) trunk muscles that run seg ...
... Below. Transverse sections through the tail (A and C) and trunk (B and D). The animal is a filter feeder, with water entering through the mouth and exiting through gill slits in the pharyngeal wall. Locomotion is via contraction of dorsal and ventral (epaxial and hypaxial) trunk muscles that run seg ...
LABORATORY EXERCISE 6 PHYLUM ARTHROPODA
... STRUCTURES OF INTERNAL ANATOMY. With your scissors, make two longitudinal dorso-lateral incisions from the triangular incision previously made to points just behind each eye. Cut laterally across the head, joining the two incisions and then carefully lift off the central portion of the carapace, gen ...
... STRUCTURES OF INTERNAL ANATOMY. With your scissors, make two longitudinal dorso-lateral incisions from the triangular incision previously made to points just behind each eye. Cut laterally across the head, joining the two incisions and then carefully lift off the central portion of the carapace, gen ...
Spinal Cord and Reflexes: An Introduction
... used much, any more – if at all. • Periodically, one will run across its use in the literature or online • Adenosine used now ...
... used much, any more – if at all. • Periodically, one will run across its use in the literature or online • Adenosine used now ...
The Nervous System
... length of the brain stem and into the upper segments of the spinal cord . _ The dorsal columns consist of first-order sensory neurons which the cell bodies of these neurons lie in the dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves . _ INFERIOR OLIVARY NUCLEUS is concerned with the control of movement and rece ...
... length of the brain stem and into the upper segments of the spinal cord . _ The dorsal columns consist of first-order sensory neurons which the cell bodies of these neurons lie in the dorsal root ganglia of spinal nerves . _ INFERIOR OLIVARY NUCLEUS is concerned with the control of movement and rece ...
Trainer 2 File
... All mammalian tissue is fairly uniform with tissue transitions that are fairly defined / complete so the cyst looks pretty aberrant (unusual) Embryo inside ...
... All mammalian tissue is fairly uniform with tissue transitions that are fairly defined / complete so the cyst looks pretty aberrant (unusual) Embryo inside ...
Chapter 13: The Spinal Cord, Spinal Nerves, and Spinal
... KEY CONCEPT (3 of 3) • Spinal cord is so highly organized: – it is possible to predict results of injuries to specific areas More on this later… ...
... KEY CONCEPT (3 of 3) • Spinal cord is so highly organized: – it is possible to predict results of injuries to specific areas More on this later… ...
NROSCI BIOSC 1070 MSNBIO 2070 December 11, 2015
... • Blood thus begins to flow through the pulmonary circulation instead of ductus arteriosus, as resistance in the ductus arteriosus is higher. ...
... • Blood thus begins to flow through the pulmonary circulation instead of ductus arteriosus, as resistance in the ductus arteriosus is higher. ...
Groups
... of mammals since it illustrates the basic anatomy of the adult mammal as well as providing information about certain features and structures present in the fetal body. In other words, what you learn by dissection of the fetal pig is broadly applicable to most other mammals. Even if your primary inte ...
... of mammals since it illustrates the basic anatomy of the adult mammal as well as providing information about certain features and structures present in the fetal body. In other words, what you learn by dissection of the fetal pig is broadly applicable to most other mammals. Even if your primary inte ...
class insecta - Queensland Science Teachers
... 3 body parts – head (with 1 pair of antennae, 1 pair of jaws and eyes), thorax (with 3 pairs of ) and abdomen Breathe by tracheae Heart and blood vessels Straight digestive tract with separate mouth and anus Brain and specialised sensory organs Sexual reproduction – Some insects such as ...
... 3 body parts – head (with 1 pair of antennae, 1 pair of jaws and eyes), thorax (with 3 pairs of ) and abdomen Breathe by tracheae Heart and blood vessels Straight digestive tract with separate mouth and anus Brain and specialised sensory organs Sexual reproduction – Some insects such as ...
File
... artery. The posterior spinal arteries, which arise either directly or indirectly from the vertebral arteries, run down the side of the spinal cord, close to the attachments of the posterior spinal nerve roots. The anterior spinal arteries, which arise from the vertebral arteries, unite to form a sin ...
... artery. The posterior spinal arteries, which arise either directly or indirectly from the vertebral arteries, run down the side of the spinal cord, close to the attachments of the posterior spinal nerve roots. The anterior spinal arteries, which arise from the vertebral arteries, unite to form a sin ...
Chapter 13
... Crossed Extensor Reflexes • Maintains balance by extending other leg • Intersegmental reflex extends up and down the spinal cord • Contralateral reflex arcs explained by pain at one foot causes muscle contraction in other leg ...
... Crossed Extensor Reflexes • Maintains balance by extending other leg • Intersegmental reflex extends up and down the spinal cord • Contralateral reflex arcs explained by pain at one foot causes muscle contraction in other leg ...
Umbilical cord

In placental mammals, the umbilical cord (also called the navel string, birth cord or funiculus umbilicalis) is a conduit between the developing embryo or fetus and the placenta. During prenatal development, the umbilical cord is physiologically and genetically part of the fetus and, (in humans), normally contains two arteries (the umbilical arteries) and one vein (the umbilical vein), buried within Wharton's jelly. The umbilical vein supplies the fetus with oxygenated, nutrient-rich blood from the placenta. Conversely, the fetal heart pumps deoxygenated, nutrient-depleted blood through the umbilical arteries back to the placenta.