Astronomy 110G Review Sheet for Exam #3 The
... have neutrons packed as closely as possible, and are about 100,000 times smaller than the Sun. Above about 3 solar masses all remnants are black holes; even light cannot escape their strong surface gravity. • Stellar remnants in some close binary systems can be detected via X-ray or γ-ray emission p ...
... have neutrons packed as closely as possible, and are about 100,000 times smaller than the Sun. Above about 3 solar masses all remnants are black holes; even light cannot escape their strong surface gravity. • Stellar remnants in some close binary systems can be detected via X-ray or γ-ray emission p ...
Space Science cource, Department of Physics, Faculty of
... Astrometry with the VERA and 1-m telescopes − 3-D map of the Milky Way − ...
... Astrometry with the VERA and 1-m telescopes − 3-D map of the Milky Way − ...
fact sheet about the Andromeda galaxy
... Andromeda, remarkable though that sounds. You can literally take the light of individual stars, spread them out into the colours of the rainbow, much more finely than a typical rainbow, into thousands of colours and from that you can measure the doppler shift of the star; how fast it’s moving toward ...
... Andromeda, remarkable though that sounds. You can literally take the light of individual stars, spread them out into the colours of the rainbow, much more finely than a typical rainbow, into thousands of colours and from that you can measure the doppler shift of the star; how fast it’s moving toward ...
Twinkle, Twinkle, Little Star
... The brightness of a star depends on both the size and temperature of the star. But, how bright it APPEARS to us depends on how far it is from Earth and how bright it truly is. ...
... The brightness of a star depends on both the size and temperature of the star. But, how bright it APPEARS to us depends on how far it is from Earth and how bright it truly is. ...
The Milky Way Galaxy is on a Collision course with Andromeda
... leaves us with new materials for new stars. And a possibility of even new planets! We also gain a bigger galaxy. And a new name… But how long is this process? It take 100’s of years to finish. But first it will take 3 billion years or so for us to actually have the tip of our galaxy to touch theirs. ...
... leaves us with new materials for new stars. And a possibility of even new planets! We also gain a bigger galaxy. And a new name… But how long is this process? It take 100’s of years to finish. But first it will take 3 billion years or so for us to actually have the tip of our galaxy to touch theirs. ...
Cos. Won edu 2 - Adler Planetarium
... All stars are formed in nebulae, or clouds of gas and dust found scattered throughout galaxies. As the core of the new star forms, the amount of mass it contains determines the type of star it is. The Sun is considered a “main sequence” star. main sequence stars are at a point in their lifecycle whe ...
... All stars are formed in nebulae, or clouds of gas and dust found scattered throughout galaxies. As the core of the new star forms, the amount of mass it contains determines the type of star it is. The Sun is considered a “main sequence” star. main sequence stars are at a point in their lifecycle whe ...
Galaxies and Stars Questions KEY
... to fuse, which causes the outer part of the star to expand forming a red giant or supergiant, depending on its original mass. 8. What kind of stars become white dwarfs? Main sequence stars, specifically small and medium stars, become white dwarfs. 9. What causes neutron stars to form? After a high m ...
... to fuse, which causes the outer part of the star to expand forming a red giant or supergiant, depending on its original mass. 8. What kind of stars become white dwarfs? Main sequence stars, specifically small and medium stars, become white dwarfs. 9. What causes neutron stars to form? After a high m ...
2.5.4 astronomical distances Parallax and Distances to Stars
... If you work it out it is – 9.461 x 1015m When you consider the ridiculous distance involved in astronomy, it makes sense to have large units! ...
... If you work it out it is – 9.461 x 1015m When you consider the ridiculous distance involved in astronomy, it makes sense to have large units! ...
Anw, samenvatting, h15+16
... He believed in the heliocentric model. He fled from Austria because of a conflict between Catholics and Protestants, he became Brahe’s assistant. Kepler inherited all the data when Brahe died. His task was to work out the orbit of mars, it took 8 years to find out it was not possible according to Co ...
... He believed in the heliocentric model. He fled from Austria because of a conflict between Catholics and Protestants, he became Brahe’s assistant. Kepler inherited all the data when Brahe died. His task was to work out the orbit of mars, it took 8 years to find out it was not possible according to Co ...
Wave in the universe - Gallaudet University
... Antares is the 15th brightest star in the sky. It is more than 1000 light years away. ...
... Antares is the 15th brightest star in the sky. It is more than 1000 light years away. ...
Astronomy 360 Physics/Geology 360
... Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms a faint reflection nebulosity around the brightest stars was thought at first to be left over from ...
... Pleiades has several meanings in different cultures and traditions. The cluster is dominated by hot blue and extremely luminous stars that have formed within the last 100 million years. Dust that forms a faint reflection nebulosity around the brightest stars was thought at first to be left over from ...
Abstract Submitted for the PHY599 Meeting of
... The Ages of Stars STEFAN WALTER, Stony Brook University — In my talk I will speak about one of the most fundamental properties of a star, namely its age. The motivation to determine a star’s age is that it allows the study of the time evolution of astronomical phenomena related to stars and their su ...
... The Ages of Stars STEFAN WALTER, Stony Brook University — In my talk I will speak about one of the most fundamental properties of a star, namely its age. The motivation to determine a star’s age is that it allows the study of the time evolution of astronomical phenomena related to stars and their su ...
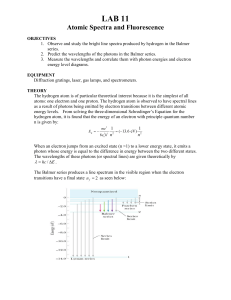
Lab 11: Atomic Spectra
... energy levels. From solving the three-dimensional Schrodinger’s Equation for the hydrogen atom, it is found that the energy of an electron with principle quantum number n is given by: ...
... energy levels. From solving the three-dimensional Schrodinger’s Equation for the hydrogen atom, it is found that the energy of an electron with principle quantum number n is given by: ...
Page 48
... 8. Meteoroid – A meteoroid is small pieces of comet that move through space. 9. Meteorite – A meteorite is a meteoroid that strikes the earth. Page 54 10. Meteor – A meteor is a small meteoroid that burns up in Earth’s atmosphere. 11. Asteroid Belt – the Asteroid Belt is a region between Mars and Ju ...
... 8. Meteoroid – A meteoroid is small pieces of comet that move through space. 9. Meteorite – A meteorite is a meteoroid that strikes the earth. Page 54 10. Meteor – A meteor is a small meteoroid that burns up in Earth’s atmosphere. 11. Asteroid Belt – the Asteroid Belt is a region between Mars and Ju ...
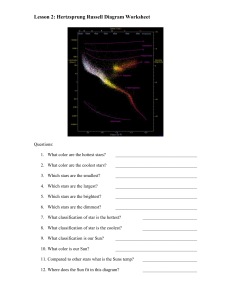
Place the stars in the proper sequence, following the
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
... 13. What is the color of the hottest stars? ___________________________________ 14. Which classification of star has the most energy? __________________________ a. How is a star’s temperature related to its energy? b. How is a star’s magnitude related to its energy? c. How is a star’s luminosity rel ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... • Once the gas and dust blow away, the star can be seen • All stars (low and high mass) start out here ...
... • Once the gas and dust blow away, the star can be seen • All stars (low and high mass) start out here ...
Stellar Remnants White Dwarfs, Neutron Stars & Black Holes
... Oxygen fuse into Silicon and Silicon into Nickel. • The energy from this event may cause the entire White Dwarf to explode leaving nothing behind. • This is called a supernova but it is a different process from that which occurs for massive stars. ...
... Oxygen fuse into Silicon and Silicon into Nickel. • The energy from this event may cause the entire White Dwarf to explode leaving nothing behind. • This is called a supernova but it is a different process from that which occurs for massive stars. ...
worksheet
... How do Astronomers know how much matter is in a galaxy? How do they know dark matter exists? In this project, you will use some real galaxy data and make some measurements in the way that astronomers do. ...
... How do Astronomers know how much matter is in a galaxy? How do they know dark matter exists? In this project, you will use some real galaxy data and make some measurements in the way that astronomers do. ...
Export To Word
... system, stars, cosmology, and telephotography. The material is clearly organized by topic using links to reference materials on the web. Images recently discovered by the Herschel telescope reveal the formation of previously unseen high-mass star formations. These new findings help us learn more abo ...
... system, stars, cosmology, and telephotography. The material is clearly organized by topic using links to reference materials on the web. Images recently discovered by the Herschel telescope reveal the formation of previously unseen high-mass star formations. These new findings help us learn more abo ...
07 May: Omnis In Exitu Eius Pulchrima
... velocity variations as large as observed, a planet would have to be as large as Jupiter, but much, much closer to the star than Mercury is to the Sun ...
... velocity variations as large as observed, a planet would have to be as large as Jupiter, but much, much closer to the star than Mercury is to the Sun ...
Explore the Galaxy - Museum of Science, Boston
... A typical Explore the Galaxy show begins on the Earth, examining several constellations, planets, and stars of interest visible in the night sky. The show then progresses through the solar system, discussing the planets, moons, asteroids, comets and dwarf planets and their properties. Outside the so ...
... A typical Explore the Galaxy show begins on the Earth, examining several constellations, planets, and stars of interest visible in the night sky. The show then progresses through the solar system, discussing the planets, moons, asteroids, comets and dwarf planets and their properties. Outside the so ...
Stellar Evolution
... • Nuclear Fusion – a nuclear reaction in which to atoms are fused together… • New elements are created and energy is released. • This process is responsible for creating ALL elements found in the universe… in other words, we are all made from star dust. ...
... • Nuclear Fusion – a nuclear reaction in which to atoms are fused together… • New elements are created and energy is released. • This process is responsible for creating ALL elements found in the universe… in other words, we are all made from star dust. ...
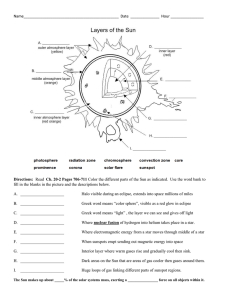
Ch. 20-2 Sun Study Gd. Revised
... 10. Clouds of gas and dust on a comet form a fuzzy outer layer called a _______________________. 11. A spherical region of comets on the outer edges surrounding the solar system is the ___________________ . 12. A doughnut-shaped region of comets that begins near Neptune’s orbit is the ______________ ...
... 10. Clouds of gas and dust on a comet form a fuzzy outer layer called a _______________________. 11. A spherical region of comets on the outer edges surrounding the solar system is the ___________________ . 12. A doughnut-shaped region of comets that begins near Neptune’s orbit is the ______________ ...
ITB - In the Beginning
... These particles formed in the first few minutes. The first atoms to form were; Hydrogen (H), Helium (He), Lithium (Li), and Beryllium (Be) These formed after ~ 600,000 years. ...
... These particles formed in the first few minutes. The first atoms to form were; Hydrogen (H), Helium (He), Lithium (Li), and Beryllium (Be) These formed after ~ 600,000 years. ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.