What Does an Astronomer Do?
... Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is a barred spiral galaxy consisting of 400 billion stars. It is about 100,000 light-years across. A light-year is the distance it would take for light to travel in one year. Since light travels at a speed of about 186,000 miles per second, a light-year is a huge distance! ...
... Our galaxy, the Milky Way, is a barred spiral galaxy consisting of 400 billion stars. It is about 100,000 light-years across. A light-year is the distance it would take for light to travel in one year. Since light travels at a speed of about 186,000 miles per second, a light-year is a huge distance! ...
Stars and Space - science
... • Smaller stars (like our Sun) then fade out and go cold. AQA Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2006 ...
... • Smaller stars (like our Sun) then fade out and go cold. AQA Science © Nelson Thornes Ltd 2006 ...
August 29 - Astronomy
... moving away from us, the farther away they are, the faster they are moving 2. The Cosmic microwave background radiation – things that are hot emit light and the universe today is filled with this light emitted when it was much hotter ...
... moving away from us, the farther away they are, the faster they are moving 2. The Cosmic microwave background radiation – things that are hot emit light and the universe today is filled with this light emitted when it was much hotter ...
8th Grade Midterm Test Review
... 24. Why is a year on Mars longer than a year on Earth? • Mars is farther from the Sun than Earth is. ...
... 24. Why is a year on Mars longer than a year on Earth? • Mars is farther from the Sun than Earth is. ...
How Far? - Science A 2 Z
... Earth’s • Simple calculation Orbit • Even the Hubble Telescope limited to 1000 LY ...
... Earth’s • Simple calculation Orbit • Even the Hubble Telescope limited to 1000 LY ...
Our Place in Space
... Group 4: Astronomers finally learned that Earth is one of at least eight other planets that travel around the Sun. Group 5: The Sun is a star at the center of the Solar System. It isn’t the biggest or the brightest star in our galaxy, but it is the star closest to Earth. Group 1: It is the largest b ...
... Group 4: Astronomers finally learned that Earth is one of at least eight other planets that travel around the Sun. Group 5: The Sun is a star at the center of the Solar System. It isn’t the biggest or the brightest star in our galaxy, but it is the star closest to Earth. Group 1: It is the largest b ...
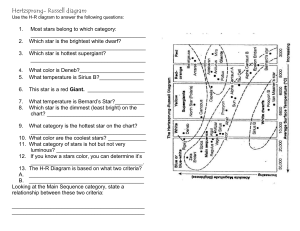
Hertzsprung - Russel Diagram
... 10. What color are the coolest stars? _____________ 11. What category of stars is hot but not very luminous? ______________________________ 12. If you know a stars color, you can determine it’s ______________________________________. 13. The H-R Diagram is based on what two criteria? A. ____________ ...
... 10. What color are the coolest stars? _____________ 11. What category of stars is hot but not very luminous? ______________________________ 12. If you know a stars color, you can determine it’s ______________________________________. 13. The H-R Diagram is based on what two criteria? A. ____________ ...
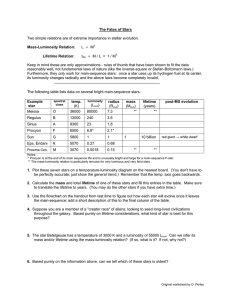
The Fates of Stars Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation:
... The Fates of Stars Two simple relations are of extreme importance in stellar evolution. Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation: ...
... The Fates of Stars Two simple relations are of extreme importance in stellar evolution. Mass-Luminosity Relation: Lifetime Relation: ...
Mechanical Waves (Chapter 17) 1. What does a wave transfer
... 3. What is dispersion? Separating of colors from white light 4. What does “opaque” mean? Object cannot be seen through at all because all light is being absorbed and/or ...
... 3. What is dispersion? Separating of colors from white light 4. What does “opaque” mean? Object cannot be seen through at all because all light is being absorbed and/or ...
Jeopardy Questions
... Q: What is the greenhouse effect and how does it relate to the different environments on Earth and Venus? A: Greenhouse effect is when an object is surrounded by an outer layer (like an atmosphere or a pane of glass) that only allows certain wavelengths of light through. For a planet, like the Earth ...
... Q: What is the greenhouse effect and how does it relate to the different environments on Earth and Venus? A: Greenhouse effect is when an object is surrounded by an outer layer (like an atmosphere or a pane of glass) that only allows certain wavelengths of light through. For a planet, like the Earth ...
PPT
... galaxies - anaemic spirals. 2. Velocity distribution - in-falling population ? 3. Mean column density 1020 atoms cm-2. 4. What is the relation between the cluster/field luminosity function and HI mass function ? 5. What debris from the galaxy formation process has or is assembling itself into the c ...
... galaxies - anaemic spirals. 2. Velocity distribution - in-falling population ? 3. Mean column density 1020 atoms cm-2. 4. What is the relation between the cluster/field luminosity function and HI mass function ? 5. What debris from the galaxy formation process has or is assembling itself into the c ...
Size scales in the solar system - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... Next time: • How far away are the stars (compared to solar system ...
... Next time: • How far away are the stars (compared to solar system ...
Lecture 3 -- Astronomical Coordinate Systems
... meters = 1 astronomical unit • Radius = 695,990 kilometers = 6.960E+08 meters (109 times radius of Earth) • If Earth were scaled to 1 foot globe size, the Sun would extend from goal line to 30 yard line at Kinnick stadium ...
... meters = 1 astronomical unit • Radius = 695,990 kilometers = 6.960E+08 meters (109 times radius of Earth) • If Earth were scaled to 1 foot globe size, the Sun would extend from goal line to 30 yard line at Kinnick stadium ...
Astronomy Seminar Cassy Davison A Search for Companions Around Cool Stars
... M dwarfs are the most common type of stellar object and comprise more than 70% of the known stars in our Galaxy. Along with being our nearest neighbors, these low mass stars have long lifetimes, which make them great targets for searching for planets upon which life may have had time to form. Our pr ...
... M dwarfs are the most common type of stellar object and comprise more than 70% of the known stars in our Galaxy. Along with being our nearest neighbors, these low mass stars have long lifetimes, which make them great targets for searching for planets upon which life may have had time to form. Our pr ...
Astrophysics and Chemistry Review Guide
... Why does the sun shine? What is stellar fusion? What isotopes of hydrogen are involved in this process? Why do stars come in different colors? What is the brightest star (apparent) in the night sky as seen from Earth? What is the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude? What are ...
... Why does the sun shine? What is stellar fusion? What isotopes of hydrogen are involved in this process? Why do stars come in different colors? What is the brightest star (apparent) in the night sky as seen from Earth? What is the difference between apparent magnitude and absolute magnitude? What are ...
ScalesOfSpace&Time
... Distribution of bright galaxies in the Virgo region indicates the Virgo cluster and presence of more distant, larger scale structure ...
... Distribution of bright galaxies in the Virgo region indicates the Virgo cluster and presence of more distant, larger scale structure ...
Astronomy 1
... The Milky Way Galaxy, commonly referred to as just the Milky Way, or sometimes simply as the Galaxy,[a] is the home galaxy of the Solar System, and of Earth. It is agreed that the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy, with observations suggesting that it is a barred spiral galaxy. It contains 100-400 billio ...
... The Milky Way Galaxy, commonly referred to as just the Milky Way, or sometimes simply as the Galaxy,[a] is the home galaxy of the Solar System, and of Earth. It is agreed that the Milky Way is a spiral galaxy, with observations suggesting that it is a barred spiral galaxy. It contains 100-400 billio ...
Earth`s Movements in Space
... - That extra ¼ day is the reason for a leap year. - Our orbit goes from more oval to more round every 100,000 years ...
... - That extra ¼ day is the reason for a leap year. - Our orbit goes from more oval to more round every 100,000 years ...
Characteristics of Stars WS Questions 1-20
... 20. Stars A and B have about the same apparent magnitude, but Star A is about twice as far from Earth as Star B. Which star has the greater absolute magnitude? ...
... 20. Stars A and B have about the same apparent magnitude, but Star A is about twice as far from Earth as Star B. Which star has the greater absolute magnitude? ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.