Objective 10 Study Guide
... galaxy, an elliptical galaxy or an irregular galaxy. Write S for a spiral galaxy, E for an elliptical galaxy, and I for an irregular galaxy. __E__16. These galaxies contain mostly old stars. __S__17. The Milky Way is probably this type of galaxy. __I__18. Many of these galaxies may have their shape ...
... galaxy, an elliptical galaxy or an irregular galaxy. Write S for a spiral galaxy, E for an elliptical galaxy, and I for an irregular galaxy. __E__16. These galaxies contain mostly old stars. __S__17. The Milky Way is probably this type of galaxy. __I__18. Many of these galaxies may have their shape ...
Scale of Apparent Magnitudes of Celestial Objects
... The modern system is not limited to six levels, and includes objects visible only to the most powerful telescopes, as well as planets and daytime objects such as the Sun and the Moon. The step size between adjacent magnitudes is now a factor of 2.512, so a magnitude 1 star has an apparent visual mag ...
... The modern system is not limited to six levels, and includes objects visible only to the most powerful telescopes, as well as planets and daytime objects such as the Sun and the Moon. The step size between adjacent magnitudes is now a factor of 2.512, so a magnitude 1 star has an apparent visual mag ...
characteristics of stars/lives of stars
... 11. A graph of stars showing surface temperature on the x-axis and absolute brightness on the y-axis is a(n) ________________________ . 12. ______________________ is often used to determine the distance to nearby stars. 13. A ______________________ is a(n) imaginary pattern of stars. 14. The brightn ...
... 11. A graph of stars showing surface temperature on the x-axis and absolute brightness on the y-axis is a(n) ________________________ . 12. ______________________ is often used to determine the distance to nearby stars. 13. A ______________________ is a(n) imaginary pattern of stars. 14. The brightn ...
Daedalon EO-85 Computerized Spectrophotometer
... 2. Measure the emission spectrum of the green, red and blue light emitting diodes in that order. The graphs will then be the same color as the LED. Capture all three spectra on the same screen. Adjust the exposure so that all three peaks are about the same height. You may have to change the exposure ...
... 2. Measure the emission spectrum of the green, red and blue light emitting diodes in that order. The graphs will then be the same color as the LED. Capture all three spectra on the same screen. Adjust the exposure so that all three peaks are about the same height. You may have to change the exposure ...
Quiz 5
... 23. (1 pt.) The planet with the largest volcano in the solar system is a. Earth. b. Mars. c. Venus. d. Mercury. ...
... 23. (1 pt.) The planet with the largest volcano in the solar system is a. Earth. b. Mars. c. Venus. d. Mercury. ...
Life Cycle of STARS
... • Are stars BORN??? • Take a moment to think about our own Sun, and write down an idea about how it was formed using what we have learned so far. ...
... • Are stars BORN??? • Take a moment to think about our own Sun, and write down an idea about how it was formed using what we have learned so far. ...
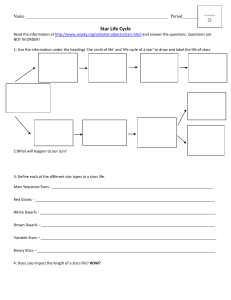
Star Life Cycle Web Quest
... 13. Magnitudes of brightness increase and decrease by a factor of 10. That means that a magnitude 2 is (number)________________ times ( brighter / dimmer ) than a magnitude 1. ...
... 13. Magnitudes of brightness increase and decrease by a factor of 10. That means that a magnitude 2 is (number)________________ times ( brighter / dimmer ) than a magnitude 1. ...
Talk to me about majoring in physics or astronomy!
... This figure shows how galaxies may have evolved, from early irregulars through active galaxies, to the normal ellipticals and spirals we ...
... This figure shows how galaxies may have evolved, from early irregulars through active galaxies, to the normal ellipticals and spirals we ...
Are we Alone? The Search for Life Beyond the
... • They pointed out that the background noise (atmosphere, Galaxy, CMB etc.) was a minimum between ~1 to 10 GHz. • This band included the (radio) Hydrogen Line at 1.4 GHz and the OH Lines at ~ 1.6 GHz. • The band from 1.4 to 1.6 GHz is called the Water Hole ...
... • They pointed out that the background noise (atmosphere, Galaxy, CMB etc.) was a minimum between ~1 to 10 GHz. • This band included the (radio) Hydrogen Line at 1.4 GHz and the OH Lines at ~ 1.6 GHz. • The band from 1.4 to 1.6 GHz is called the Water Hole ...
OH Science Standards for STARS
... The solar system includes the sun and all celestial bodies that orbit the sun. Each planet in the solar system has unique characteristics. o The distance from the sun, size, composition and movement of each planet are unique. Planets revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits. Some of the planets ...
... The solar system includes the sun and all celestial bodies that orbit the sun. Each planet in the solar system has unique characteristics. o The distance from the sun, size, composition and movement of each planet are unique. Planets revolve around the sun in elliptical orbits. Some of the planets ...
SNC1 Practice Astronomy Exam 1) If something were to happen to
... 18) The Earth experiences different seasons because... a) its orbit is not circular and its distance to the sun changes throughout the year. b) the sun is a Cepheid variable and its luminosity changes regularly. c) the Earth’s rotation axis is tilted relative to its orbit around the sun. Questions ...
... 18) The Earth experiences different seasons because... a) its orbit is not circular and its distance to the sun changes throughout the year. b) the sun is a Cepheid variable and its luminosity changes regularly. c) the Earth’s rotation axis is tilted relative to its orbit around the sun. Questions ...
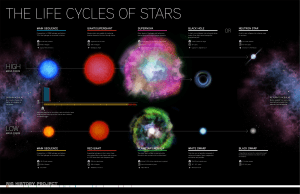
Life Cycles of Stars
... High-mass stars live for one million to tens of millions of years while low-mass stars, like our Sun, live for tens of millions to trillions of years. ...
... High-mass stars live for one million to tens of millions of years while low-mass stars, like our Sun, live for tens of millions to trillions of years. ...
File Space Test (March 11th) - Bonus Points
... When the phases are said to be waxing, the visible portion of the moon seems to be getting larger. When they are waning, the visible part seems to be getting ...
... When the phases are said to be waxing, the visible portion of the moon seems to be getting larger. When they are waning, the visible part seems to be getting ...
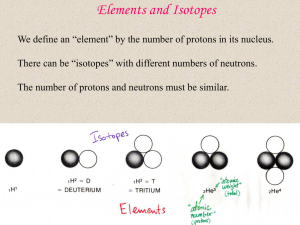
Elements and Isotopes - University of California, Berkeley
... We define an “element” by the number of protons in its nucleus. There can be “isotopes” with different numbers of neutrons. The number of protons and neutrons must be similar. ...
... We define an “element” by the number of protons in its nucleus. There can be “isotopes” with different numbers of neutrons. The number of protons and neutrons must be similar. ...
Clase-06_Star_Formation - Departamento de Astronomía
... collapse of the core temperature continues rising and H becomes ionized (HII) free e- pressure starts to balance the collapse that eventually halts in the core convective proto-star reachs the Hayashi limit in the CM diagram and enter the hydrostatic equilibrium regime (becoming a T-Tauri star ...
... collapse of the core temperature continues rising and H becomes ionized (HII) free e- pressure starts to balance the collapse that eventually halts in the core convective proto-star reachs the Hayashi limit in the CM diagram and enter the hydrostatic equilibrium regime (becoming a T-Tauri star ...
CBradleyLoutl
... Stars start from these larger, denser clouds of gas. Any small deviation in density will break the whole cloud into a number of condensed groups, if a group has over a certain mass, gravity will be strong enough to condense it into a star. First, a high mass cloud will contract, then begin breaking ...
... Stars start from these larger, denser clouds of gas. Any small deviation in density will break the whole cloud into a number of condensed groups, if a group has over a certain mass, gravity will be strong enough to condense it into a star. First, a high mass cloud will contract, then begin breaking ...
January 28
... Galaxies • Galaxies are massive gravitationally bound systems of stars and stellar remnants, gas, dust, planets, and dark matter • Dark matter is matter that you can’t see but whose gravity affects visible matter and background radiation ...
... Galaxies • Galaxies are massive gravitationally bound systems of stars and stellar remnants, gas, dust, planets, and dark matter • Dark matter is matter that you can’t see but whose gravity affects visible matter and background radiation ...
Waves Test Review
... 15. Which electromagnetic wave kills cancer cells? 16. Which electromagnetic wave causes sunburns? 17. Which electromagnetic wave is the only one humans can see? 18. Which electromagnetic wave is used to detect heat? 19. Why can we see light in space, but not hear sound? ...
... 15. Which electromagnetic wave kills cancer cells? 16. Which electromagnetic wave causes sunburns? 17. Which electromagnetic wave is the only one humans can see? 18. Which electromagnetic wave is used to detect heat? 19. Why can we see light in space, but not hear sound? ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.