Unit 1
... • c. always emits the same spectrum of light, whatever its temperature • d. reflects all radiation which falls upon it, never heating up and always appearing black. ...
... • c. always emits the same spectrum of light, whatever its temperature • d. reflects all radiation which falls upon it, never heating up and always appearing black. ...
Origin and Formation of the Universe – PowerPoint notes
... 2. This redness is the result of light being ______________________ as objects in the universe move _____________ from each other (the result of the big bang). ...
... 2. This redness is the result of light being ______________________ as objects in the universe move _____________ from each other (the result of the big bang). ...
Chapter 13 Lesson 3 Notes
... The planets are divided into four ___________________ planets and four ___________________ planets. The planets are separated by a huge ___________________ ___________________ between Mars and ___________________. The asteroid ___________________ is a ring shaped area where many small, rocky bodies ...
... The planets are divided into four ___________________ planets and four ___________________ planets. The planets are separated by a huge ___________________ ___________________ between Mars and ___________________. The asteroid ___________________ is a ring shaped area where many small, rocky bodies ...
How is Light Made?
... Now the particle nature of EM radiation. These little packets of light is known as photons. These photons carry a certain energy which is related to its frequency. This energy is equal to Planck’s constant (h) multiplied by the frequency of the photon. By substituting “nu” with the equation in the p ...
... Now the particle nature of EM radiation. These little packets of light is known as photons. These photons carry a certain energy which is related to its frequency. This energy is equal to Planck’s constant (h) multiplied by the frequency of the photon. By substituting “nu” with the equation in the p ...
1 The Big Bang • The Big Bang Theory postulates that the universe
... It was predicted to be at a current temperature of 2·7 K, with an associated peak wavelength in the microwave region. This radiation would be observable in every direction and spread uniformly throughout the universe – the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). In 1965 the CMB was observed; o ...
... It was predicted to be at a current temperature of 2·7 K, with an associated peak wavelength in the microwave region. This radiation would be observable in every direction and spread uniformly throughout the universe – the cosmic microwave background radiation (CMB). In 1965 the CMB was observed; o ...
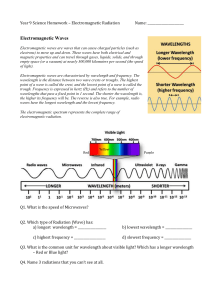
Electromagnetic Radiation Name
... Electromagnetic waves are waves that can cause charged particles (such as electrons) to move up and down. These waves have both electrical and magnetic properties and can travel through gases, liquids, solids, and through empty space (or a vacuum) at nearly 300,000 kilometers per second (the speed o ...
... Electromagnetic waves are waves that can cause charged particles (such as electrons) to move up and down. These waves have both electrical and magnetic properties and can travel through gases, liquids, solids, and through empty space (or a vacuum) at nearly 300,000 kilometers per second (the speed o ...
Key Areas covered
... concentrated in a tiny point known as a singularity (smaller than an atom). It caused our universe to expand suddenly from the singularity bringing time and space into existence. Following the Big Bang, temperatures rapidly cooled and tiny particles of matter began to form. The first atoms to form w ...
... concentrated in a tiny point known as a singularity (smaller than an atom). It caused our universe to expand suddenly from the singularity bringing time and space into existence. Following the Big Bang, temperatures rapidly cooled and tiny particles of matter began to form. The first atoms to form w ...
Observing the Universe 3
... 11. What have astronomers observed in distant galaxies that have enabled them to work out the distance of the galaxy from Earth? ...
... 11. What have astronomers observed in distant galaxies that have enabled them to work out the distance of the galaxy from Earth? ...
PHYXXXX UNIVERSITY OF EXETER PHYSICS XXX/YYY 20XX
... Star B is thought to have a massive exoplanet in orbit around it and the astronomer decides to carry out a photometric monitoring study in search for evidence of a dip in the light curve due to the planet transiting the star. The possible transit is predicted to result in a 1% dip in the stellar flu ...
... Star B is thought to have a massive exoplanet in orbit around it and the astronomer decides to carry out a photometric monitoring study in search for evidence of a dip in the light curve due to the planet transiting the star. The possible transit is predicted to result in a 1% dip in the stellar flu ...
Star Life Cycles
... After becoming a planetary nebula, the remains of the core of the star become a white dwarf. A white dwarf is a star that has exhausted most or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size; such a star is near its final stage of life. White dwarfs eventually become black dwarfs ...
... After becoming a planetary nebula, the remains of the core of the star become a white dwarf. A white dwarf is a star that has exhausted most or all of its nuclear fuel and has collapsed to a very small size; such a star is near its final stage of life. White dwarfs eventually become black dwarfs ...
Chapter 30 Graphing skills worksheet
... Line Graphs and the Surface Temperature of Stars Astronomers can determine the temperature of individual stars based on their color. The temperature of the star is higher as you move across the spectrum from red to blue. The data that shows this is found in the table below. Surface Temperature of St ...
... Line Graphs and the Surface Temperature of Stars Astronomers can determine the temperature of individual stars based on their color. The temperature of the star is higher as you move across the spectrum from red to blue. The data that shows this is found in the table below. Surface Temperature of St ...
Spectral lines, wavelength of light, Rydberg constant
... order maximum? How does it compare with the first order? Calculate the wavelength range of visible light for your measurements. 3) Replace the incandescent source with either a helium or mercury source. Record the deviation angle, to the nearest arc minute, for the two brightest lines in the spectra ...
... order maximum? How does it compare with the first order? Calculate the wavelength range of visible light for your measurements. 3) Replace the incandescent source with either a helium or mercury source. Record the deviation angle, to the nearest arc minute, for the two brightest lines in the spectra ...
galaxies - GEOCITIES.ws
... no light of their own; they either reflect light from stars, or stars illuminate them from their interior. • However, the only nebulae that are classified under "dark" are the ones that are dark. They have no stars near or within them with which to illuminate themselves. They are only seen when they ...
... no light of their own; they either reflect light from stars, or stars illuminate them from their interior. • However, the only nebulae that are classified under "dark" are the ones that are dark. They have no stars near or within them with which to illuminate themselves. They are only seen when they ...
A Poetic Interlude
... The Earth, formed out of the same debris of which the sun was born, existed at the center of a star that exploded many billions of years ago. Isaac Asimov ...
... The Earth, formed out of the same debris of which the sun was born, existed at the center of a star that exploded many billions of years ago. Isaac Asimov ...
il 3 ~ )
... (a) What is this in absolute units (Kelvin)? What is the peak wavelength emitted by a person with this temperature? (b) In what region of the spectrum is this wavelength? Is this consistent with the fact that humans do not appear to glow (optically) in the dark? (c) Estimate the surface area of your ...
... (a) What is this in absolute units (Kelvin)? What is the peak wavelength emitted by a person with this temperature? (b) In what region of the spectrum is this wavelength? Is this consistent with the fact that humans do not appear to glow (optically) in the dark? (c) Estimate the surface area of your ...
wk11noQ
... Ionized Hydrogen (HII) • While ionized hydrogen (protons, electrons) forms the majority of the ionized phase of the ISM, it also contains ionized forms of other elements: e.g., OII, OIII, CIV, MgII. • Highest temperature and lowest density of the three gaseous phases (hot, tenuous phase of the ISM): ...
... Ionized Hydrogen (HII) • While ionized hydrogen (protons, electrons) forms the majority of the ionized phase of the ISM, it also contains ionized forms of other elements: e.g., OII, OIII, CIV, MgII. • Highest temperature and lowest density of the three gaseous phases (hot, tenuous phase of the ISM): ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.