Space - Milky Way
... 6. Why is our galaxy called the Milky Way? a. Because of its dense, fluid center b. It's a translation of an ancient name for "galaxy" c. Because it's relatively homogeneous d. Because it looks hazy and milky from Earth 7. How is the center of the Milky Way different from the arms? a. The center is ...
... 6. Why is our galaxy called the Milky Way? a. Because of its dense, fluid center b. It's a translation of an ancient name for "galaxy" c. Because it's relatively homogeneous d. Because it looks hazy and milky from Earth 7. How is the center of the Milky Way different from the arms? a. The center is ...
9 - WordPress.com
... Continual technical advancement has resulted in a range of devices extending from optical and radio-telescopes on Earth to orbiting telescopes, such as Hipparcos, Chandra and HST. Explanations for events in our spectacular Universe, based on our understandings of the electromagnetic spectrum, allow ...
... Continual technical advancement has resulted in a range of devices extending from optical and radio-telescopes on Earth to orbiting telescopes, such as Hipparcos, Chandra and HST. Explanations for events in our spectacular Universe, based on our understandings of the electromagnetic spectrum, allow ...
Stars - Clover Sites
... 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are the letters of the Greek alphabet used to name stars in a constellation? Give five illustrations of the use of the letters of the Greek alphabet ...
... 11. At what time of year is the constellation Orion best seen? Locate and idenify in the sky the three brightest stars of this constellation. 12. How are the letters of the Greek alphabet used to name stars in a constellation? Give five illustrations of the use of the letters of the Greek alphabet ...
DETAILED STELLAR POPULATION ANALYSIS OF GALAXY
... were chosen based on their X-ray luminosities. The sample is limited to clusters with X-ray luminosities larger than LX = 2 × 1044 ergs per second and is intended to be representative of rich galaxy clusters. The galaxies for which spectra were obtained can be several times less luminous than the Mi ...
... were chosen based on their X-ray luminosities. The sample is limited to clusters with X-ray luminosities larger than LX = 2 × 1044 ergs per second and is intended to be representative of rich galaxy clusters. The galaxies for which spectra were obtained can be several times less luminous than the Mi ...
ppt
... Test the impact of stellar populations modelling in the observed galaxy properties. In past evolutionary population synthesis codes, the K-band was mostly determined by old populations (e.g. Bruzual & Charlot 2003, PEGASE, Starburst99) ...
... Test the impact of stellar populations modelling in the observed galaxy properties. In past evolutionary population synthesis codes, the K-band was mostly determined by old populations (e.g. Bruzual & Charlot 2003, PEGASE, Starburst99) ...
PG_Lecture_Dec18_2008
... Mg, Al, Si, K, Ca, Fe are enhanced relative to the photosphere – up to x 4. These elements all have low first ionization potentials, FIPs (< 10 eV) Possibly a magnetic/electric field mechanism which takes the partially ionized material of photosphere into the corona as it rises. For some or even mos ...
... Mg, Al, Si, K, Ca, Fe are enhanced relative to the photosphere – up to x 4. These elements all have low first ionization potentials, FIPs (< 10 eV) Possibly a magnetic/electric field mechanism which takes the partially ionized material of photosphere into the corona as it rises. For some or even mos ...
Problem 4 : a. (20 points)
... As we’ve discussed many times in class, for a mass m moving with speed v in a circular orbit of radius r about a much larger mass M, F=ma is written as v2 GMm -------------- = m ----r r2 which tells us that the “mass in the middle” is ...
... As we’ve discussed many times in class, for a mass m moving with speed v in a circular orbit of radius r about a much larger mass M, F=ma is written as v2 GMm -------------- = m ----r r2 which tells us that the “mass in the middle” is ...
Mechanisms of Radio Wave Emission
... Blackbody Radiation • One of the most common forms of E/M waves • A “Blackbody” glows because it is hot. It also: – Absorbs all radiation that hits it – Have atoms and molecules which move faster with the absorption of more heat – Reradiates ALL that energy back out into it’s environment – Radiates ...
... Blackbody Radiation • One of the most common forms of E/M waves • A “Blackbody” glows because it is hot. It also: – Absorbs all radiation that hits it – Have atoms and molecules which move faster with the absorption of more heat – Reradiates ALL that energy back out into it’s environment – Radiates ...
Nuclear Fusion – when two H atoms combine to form one atom thus
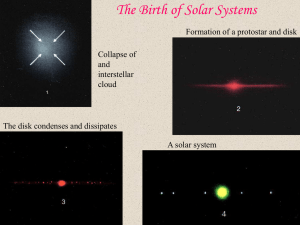
... Nebula – Stars are formed or “born” in a nebula. Massive cosmic cloud of matter from which stars are created. Light Year – distance light travels in one year. 186,000 miles/sec – speed of light Life Cycle of a Star Stars start off as a nebula until a nuclear explosion causes the star to shine. The n ...
... Nebula – Stars are formed or “born” in a nebula. Massive cosmic cloud of matter from which stars are created. Light Year – distance light travels in one year. 186,000 miles/sec – speed of light Life Cycle of a Star Stars start off as a nebula until a nuclear explosion causes the star to shine. The n ...
Tests and Constraints on Theories of Galaxy Formation and
... for a NIRBE at 1.6 mm. The IRTS NIRBE is probably zodiacal flux. Any NIRBE must be either maximally flat or maximally clumped. The star formation history of the universe is roughly constant from z=1-6. The vast majority of star formation occurs in a minority of galaxies at any one time. ...
... for a NIRBE at 1.6 mm. The IRTS NIRBE is probably zodiacal flux. Any NIRBE must be either maximally flat or maximally clumped. The star formation history of the universe is roughly constant from z=1-6. The vast majority of star formation occurs in a minority of galaxies at any one time. ...
Review for Midterm 1
... Why do some stars use the CNO cycle while other ones that use the proton-proton chain (and which types of stars do which)? Why is fusion so difficult to do even in the cores of stars? How does the huge temperature dependence of fusion affect the different masses of stars? Why does fusion generate en ...
... Why do some stars use the CNO cycle while other ones that use the proton-proton chain (and which types of stars do which)? Why is fusion so difficult to do even in the cores of stars? How does the huge temperature dependence of fusion affect the different masses of stars? Why does fusion generate en ...
Work sheet –chapter 2 CLASS - XI CHEMISTRY (Structure of Atom
... 7. Calculate energy of 2mole of photons of radiation whose frequency is 51014Hz. 8. What is emission and absorption spectra? 9. What transition in the hydrogen spectrum would have the same wavelength as the Balmer transition, n = 4 to n = 2 of He+ spectrum? 10. Spectral lines are regarded as the fi ...
... 7. Calculate energy of 2mole of photons of radiation whose frequency is 51014Hz. 8. What is emission and absorption spectra? 9. What transition in the hydrogen spectrum would have the same wavelength as the Balmer transition, n = 4 to n = 2 of He+ spectrum? 10. Spectral lines are regarded as the fi ...
English Summary
... Extremely dense objects with the mass of a million to a billion solar masses are thought to lie at the center of most large galaxies, including our own Milky Way. Their gravitational fields are so intense that within a certain distance of it, nothing, not even light, can escape their attraction. Hen ...
... Extremely dense objects with the mass of a million to a billion solar masses are thought to lie at the center of most large galaxies, including our own Milky Way. Their gravitational fields are so intense that within a certain distance of it, nothing, not even light, can escape their attraction. Hen ...
Stars and Their Characteristics
... • core temperature rises enough for helium to fuse into heavier elements, producing a carbon-oxygen core • surface gases are blown away, leaving core (white ...
... • core temperature rises enough for helium to fuse into heavier elements, producing a carbon-oxygen core • surface gases are blown away, leaving core (white ...
Introduction to the Big Bang Theory
... • If you could play the movie backwards, what would the objects be doing?_______________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ • Following that thought back to the very beginning…what ...
... • If you could play the movie backwards, what would the objects be doing?_______________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ _____________________________________________ • Following that thought back to the very beginning…what ...
Coords
... The French philosopher and mathematician Rene Descartes invented a system for locating objects in three-dimensional space. Called the Cartesian Coordinate System, it requires a starting point and three axes (called X, Y, and Z) for horizontal, vertical, and radial distance respectively. Any object c ...
... The French philosopher and mathematician Rene Descartes invented a system for locating objects in three-dimensional space. Called the Cartesian Coordinate System, it requires a starting point and three axes (called X, Y, and Z) for horizontal, vertical, and radial distance respectively. Any object c ...
Active Galaxies and Quasars: the most luminous objects in the
... The discovery of the quasar 3C273 (Schmidt 1963) Optical image ...
... The discovery of the quasar 3C273 (Schmidt 1963) Optical image ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.