Fertilization - Formatted
... specific. The sperms are delivered directly to the eggs immediately after laying. In marine forms the time interval between shedding of gametes may be longer by weeks or months. The task of meeting sperm and egg is further intensified as they release their gametes into the open sea, where they are ...
... specific. The sperms are delivered directly to the eggs immediately after laying. In marine forms the time interval between shedding of gametes may be longer by weeks or months. The task of meeting sperm and egg is further intensified as they release their gametes into the open sea, where they are ...
Angiosperms - OpenStax CNX
... found in monocots. In palm trees, vascular and parenchyma tissues produced by the primary and secondary thickening meristems form the trunk. The pollen from the rst angiosperms was monosulcate, containing a single furrow or pore through the outer layer. This feature is still seen in the modern mono ...
... found in monocots. In palm trees, vascular and parenchyma tissues produced by the primary and secondary thickening meristems form the trunk. The pollen from the rst angiosperms was monosulcate, containing a single furrow or pore through the outer layer. This feature is still seen in the modern mono ...
Botany - Merrillville Community School
... Fruit facilitates seed dispersal through a wide variety of mechanisms: wind, water, animals ...
... Fruit facilitates seed dispersal through a wide variety of mechanisms: wind, water, animals ...
1 Biology 4361 Developmental Biology Fertilization October 19
... 1) Contact and recognition between sperm and egg. - also ensures that egg and sperm are of the same species 2) Regulation of sperm entry into the egg - only one sperm can fertilize - usually, only one sperm is allowed to enter the egg; others are excluded 3) Fusion of the genetic material of the spe ...
... 1) Contact and recognition between sperm and egg. - also ensures that egg and sperm are of the same species 2) Regulation of sperm entry into the egg - only one sperm can fertilize - usually, only one sperm is allowed to enter the egg; others are excluded 3) Fusion of the genetic material of the spe ...
Chapter 12 Soil & Sand Analysis
... plant provides a pollen fingerprint—a specific type of pollen grain. They also know there will be a certain number of grains found in a specific geographical area during particular times of the year. – Examples of non-seed plants (spores) would be ferns, mosses, liverworts, and horsetails. – Example ...
... plant provides a pollen fingerprint—a specific type of pollen grain. They also know there will be a certain number of grains found in a specific geographical area during particular times of the year. – Examples of non-seed plants (spores) would be ferns, mosses, liverworts, and horsetails. – Example ...
flower
... •It occurs only in angiospermes and is the production of 2 sperm nuclei, both of which contribute to fertilization. •The male gametophyte, comprising the pollen grain and pollen tube, contains 2 sperm nuclei and 1 vegetative nucleus. •The vegetative nucleus degenerates once the pollen tube has penet ...
... •It occurs only in angiospermes and is the production of 2 sperm nuclei, both of which contribute to fertilization. •The male gametophyte, comprising the pollen grain and pollen tube, contains 2 sperm nuclei and 1 vegetative nucleus. •The vegetative nucleus degenerates once the pollen tube has penet ...
Biology 203
... Please look at the diagram of the conifer life cycle and follow along as the life cycle is described. This diagram shows a monoecious plant, i.e., it produces the male and female cone on the same tree. Pollen cones are small and usually found in clumps at the tips of branches. They are not woody. In ...
... Please look at the diagram of the conifer life cycle and follow along as the life cycle is described. This diagram shows a monoecious plant, i.e., it produces the male and female cone on the same tree. Pollen cones are small and usually found in clumps at the tips of branches. They are not woody. In ...
Chapter 17
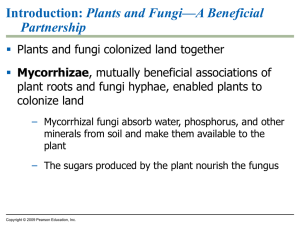
... Most fungi consist of a mass of threadlike hyphae making up a mycelium – Hyphal cells are separated by cross-walls with pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and nuclei to cross – Some are multinucleate without cross-walls – Hyphae have a huge surface area to secrete digestive enzymes an ...
... Most fungi consist of a mass of threadlike hyphae making up a mycelium – Hyphal cells are separated by cross-walls with pores large enough for ribosomes, mitochondria, and nuclei to cross – Some are multinucleate without cross-walls – Hyphae have a huge surface area to secrete digestive enzymes an ...
What is in vitro fertilisation (IVF) and how does it work?
... After egg collection, you are given medication to help prepare the lining of the womb for embryo transfer. This is given as pessaries, injection or gel. Step 6: embryo transfer For women under the age of 40, one or two embryos can be transferred. If you are 40, or over, a maximum of three can be use ...
... After egg collection, you are given medication to help prepare the lining of the womb for embryo transfer. This is given as pessaries, injection or gel. Step 6: embryo transfer For women under the age of 40, one or two embryos can be transferred. If you are 40, or over, a maximum of three can be use ...
1) Pollen sticks to animal or released into wind 2
... • Seeds enclosed in cones – Male cones: produce pollen (sperm) – Female cones: produce eggs • Zygote hardens into seed (protected inside cones) ...
... • Seeds enclosed in cones – Male cones: produce pollen (sperm) – Female cones: produce eggs • Zygote hardens into seed (protected inside cones) ...
Reproductive Life Cycles of Vascular Plants
... Nuclei in the embryo sac from by meiosis. In meiosis I, there is an initial cell division to give two cells with diploid nuclei. At the end of meiosis II, there are four linear haploid nuclei formed. Only one nucleus survives to duplicates to form the archegonia in gymnosperms or the contents of the ...
... Nuclei in the embryo sac from by meiosis. In meiosis I, there is an initial cell division to give two cells with diploid nuclei. At the end of meiosis II, there are four linear haploid nuclei formed. Only one nucleus survives to duplicates to form the archegonia in gymnosperms or the contents of the ...
Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
... in two nuclei results the formation of 8 nucleate embryo soc. After this stage, cell walls are laid down leading to the organization of the typical female gametophyte or embryo sac. Six of the eight nuclei are surrounded by cell walls and organized into cells. Three cells present towards the micropy ...
... in two nuclei results the formation of 8 nucleate embryo soc. After this stage, cell walls are laid down leading to the organization of the typical female gametophyte or embryo sac. Six of the eight nuclei are surrounded by cell walls and organized into cells. Three cells present towards the micropy ...
Reproductive Life Cycles of Vascular Plants
... In the angiosperm flower, the female gametophyte consists of nucellar tissue that is surrounded by either a single or a double outer tissue layer called the integuments. The integuments will become the seed coat. ...
... In the angiosperm flower, the female gametophyte consists of nucellar tissue that is surrounded by either a single or a double outer tissue layer called the integuments. The integuments will become the seed coat. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Chapter 29 Plant Diversity I
... In bryophytes, gametophytes are the largest and most conspicuous phase of the life cycle. Sporophytes are smaller and are present only part of the time. Bryophyte spores germinate in favorable habitats and grow into gametophytes by mitosis. ...
... In bryophytes, gametophytes are the largest and most conspicuous phase of the life cycle. Sporophytes are smaller and are present only part of the time. Bryophyte spores germinate in favorable habitats and grow into gametophytes by mitosis. ...
Biology 20 Laboratory Quiz Quiz # Animal Reproduction – Take
... E) It may stimulate infant cardiovascular problems. 9) Which developmental sequence is correct? A) cleavage, gastrula, morula, blastula B) cleavage, morula, blastula, gastrula C) gastrula, morula, blastula, cleavage D) morula, cleavage, gastrula, blastula E) cleavage, blastula, gastrula, morula 10) ...
... E) It may stimulate infant cardiovascular problems. 9) Which developmental sequence is correct? A) cleavage, gastrula, morula, blastula B) cleavage, morula, blastula, gastrula C) gastrula, morula, blastula, cleavage D) morula, cleavage, gastrula, blastula E) cleavage, blastula, gastrula, morula 10) ...
Infertility
... to, ovulation induction, intrauterine insemination, in-vitro fertilization, uterine embryo lavage, embryo transfer, gamete intra-fallopian transfer, zygote intra-fallopian transfer and low tubal ovum transfer. HealthyCT can apply policy limitations, maximums and requirements that are not in conflict ...
... to, ovulation induction, intrauterine insemination, in-vitro fertilization, uterine embryo lavage, embryo transfer, gamete intra-fallopian transfer, zygote intra-fallopian transfer and low tubal ovum transfer. HealthyCT can apply policy limitations, maximums and requirements that are not in conflict ...
Do you know? - Sakshieducation.com
... Now a days we are able to develop seedless fruits like watermelon, grapes etc. This is a process of reproduction where there is a shift from sexual to asexual mode of reproduction. • How do you think this happens? This process also occurs in nature. An organism which reproduce sexually sometimes ase ...
... Now a days we are able to develop seedless fruits like watermelon, grapes etc. This is a process of reproduction where there is a shift from sexual to asexual mode of reproduction. • How do you think this happens? This process also occurs in nature. An organism which reproduce sexually sometimes ase ...
Genetics Year 3 Notes and worksheets
... Pollen grains are produced by the male part of the plant. ...
... Pollen grains are produced by the male part of the plant. ...
Chapter 36 Human Reproduction and Development
... meiotic divi–sion is completed. Then, once each menstrual cycle dur–ing the reproductive years, meiosis continues for a single developing oocyte. The res ulting structures at the end of the first meiotic division of the oocyte are of unequal size. The smaller of the two structures is called a polar ...
... meiotic divi–sion is completed. Then, once each menstrual cycle dur–ing the reproductive years, meiosis continues for a single developing oocyte. The res ulting structures at the end of the first meiotic division of the oocyte are of unequal size. The smaller of the two structures is called a polar ...
Gametophyte development
... Depending on the pattern of subsequent cell divisions, four types of female gametophyte development have been described. In most flowering plant species, including Arabidopsis and maize, the megaspore undergoes a polygonum-type pathway that results in a seven-celled female gametophyte (Figure 2B). D ...
... Depending on the pattern of subsequent cell divisions, four types of female gametophyte development have been described. In most flowering plant species, including Arabidopsis and maize, the megaspore undergoes a polygonum-type pathway that results in a seven-celled female gametophyte (Figure 2B). D ...
30_Plant Diversity II The Evolution of Seed Plants
... • A pollen grain that has landed on a stigma germinates and the pollen tube of the male gametophyte grows down to the ovary • The ovule is entered by a pore called the micropyle • Double fertilization occurs when the pollen tube discharges two sperm into the female gametophyte within an ovule ...
... • A pollen grain that has landed on a stigma germinates and the pollen tube of the male gametophyte grows down to the ovary • The ovule is entered by a pore called the micropyle • Double fertilization occurs when the pollen tube discharges two sperm into the female gametophyte within an ovule ...
Seed Plants
... FIGURE 21-11 Life cycle of a flowering plant The dominant plant body (upper right) is the diploid sporophyte, whose flowers normally produce both male and female gametophytes. Male gametophytes (pollen grains) are produced within anthers. The female gametophyte develops from a spore within the ovul ...
... FIGURE 21-11 Life cycle of a flowering plant The dominant plant body (upper right) is the diploid sporophyte, whose flowers normally produce both male and female gametophytes. Male gametophytes (pollen grains) are produced within anthers. The female gametophyte develops from a spore within the ovul ...
Gymnosperms + Seed and Pollen Basics
... wood that has been digested so that the individual cells separate from one another. Then the suspension of cells is mounted and the result is known as a maceration in which we can determine the types of cells present. Keep in mind that this sample is secondary xylem only so only those cells describe ...
... wood that has been digested so that the individual cells separate from one another. Then the suspension of cells is mounted and the result is known as a maceration in which we can determine the types of cells present. Keep in mind that this sample is secondary xylem only so only those cells describe ...
Fertilisation

Fertilisation (also known as conception, fecundation and syngamy) is the fusion of gametes to initiate the development of a new individual organism. In animals, the process involves the fusion of an ovum with a sperm, which first creates a zygote and then leads to the development of an embryo. Depending on the animal species, the process can occur within the body of the female in internal fertilisation, or outside (external fertilisation). The cycle of fertilisation and development of new individuals is called sexual reproduction.